前後端分離之Java後端
前後端分離的思想由來已久,不妨嘗試一下,從上手開始,先把程式碼寫出來再究細節。
程式碼下載:https://github.com/jimolonely/AuthServer
前言
以前服務端為什麼能識別使用者呢?對,是session,每個session都存在服務端,瀏覽器每次請求都帶著sessionId(就是一個字串),於是伺服器根據這個sessionId就知道是哪個使用者了。
那麼問題來了,使用者很多時,伺服器壓力很大,如果採用分散式儲存session,又可能會出現不同步問題,那麼前後端分離就很好的解決了這個問題。
前後端分離思想:
在使用者第一次登入成功後,服務端返回一個token回來,這個token是根據userId進行加密的,金鑰只有伺服器知道,然後瀏覽器每次請求都把這個token放在Header裡請求,這樣伺服器只需進行簡單的解密就知道是哪個使用者了。這樣伺服器就能專心處理業務,使用者多了就加機器。當然,如果非要討論安全性,那又有說不完的話題了。
下面通過SpringBoot框架搭建一個後臺,進行token構建。
構建springboot專案
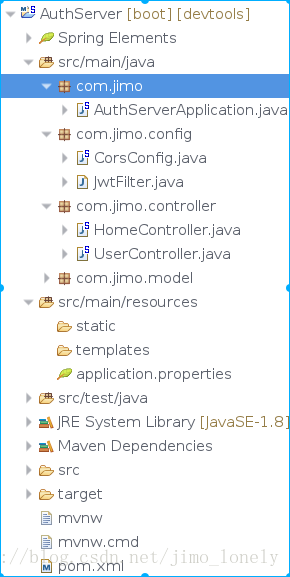
我的目錄結構:(結果未按標準書寫,僅作說明)
不管用什麼IDE,最後我們只看pom.xml裡的依賴:
為了儘可能簡單,就不連資料庫了,登陸時用固定的。
devtools:用於修改程式碼後自動重啟;
jjwt:加密這麼麻煩的事情可以用現成的,檢視https://github.com/jwtk/jjwt
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>1.5.2.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath /> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- JJWT -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.jsonwebtoken</groupId>
<artifactId>jjwt</artifactId>
<version>0.6.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
登入
這裡的加密金鑰是:base64EncodedSecretKey
import java.util.Date;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import io.jsonwebtoken.Jwts;
import io.jsonwebtoken.SignatureAlgorithm;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/")
public class HomeController {
@PostMapping("/login")
public String login(@RequestParam("username") String name, @RequestParam("password") String pass)
throws ServletException {
String token = "";
if (!"admin".equals(name)) {
throw new ServletException("找不到該使用者");
}
if (!"1234".equals(pass)) {
throw new ServletException("密碼錯誤");
}
token = Jwts.builder().setSubject(name).claim("roles", "user").setIssuedAt(new Date())
.signWith(SignatureAlgorithm.HS256, "base64EncodedSecretKey").compact();
return token;
}
}
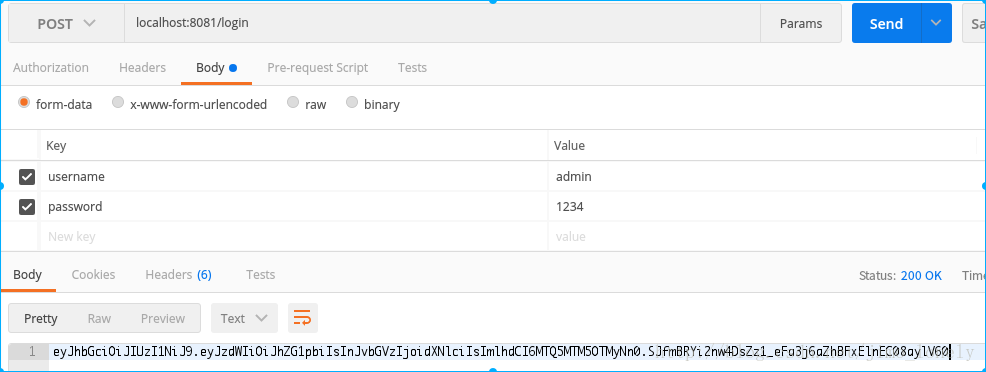
測試token
現在就可以測試生成的token了,我們採用postman:
過濾器
這肯定是必須的呀,當然,也可以用AOP。
過濾要保護的url,同時在過濾器裡進行token驗證
token驗證:
public class JwtFilter extends GenericFilterBean {
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) req;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) res;
String authHeader = request.getHeader("Authorization");
if ("OPTIONS".equals(request.getMethod())) {
response.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_OK);
chain.doFilter(req, res);
} else {
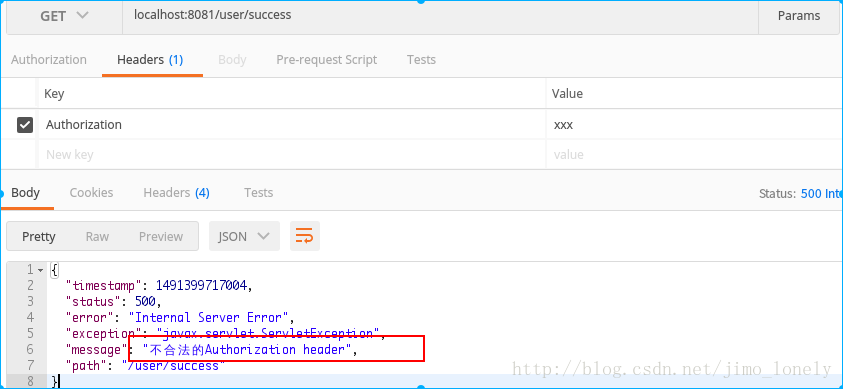
if (authHeader == null || !authHeader.startsWith("Bearer ")) {
throw new ServletException("不合法的Authorization header");
}
// 取得token
String token = authHeader.substring(7);
try {
Claims claims = Jwts.parser().setSigningKey("base64EncodedSecretKey").parseClaimsJws(token).getBody();
request.setAttribute("claims", claims);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new ServletException("Invalid Token");
}
chain.doFilter(req, res);
}
}
}
要保護的url:/user下的:
@SpringBootApplication
public class AuthServerApplication {
@Bean
public FilterRegistrationBean jwtFilter() {
FilterRegistrationBean rbean = new FilterRegistrationBean();
rbean.setFilter(new JwtFilter());
rbean.addUrlPatterns("/user/*");// 過濾user下的連結
return rbean;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(AuthServerApplication.class, args);
}
}
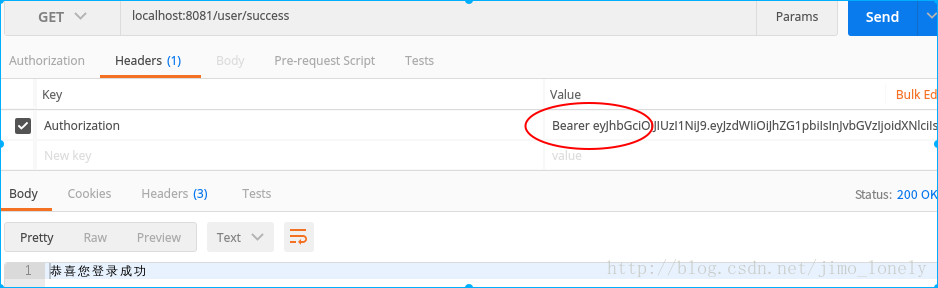
關鍵測試
假設我們的Authorization錯了,肯定是通不過的:
當輸入剛才伺服器返回的正確token:
允許跨域請求
現在來說前端和後端是兩個伺服器了,所以需要允許跨域:
@Configuration
public class CorsConfig {
@Bean
public FilterRegistrationBean corsFilter() {
UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource source = new UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource();
CorsConfiguration config = new CorsConfiguration();
config.setAllowCredentials(true);
config.addAllowedOrigin("*");
config.addAllowedHeader("*");
config.addAllowedMethod("OPTION");
config.addAllowedMethod("GET");
config.addAllowedMethod("POST");
config.addAllowedMethod("PUT");
config.addAllowedMethod("HEAD");
config.addAllowedMethod("DELETE");
source.registerCorsConfiguration("/**", config);
FilterRegistrationBean bean = new FilterRegistrationBean(new CorsFilter(source));
bean.setOrder(0);
return bean;
}
@Bean
public WebMvcConfigurer mvcConfigurer() {
return new WebMvcConfigurerAdapter() {
@Override
public void addCorsMappings(CorsRegistry registry) {
registry.addMapping("/**").allowedMethods("GET", "PUT", "POST", "GET", "OPTIONS");
}
};
}
}
下次是採用VueJS寫的前端如何請求。