Java中關於String類的基本操作
1 字元與字串的相互轉換
字串就是一個字元陣列,所以在String類裡面支援有字元陣列轉為字串以及字串轉為字元的操作方法。
//取得字串長度:public int length();
//陣列的長度:陣列名.length;
1.1 將字元陣列轉為字串
用String類的構造方法!
/**
1. public String(char [] value);將字元陣列value中的所有內容變為字串
2. public String(char [] value,int offset,int count);將字元陣列value中的部分內容變為字串
offset為開始索引、count為個數
均為成員方法,通過物件呼叫!!!
*/ 
1.2 將字串轉為字元陣列
/**
將字串該為字元陣列
1. public char[] tocharArray();
*/
public class Test{
public 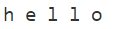
1.3 將字串轉為單個字元
/**
1. public char charAt(int index);取得指定索引位置上的字元
index:索引
*/
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
//取得索引為0的位置的字元
System.out.println("hello".charAt(0));
//如果索引越界,會報陣列越界異常StringIndexOutOfBoundsException
System.out.println("hello".charAt(6));
}
}

1.4 判斷一個字串是否由數字組成?
/**
判斷一個字串是否由陣列組成
取得字串長度:public int length();
取得陣列的長度:陣列名.length
*/
public class Test{
public static boolean isNumber1(String str)
{
for(int i=0;i<str.length();i++)
{
//將字串根據索引轉成單個字元
char result=str.charAt(i);
if(result<'0'||result>'9')
{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public static boolean isNumber2(String str)
{
//將字串轉為字元陣列
char [] data=str.toCharArray();
for(int i=0;i<data.length;i++)
{
if(data[i]<'0'||data[i]>'9')
{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String str="14263";
System.out.println(isNumber1(str));
System.out.println(isNumber2(str));
}
}

2 位元組與字串的相互轉換
2.1 將位元組陣列轉為字串
用String類的構造方法!
/**
1. public String(byte[] value);將位元組陣列中的所有內容轉為字串
2. public String(byte[] value,int offset,int count);將位元組陣列中的部分內容轉為字串
offset為開始索引,count為個數
*/
public class TestByte{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
byte [] data=new byte[]{1,2,3,4,5};
//將位元組陣列中的所有內容變為字串
String str1=new String(data);
System.out.println(str1);
//將位元組陣列中的部分內容變為字串offset為開始點,count為個數
String str2=new String(data,2,3);
System.out.println(str2);
//如果字元的個數超出了陣列的索引,會報陣列越界異常
String str3=new String(data,2,4);
System.out.println(str3);
}
}

2.2 將字串轉為位元組陣列
/**
//將字串改為位元組陣列
1. public byte[] getBytes();
*/
public class TestByte{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
byte [] result="HELLO".getBytes();
for(byte i:result)
{
System.out.print(i+" ");
}
}
}
 位元組不適合中文,只有字元適合處理中文!
位元組不適合中文,只有字元適合處理中文!
3 字串比較
3.1 不區分大小相等比較
/**
不區分大小寫的相等比較
public boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String anotherString)
區分大小寫
public boolean equals(String anotherString)
*/
public class TestByte{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String str1="Hello";
//不區分大小寫
System.out.println("hello".equalsIgnoreCase(str1));
//區分大小寫
System.out.println("hello".equals(str1));
}
}

3.2 比較兩個字串的大小
/**
比較兩個字串的大小
public int compareTo(String anotherString)
返回值:(返回值正好是兩個字元的差)
① >0 表示該字串大於比較物件
② <0 表示該字串小於比較物件
③ =0 表示該字串等於比較物件
*/
public class TestByte{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println("ABCD".compareTo("ABCD"));
System.out.println("abcd".compareTo("aBcd"));
System.out.println("abCd".compareTo("abcD"));
System.out.println("AB".compareTo("AC"));
}
}
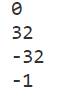
4 字串查詢
4.1 判斷字串在源字串中是否存在
/**
判斷字串str在源字串中是否存在
public boolean contains(String str);
*/
public class TestByte{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String str="helloworld";
System.out.println(str.contains("hello"));
System.out.println(str.contains("he"));
System.out.println(str.contains("hep"));
}
}

4.2 判斷字串是否以指定的字串開始
/**
判斷字串是否以指定的字串開始
public boolean startsWith(String str);
*/
public class TestByte{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String str="helloworld";
System.out.println(str.startsWith("hello"));
System.out.println(str.startsWith("he"));
System.out.println(str.startsWith("hep"));
}
}

4.3 從指定位置開始判斷是否以指定的字串開頭
/**
從指定位置開始判斷是否以指定的字串開頭
public boolean startsWith(String str,intdex);
*/
public class TestByte{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String str="helloworld";
System.out.println(str.startsWith("hello",0));
System.out.println(str.startsWith("wo",5));
System.out.println(str.startsWith("hep",3));
}
}

4.4 判斷是否以指定的字串結尾
/**
判斷是否以指定的字串結尾
public boolean endsWith(String str);
*/
public class TestByte{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String str="helloworld";
System.out.println(str.endsWith("hello"));
System.out.println(str.endsWith("wo"));
System.out.println(str.endsWith("world"));
System.out.println(str.endsWith("ld"));
}
}

4.5 查詢字串的位置
| public int indexOf (String str) | 從頭開始查詢指定字串的位置,查到了返回位置的開始索引,查不到返回-1 |
|---|---|
| public int indexOf (String str,int fromIndex) | 從指定位置開始查詢指定字串的位置 |
| public int lastIndexOf(String str) | 從最後一個元素開始由後向前查詢字串的位置 |
| public int lastIndexOf(String str,int fromIndex) | 從指定位置由後向前查詢字串的位置 |
public class TestByte{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String str="helloworld";
//從頭開始查詢字串hlo的位置 沒有找到返回-1
System.out.println(str.indexOf("hlo"));
//從頭開始查詢字串llo的位置 返回2
System.out.println(str.indexOf("llo"));
//從下表為4的位置開始,向後找字串h的位置 沒有找到返回-1
System.out.println(str.indexOf("h",4));
//從下表為4的位置開始,向後找字串w的位置 返回5
System.out.println(str.indexOf("w",4));
//從最後一個元素開始由後向前查詢字串world的位置,返回5
System.out.println(str.lastIndexOf("world"));
//從第4個元素開始由後向前查詢字串world的位置,沒有找到返回-1
System.out.println(str.lastIndexOf("world",4));
//從第6個元素開始由後向前查詢字串world的位置,找到返回5
System.out.println(str.lastIndexOf("world",6));
//從第6個元素開始由後向前查詢字串l的位置,返回3
System.out.println(str.lastIndexOf("l",6));
}
}
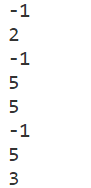
5 字串替換
5.1 替換全部內容
/**
替換全部內容
public String replaceAll(String regex,String replacement)
*/
public class TestReplace{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String str="hello";
String result = str.replaceAll("l","*");
System.out.println(result);
}
}

5.2 替換首個內容
/**
替換首個內容
public String replaceFirst(String regex,String replacement)
*/
public class TestReplace{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String str="hello";
String result = str.replaceFirst("l","*");
System.out.println(result);
}
}
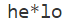
6 字串拆分
6.1 將字串全部拆分
/**
將字串按照指定格式全部拆分
public String[] split(String regex);
*/
public class TestSplit{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String str="192 168 106 1";
String [] result = str.split(" ");
for(String i:result)
{
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
/**
將字串部分拆分
public String[] split(String regex,int limit);
拆分後陣列的長度為limit
*/
public class TestSplit{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String str="192.168.106.1";
//轉義字元
String [] result = str.split("\\.");
for(String i:result)
{
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}

6.2 將字串部分拆分
/**
將字串部分拆分
public String[] split(String regex,int limit);
拆分後陣列的長度為limit
*/
public class TestSplit{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String str="192 168 106 1";
String [] result = str.split(" ",3);
for(String i:result)
{
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}

6.3 一個拆分的例項
public class TestSplit{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String str="苗:20|萌:22|昕:10";
//需要轉義字元
String [] result = str.split("\\|");
for(int i=0;i<result.length;i++)
{
String [] data = result[i].split(":");
System.out.println(data[0]+" "+data[1]);
}
}
}

7 字串擷取
7.1 從指定位置開始擷取到檔案末尾
/**
字串擷取
public String substring (int beginIndex)從指定位置擷取到檔案末尾
*/
public class TestSubString{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String str="helloworld";
System.out.print(str.substring(3));
}
}

7.1 從指定位置開始擷取部分內容
/**
字串擷取
public String substring (int beginIndex,int endIndex) 從指定位置開始擷取部分內容(左閉右開)
*/
public class TestSubString{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String str="helloworld";
System.out.print(str.substring(3,7));
}
}

8 字串的其他操作
8.1 去掉左右空格,保留中間空格
/**
去掉左右空格,保留中間空格:public String trim();
*/
public class Test2{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
//去掉左右空格保留中間空格
String str=" ha ha ";
System.out.println(str.trim());
}
}

8.2 轉大小寫
/**
轉大寫:public String toUpperCase();
轉小寫:public String toLowerCase();
*/
public class Test2{
public static void main(String[] args
相關推薦
在Java中String類為什麽要設計成final?String真的不可變嗎?其他基本類型的包裝類也是不可變的嗎?
數據 pri 創建 long tde 繼承 set 字符串常量 通過 最近突然被問到String為什麽被設計為不可變,當時有點懵,這個問題一直像bug一樣存在,竟然沒有發現,沒有思考到,在此總結一下。
1.String的不可變String類被final修飾,是不可繼承和修改
java中String類型轉換為yyyy-MM-dd的Date類型
col code edate birt mat led div get sys
String birthday ="2017-02-22";
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat(("yyyy-MM-dd"));
jav
在java中String類為什麽要設計成final?
tro cli lai 這一 引用 沒有 num 重新 static 大神鏈接:在java中String類為什麽要設計成final? - 程序員 - 知乎
我進行了重新排版,並且更換了其中的一個例子,讓我們更好理解。
String很多實用的特性,比如說“不可變性”,是工
java中String類常用方法、屬性等
col clas equal ack length ++ ava eal rgs
package Head18;
public class java09 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
St
Java中Properties類的操作
文件中 配置文件 所有 技術分享 set nbsp str 宋體 java Java中有個比較重要的類Properties(Java.util.Properties),主要用於讀取Java的配置文件,就是像讀取數據庫賬號密碼一樣,其配置文件常為.properties文件,格
Java中String類中常見方法以及類與類之間的轉換
String類中的方法描述
public String() 空引數構造方法
public String(byte[] bytes) 把位元組陣列轉換成字串物件
public String(byte[] bytes,int index,int length) 把位元組陣
Java筆記-File類基本操作
使用File類操作檔案或目錄屬性
java.io 包為我們提供了一些介面和類,對檔案進行基本的操作,包括對檔案和目錄屬性的操作、對檔案讀寫的操作等。
File類構造方法
如何使用File 類操作檔案或目錄:
一個File 物件可以代表一個檔案或目錄。利用它可以對
關於java中string類的用法!
String類代表字串
字串是常量,他們的值在建立之後不能改變
String類包括的方法有:檢查序列的單個字元;比較字串;搜尋字串;提取子字串;建立字串副本(在該副本中,所有的字元都被轉換為大寫或小寫形式)。
Java語言提供對字串串聯符號(“+”)和其他物件到
java中String類的使用理解
1_String類的概述
A:String類的概述
通過JDK提供的API,檢視String類的說明
可以看到這樣的兩句話。
a:字串字面值"abc"也可以看成是一個字串物件。
b:字串是常量,一
java中String類為什麼不可變?
在面試中經常遇到這樣的問題:1、什麼是不可變物件。不可變物件有什麼好處。在什麼情景下使用它,或者更具體一點,java的String類為什麼要設定成不可變型別?
1、不可變物件,顧名思義就是建立後的物件不可以改變,典型的例子有java中的String型別。
2、相比於可變物
java中String類詳解
String類
String類存在java.lang包中,專門儲存字串。是引用資料型別。
String類的兩種例項化方法
1.直接賦值
String str1= "hello";
2.傳統賦值
Str
Java中String類常用方法(轉)
轉自:https://blog.csdn.net/kaishizhangcheng/article/details/52332543int indexOf(String str)該方法用於返回當給定字串在當前字串中的位置,若當前字串不包含給定字串則返回-1。過載的方法int
在Java中String類為什麼要設計成final?String真的不可變嗎?其他基本型別的包裝類也是不可變的嗎?
最近突然被問到String為什麼被設計為不可變,當時有點懵,這個問題一直像bug一樣存在,竟然沒有發現,沒有思考到,在此總結一下。
1.String的不可變 String類被final修飾,是不可繼承和修改的。當一個String變數被第二次賦值時,不是在原有記憶體地址上修改資料,而是在記憶體中重
java中String類、StringBuffer類、StringBuilder類的區別(未完待續)
);}
public CharSequence subSequence(int beginIndex, int endIndex) {
return this.substring(beginIndex, endIndex);
}
/**
* 字串拼接
Java中String類的isEmpty方法、null以及""的區別
一直以來對String的這三個空挺暈的,剛好同事問我,我也學習下。從別人部落格上看到的是這樣的:
isEmpty()
分配了記憶體空間,值為空,是絕對的空,是一種有值(值 =
java中String類常用方法I(判斷 Java 檔名是否正確,判斷郵箱格式是否正確)
內容摘自慕課網
具體程式碼:
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Java檔名
String fileName
JAVA中String類的split方法的易錯點
最近在專案中遇到了一個問題,就是解析字串成陣列進行比對的,比如: { "imageDetail": "123&234&&", "imageType": "O&A&B&C"
java中String類的hashCode方法實現
public int hashCode() {
int h = hash;
if (h == 0 && value.length > 0) {
char val[] = value;
Java中 String類、StringBuilder類、StringBuffer類 區別與如何選擇
1. 概述: 1.1 String 字串常量,但是它具有不可變性,就是一旦建立,對它進行的任何修改操作都會建立一個新的字串物件。 1.2 StringBuffer
對Java中String類的忽略大小寫比較器(CaseInsensitiveComparator)的compare方法的一點疑問
最近我在看jdk原始碼,無意中看到String類的忽略大小寫比較器的原始碼,其原始碼如下。
private static class CaseInsensitiveComparator
implements Comparator<Str
