Ultra-QuickSort POJ
In this problem, you have to analyze a particular sorting algorithm. The algorithm processes a sequence of n distinct integers by swapping two adjacent sequence elements until the sequence is sorted in ascending order. For the input sequence
9 1 0 5 4 ,
Ultra-QuickSort produces the output
0 1 4 5 9 .
Your task is to determine how many swap operations Ultra-QuickSort needs to perform in order to sort a given input sequence.
Input
The input contains several test cases. Every test case begins with a line that contains a single integer n < 500,000 -- the length of the input sequence. Each of the the following n lines contains a single integer 0 ≤ a[i] ≤ 999,999,999, the i-th input sequence element. Input is terminated by a sequence of length n = 0. This sequence must not be processed.
Output
For every input sequence, your program prints a single line containing an integer number op, the minimum number of swap operations necessary to sort the given input sequence.
Sample Input
5 9 1 0 5 4 3 1 2 3 0
Sample Output
6 0
題意說的很明白了就是簡單地求逆序對。當然也可以使用樹狀陣列加離散化來處理,但是這裡我們選擇更加好寫的歸併排序來寫
歸併排序求逆序對原理簡介:
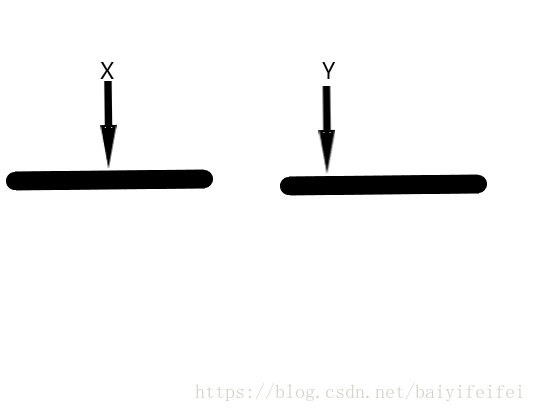
假設我們手頭有兩個已經從小到大排好序的陣列,且他們分別是原來的一段大陣列的前半段和後半段,現在我們的比較到了x,y位置
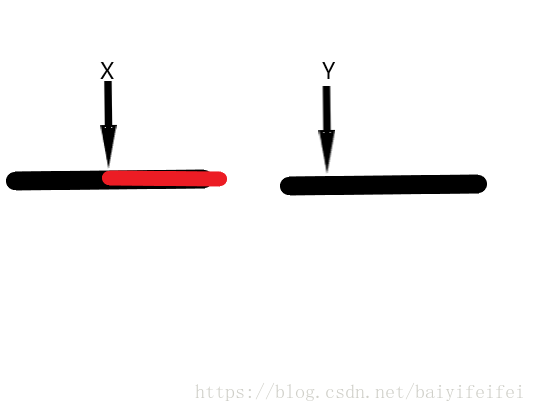
假使X>Y則其必然構成一對逆序對,與此同時我所畫出的紅色的這一段的的數均大於Y,所以逆序對的數量就要加上這一段的長度
而對整個陣列都歸併排序完畢後最終就可以得到逆序對的和
附帶上一個逆序對的模板(大佬小夥伴寫的)
int A[100010];//輸入的任意序列
int T[100010];//臨時空間
long long cnt;
void merge_sort(int *A,int x,int y,int *T)
{
if(y-x>1)//如果序列非空
{ 05
int m=x+(y-x)/2;//如果序列長度為奇數左邊序列比右邊少一個,如果偶數則一樣
int p=x,q=m,i=x;//p,q是當前左右序列第一個元素的位置(最小的那個)
merge_sort(A,x,m,T);//遞迴排序
merge_sort(A,m,y,T);
while(p<m || q<y)//只要有一個序列非空就繼續合併
{
if(q>=y || p<m&&A[p]<=A[q]) T[i++]=A[p++];//如果右邊或左邊非空且左邊第一個元素小與右邊第一個,
//就把左邊那個加到臨時空間裡
else
{
T[i++]=A[q++];
cnt+=m-p;// 逆序數
}
}
for(i=x;i<y;i++) A[i]=T[i];//把排序好的T複製回A,A的範圍是[x,y)
}
}
AC程式碼:
#include<algorithm>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<string>
#include<cstdio>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
#include<cmath>
#include<queue>
#include<set>
#include<map>
#define endl '\n'
#define sc(x) scanf("%lld",&x)
#define md(a,b) a+(b-a)/2
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int size=5e5+5;
LL arr[size],Temp[size];
LL ans=0;
void MergeSort(int x,int y)
{
if(y-x>1)
{
int m=md(x,y);
int p=x,q=m,i=x;
MergeSort(x,m);
MergeSort(m,y);
while(p<m||q<y)
{
if(q>=y|| p<m&&arr[p]<=arr[q]) Temp[i++]=arr[p++];
else
{
Temp[i++]=arr[q++];
ans+=(m-p);
}
}
for(int i=x;i<y;i++) arr[i]=Temp[i];
}
}
int main()
{
int n;
while(~scanf("%d",&n)&&n)
{
memset(arr,0,sizeof(arr));
memset(Temp,0,sizeof(Temp));
ans=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
sc(arr[i]);
}
MergeSort(0,n);
cout<<ans<<endl;
}
return 0;
}