算法筆記_212:第七屆藍橋杯軟件類決賽真題(Java語言B組)
阿新 • • 發佈:2017-05-20
技術 emp 字符串表 求解 如果 過去 系統 多少 ann
目錄
1 憤怒小鳥
2 反幻方
3 打靶
4 路徑之謎
5 堿基
6 圓圈舞
前言:以下代碼僅供參考,若有錯誤歡迎指正哦~
1 憤怒小鳥
憤怒小鳥 X星球憤怒的小鳥喜歡撞火車! 一根平直的鐵軌上兩火車間相距 1000 米 兩火車 (不妨稱A和B) 以時速 10米/秒 相對行駛。 憤怒的小鳥從A車出發,時速50米/秒,撞向B車, 然後返回去撞A車,再返回去撞B車,如此往復.... 兩火車在相距1米處停車。 問:這期間憤怒的小鳥撞 B 車多少次? 註意:需要提交的是一個整數(表示撞B車的次數),不要填寫任何其它內容。 答案:9
參考資料: 藍橋杯決賽真題—憤怒的小鳥
1public class Main { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { //PS:相對行駛,即面對面行駛 4 double a=0,b=1000; 5 while(b>=1){ 6 b = b- 20 * (b/60); //由a向b行駛 7 b = b - 20 * (b/60); //由b向a行駛 8 System.err.println(b); 9 a++; 10 } 11 System.out.println(a);12 } 13 }
2 反幻方
反幻方 我國古籍很早就記載著 2 9 4 7 5 3 6 1 8 這是一個三階幻方。每行每列以及對角線上的數字相加都相等。 下面考慮一個相反的問題。 可不可以用 1~9 的數字填入九宮格。 使得:每行每列每個對角線上的數字和都互不相等呢? 這應該能做到。 比如: 9 1 2 8 4 3 7 5 6 你的任務是搜索所有的三階反幻方。並統計出一共有多少種。 旋轉或鏡像算同一種。 比如: 9 1 2 8 4 3 7 5 6 7 8 9 5 4 1 6 3 2 2 1 9 3 4 8 6 5 7 等都算作同一種情況。 請提交三階反幻方一共多少種。這是一個整數,不要填寫任何多余內容。 答案:3120
1 import java.util.HashSet; 2 3 public class Main { 4 public static int count = 0; 5 6 public void swap(int[] A, int i, int j) { 7 int temp = A[i]; 8 A[i] = A[j]; 9 A[j] = temp; 10 } 11 12 public void check(int[] A) { 13 int[] sum = new int[8]; 14 sum[0] = A[0] + A[1] + A[2]; 15 sum[1] = A[3] + A[4] + A[5]; 16 sum[2] = A[6] + A[7] + A[8]; 17 sum[3] = A[0] + A[3] + A[6]; 18 sum[4] = A[1] + A[4] + A[7]; 19 sum[5] = A[2] + A[5] + A[8]; 20 sum[6] = A[0] + A[4] + A[8]; 21 sum[7] = A[2] + A[4] + A[6]; 22 HashSet<Integer> set = new HashSet<Integer>(); 23 for(int i = 0;i < 8;i++) 24 set.add(sum[i]); 25 if(set.size() == 8) 26 count++; 27 } 28 29 public void dfs(int[] A, int step) { 30 if(step == A.length) { 31 check(A); 32 return; 33 } else { 34 for(int i = step;i < A.length;i++) { 35 swap(A, i, step); 36 dfs(A, step + 1); 37 swap(A, i, step); 38 } 39 } 40 } 41 42 public static void main(String[] args) { 43 Main test = new Main(); 44 int[] A = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9}; 45 test.dfs(A, 0); 46 System.out.println(count / 8); 47 } 48 }
3 打靶
打靶 小明參加X星球的打靶比賽。 比賽使用電子感應計分系統。其中有一局,小明得了96分。 這局小明共打了6發子彈,沒有脫靶。 但望遠鏡看過去,只有3個彈孔。 顯然,有些子彈準確地穿過了前邊的彈孔。 不同環數得分是這樣設置的: 1,2,3,5,10,20,25,50 那麽小明的6發子彈得分都是多少呢?有哪些可能情況呢? 下面的程序解決了這個問題。 仔細閱讀分析代碼,填寫劃線部分缺失的內容。 public class Main { static void f(int[] ta, int[] da, int k, int ho, int bu, int sc) { if(ho<0 || bu<0 || sc<0) return; if(k==ta.length){ if(ho>0 || bu>0 || sc>0) return; for(int i=0; i<da.length; i++){ for(int j=0; j<da[i]; j++) System.out.print(ta[i] + " "); } System.out.println(); return; } for(int i=0; i<=bu; i++){ da[k] = i; f(ta, da, k+1, __________________ , bu-i, sc-ta[k]*i); // 填空位置 } da[k] = 0; } public static void main(String[] args) { int[] ta = {1,2,3,5,10,20,25,50}; int[] da = new int[8]; f(ta, da, 0, 3, 6, 96); } } 註意:只填寫劃線處缺少的內容,不要填寫已有的代碼或符號,也不要填寫任何解釋說明文字等。 答案:ho - (i == 0 ? 0 : 1)
4 路徑之謎
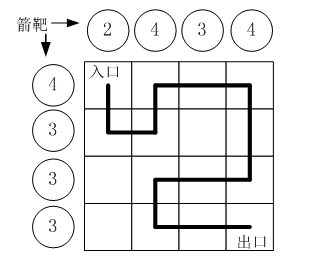
路徑之謎 小明冒充X星球的騎士,進入了一個奇怪的城堡。 城堡裏邊什麽都沒有,只有方形石頭鋪成的地面。 假設城堡地面是 n x n 個方格。【如圖1.png】所示。 按習俗,騎士要從西北角走到東南角。 可以橫向或縱向移動,但不能斜著走,也不能跳躍。 每走到一個新方格,就要向正北方和正西方各射一箭。 (城堡的西墻和北墻內各有 n 個靶子) 同一個方格只允許經過一次。但不必做完所有的方格。 如果只給出靶子上箭的數目,你能推斷出騎士的行走路線嗎? 有時是可以的,比如圖1.png中的例子。 本題的要求就是已知箭靶數字,求騎士的行走路徑(測試數據保證路徑唯一) 輸入: 第一行一個整數N(0<N<20),表示地面有 N x N 個方格 第二行N個整數,空格分開,表示北邊的箭靶上的數字(自西向東) 第三行N個整數,空格分開,表示西邊的箭靶上的數字(自北向南) 輸出: 一行若幹個整數,表示騎士路徑。 為了方便表示,我們約定每個小格子用一個數字代表,從西北角開始編號: 0,1,2,3.... 比如,圖1.png中的方塊編號為: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 示例: 用戶輸入: 4 2 4 3 4 4 3 3 3 程序應該輸出: 0 4 5 1 2 3 7 11 10 9 13 14 15 資源約定: 峰值內存消耗 < 256M CPU消耗 < 1000ms 請嚴格按要求輸出,不要畫蛇添足地打印類似:“請您輸入...” 的多余內容。 所有代碼放在同一個源文件中,調試通過後,拷貝提交該源碼。 註意:不要使用package語句。不要使用jdk1.7及以上版本的特性。 註意:主類的名字必須是:Main,否則按無效代碼處理。
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 3 public class Main { 4 public static int n; 5 public static int[] row, ring; 6 public static boolean[][] visited; 7 public static int[][] move = {{-1,0},{1,0},{0,-1},{0,1}}; 8 9 public void dfs(int[] s_row, int[] s_ring, int x, int y, int[] roat, int num) { 10 if(x == n - 1 && y == n - 1) { 11 boolean judgeX = true, judgeY = true; 12 for(int i = 0;i < n;i++) { 13 if(s_row[i] != row[i]) 14 judgeX = false; 15 if(s_ring[i] != ring[i]) 16 judgeY = false; 17 } 18 if(judgeX && judgeY) { 19 System.out.print("0 "); 20 for(int i = 0;i < num;i++) 21 System.out.print(roat[i]+" "); 22 System.out.println(); 23 } 24 return; 25 } 26 for(int i = 0;i < 4;i++) { 27 int tempX = x + move[i][0]; 28 int tempY = y + move[i][1]; 29 if(tempX >= 0 && tempX < n && tempY >= 0 && tempY < n && 30 !visited[tempX][tempY]) { 31 visited[tempX][tempY] = true; 32 s_row[tempX]++; 33 s_ring[tempY]++; 34 roat[num] = tempX * n + tempY; 35 dfs(s_row, s_ring, tempX, tempY, roat, num + 1); 36 visited[tempX][tempY] = false; 37 s_row[tempX]--; 38 s_ring[tempY]--; 39 } 40 } 41 } 42 43 public void getResult() { 44 int[] roat = new int[n * n + 1]; 45 int[] s_row = new int[n]; 46 int[] s_ring = new int[n]; 47 visited[0][0] = true; 48 s_row[0]++; 49 s_ring[0]++; 50 dfs(s_row, s_ring, 0, 0, roat, 0); 51 } 52 53 public static void main(String[] args) { 54 Main test = new Main(); 55 Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); 56 n = in.nextInt(); 57 row = new int[n]; 58 ring = new int[n]; 59 visited = new boolean[n][n]; 60 for(int i = 0;i < n;i++) 61 ring[i] = in.nextInt(); 62 for(int i = 0;i < n;i++) 63 row[i] = in.nextInt(); 64 test.getResult(); 65 } 66 }
5 堿基
堿基 生物學家正在對n個物種進行研究。 其中第i個物種的DNA序列為s[i],其中的第j個堿基為s[i][j],堿基一定是A、T、G、C之一。 生物學家想找到這些生物中一部分生物的一些共性,他們現在關註那些至少在m個生物中出現的長度為k的連續堿基序列。準確的說,科學家關心的序列用2m元組(i1,p1,i2,p2....im,pm)表示, 滿足: 1<=i1<i2<....<im<=n; 且對於所有q(0<=q<k), s[i1][p1+q]=s[i2][p2+q]=....=s[im][pm+q]。 現在給定所有生物的DNA序列,請告訴科學家有多少的2m元組是需要關註的。如果兩個2m元組有任何一個位置不同,則認為是不同的元組。 【輸入格式】 輸入的第一行包含三個整數n、m、k,兩個整數之間用一個空格分隔,意義如題目所述。 接下來n行,每行一個字符串表示一種生物的DNA序列。 DNA序列從1至n編號,每個序列中的堿基從1開始依次編號,不同的生物的DNA序列長度可能不同。 【輸出格式】 輸出一個整數,表示關註的元組個數。 答案可能很大,你需要輸出答案除以1000000007的余數。 【樣例輸入】 3 2 2 ATC TCG ACG 【樣例輸出】 2 再例如: 【樣例輸入】 4 3 3 AAA AAAA AAA AAA 【樣例輸出】 7 【數據規模與約定】 對於20%的數據,k<=5,所有字符串總長L滿足L <=100 對於30%的數據,L<=10000 對於60%的數據,L<=30000 對於100%的數據,n<=5,m<=5,1<=k<=L<=100000 保證所有DNA序列不為空且只會包含’A’ ’G’ ’C’ ’T’四種字母 資源約定: 峰值內存消耗 < 256M CPU消耗 < 1000ms 請嚴格按要求輸出,不要畫蛇添足地打印類似:“請您輸入...” 的多余內容。 所有代碼放在同一個源文件中,調試通過後,拷貝提交該源碼。 註意:不要使用package語句。不要使用jdk1.7及以上版本的特性。 註意:主類的名字必須是:Main,否則按無效代碼處理。 以下代碼為暴力求解,對於數據較大情況會超時,代碼僅供參考。
1 import java.util.ArrayList; 2 import java.util.HashSet; 3 import java.util.Scanner; 4 5 public class Main { 6 public static int n, m, k; 7 public static String[] S; 8 public static String[] num; 9 public static int[] start; 10 public static long MOD = 1000000007; 11 public static long count = 0; 12 public static HashSet<String> result = new HashSet<String>(); 13 14 public void dfs(int step, int sum) { 15 if(step == n || sum >= m) { 16 if(sum >= m) { 17 ArrayList<String> set = new ArrayList<String>(); 18 StringBuffer[] s = new StringBuffer[sum]; 19 for(int i = 0;i < sum;i++) 20 s[i] = new StringBuffer(""); 21 for(int i = 0;i < n;i++) { 22 if(!num[i].equals("-")) { 23 if(!set.contains(num[i])) { 24 set.add(num[i]); 25 s[set.size() - 1].append(i); 26 s[set.size() - 1].append(start[i]); 27 } else { 28 int j = set.indexOf(num[i]); 29 s[j].append(i); 30 s[j].append(start[i]); 31 } 32 } 33 } 34 if(set.size() == sum - m + 1) { 35 for(int i = 0;i < sum;i++) { 36 if(s[i].toString().length() == k * 2) { 37 if(!result.contains(s[i].toString())) 38 count = (count + 1) % MOD; 39 result.add(s[i].toString()); 40 break; 41 } 42 } 43 } 44 } 45 return; 46 } else { 47 for(int i = 0;i < S[step].length();i++) { 48 if(i + k <= S[step].length()) { 49 num[step] = S[step].substring(i, i + k); 50 start[step] = i; 51 dfs(step + 1, sum + 1); 52 num[step] = "-"; 53 } 54 dfs(step + 1, sum); 55 } 56 } 57 } 58 59 public static void main(String[] args) { 60 Main test = new Main(); 61 Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); 62 n = in.nextInt(); 63 m = in.nextInt(); 64 k = in.nextInt(); 65 S = new String[n]; 66 for(int i = 0;i < n;i++) 67 S[i] = in.next(); 68 num = new String[n + 1]; 69 start = new int[n + 1]; 70 for(int i = 0;i <= n;i++) 71 num[i] = "-"; 72 test.dfs(0, 0); 73 System.out.println(count); 74 } 75 76 }
6 圓圈舞
圓圈舞 春天溫暖的陽光照耀著大地,正是草原上的小動物們最快樂的時候。小動物們在草原上開了一個舞會,歡度這美好的時光。 舞會上最重要的一個環節就是跳圓舞曲,n只小動物手拉手圍成一大圈,隨著音樂跳起來。在跳的過程中,小動物們可能會變換隊形。它們的變換方式是動物A松開自己右手,動物B松開自己的左手,動物A和B手拉到一起,而它們對應的松開的手(如果有的話)也拉到一起。 例如,假設有10只小動物,按順序圍成一圈,動物1的右手拉著動物2的左手,動物2的右手拉著動物3的左手,依次類推,最後動物10的右手拉著動物1的左手。如果通過動物2和8變換隊形,則動物2的右手拉著動物8的左手,而對應的動物3的左手拉著動物7的右手,這樣形成了1-2-8-9-10和3-4-5-6-7兩個圈。如果此時通過動物2和6變換隊形,則將形成1-2-6-7-3-4-5-8-9-10一個大圈。註意,如果此時通過動物1和2變換隊形,那麽隊形不會改變,因為動物1的右手和動物2的左手松開後又拉到一起了。 在跳舞的過程中,每個動物i都有一個歡樂值Hi和一個感動值Fi。 如果兩個動物在一個圈中,歡樂值會彼此影響,產生歡樂能量。如果兩個動物i, j(i≠j)在同一個大小為t的圈中,而動物i在動物j右手的第p個位置(動物j右手的第1個位置就是動物j右手所拉著的動物,而第2個位置就是右手第1個位置的動物右手拉著的動物,依次類推),則產生的歡樂能量為(t-p)*Hj*Fi。在跳舞的過程中,動物們的歡樂值和感動值有可能發生變化。 圓舞曲開始的時候,所有的動物按編號順序圍成一個圈,動物n右手的第i個位置正好是動物i。現在已知小動物們變換隊形的過程和歡樂值、感動值變化的過程,求每次變換後所有動物所產生的歡迎能量之和。 【輸入格式】 輸入的第一行包含一個整數n,表示動物的數量。 接下來n行,每行兩個用空格分隔的整數Hi, Fi,按編號順序給出每只動物的歡樂值和感動值。 接下來一行包含一個整數m,表示隊形、歡樂值、感動值的變化次數。 接下來m行,每行三個用空格分隔的整數k, p, q,當k=1時,表示小動物們通過動物p和動物q變換了隊形,當k=2時,表示動物p的歡樂值變為q,當k=3時,表示動物p的感動值變為了q。 【輸出格式】 輸出m行,每行一個整數,表示每次變化後所有動物產生的能量之和。 答案可能很大,你需要計算答案除以1000000007的余數。 【樣例輸入】 10 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 9 1 2 8 1 2 6 2 8 10 3 5 10 1 1 2 1 2 1 2 5 5 1 4 8 1 4 5 【樣例輸出】 100 450 855 1341 1341 811 923 338 923 【數據規模與約定】 對於20%的數據,2<=n,m<=100。 對於30%的數據,2<=n,m<=1000。 另有20%的數據,只有k=1的操作且Hi,Fi均為1。 另有20%的數據,只有k=1或2的操作且Fi均為1。 對於100%的數據,2<=n,m<=100000,0<=Hi,Fi<=10^9,1<=k<=3,k=1時1<=p,q<=n且p≠q,k=2或3時1<=p<=n且0<=q<=10^9。 資源約定: 峰值內存消耗 < 256M CPU消耗 < 5000ms 請嚴格按要求輸出,不要畫蛇添足地打印類似:“請您輸入...” 的多余內容。 所有代碼放在同一個源文件中,調試通過後,拷貝提交該源碼。 註意:不要使用package語句。不要使用jdk1.7及以上版本的特性。 註意:主類的名字必須是:Main,否則按無效代碼處理。 以下代碼為暴力求解,對於數據較大情況會超時,代碼僅供參考。
1 import java.util.ArrayList; 2 import java.util.Scanner; 3 4 public class Main { 5 public static int n, m; 6 public static Animal[] num; 7 public static long MOD = 1000000007; 8 public static long[] result; 9 10 static class Animal{ 11 public int id; 12 public int h; 13 public int f; 14 public int id_left; 15 public int id_right; 16 17 public Animal(int id, int h, int f, int id_left, int id_right) { 18 this.id = id; 19 this.h = h; 20 this.f = f; 21 this.id_left = id_left; 22 this.id_right = id_right; 23 } 24 } 25 26 public void changQueue(int p, int q) { 27 int p_right = num[p].id_right; 28 int q_left = num[q].id_left; 29 num[p].id_right = q; 30 num[q].id_left = p; 31 num[p_right].id_left = q_left; 32 num[q_left].id_right = p_right; 33 } 34 35 public long getResult() { 36 long ans = 0; 37 boolean[] used = new boolean[n + 1]; 38 for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++) { 39 if(used[i] == true) 40 continue; 41 ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>(); 42 int begin = num[i].id; 43 int start = begin; 44 int end = num[i].id_right; 45 list.add(start); 46 used[start] = true; 47 while(begin != end) { 48 start = end; 49 end = num[start].id_right; 50 list.add(start); 51 used[start] = true; 52 } 53 int len = list.size(); 54 for(int a = 0;a < len;a++) { 55 for(int b = a + 1;b < len;b++) { 56 int id_a = list.get(a); 57 int id_b = list.get(b); 58 int p1 = len - b + a; 59 ans = ans + (len - p1) * num[id_b].h * num[id_a].f; 60 ans = ans % MOD; 61 int p2 = b - a; 62 ans = ans + (len - p2) * num[id_a].h * num[id_b].f; 63 ans = ans % MOD; 64 } 65 } 66 } 67 return ans; 68 } 69 70 public static void main(String[] args) { 71 Main test = new Main(); 72 Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); 73 n = in.nextInt(); 74 num = new Animal[n + 1]; 75 for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++) { 76 int h = in.nextInt(); 77 int f = in.nextInt(); 78 if(i == 1) 79 num[i] = new Animal(i, h, f, n, i + 1); 80 else if(i == n) 81 num[i] = new Animal(i, h, f, i - 1, 1); 82 else 83 num[i] = new Animal(i, h, f, i - 1, i + 1); 84 } 85 m = in.nextInt(); 86 result = new long[m]; 87 for(int i = 0;i < m;i++) { 88 int k = in.nextInt(); 89 int p = in.nextInt(); 90 int q = in.nextInt(); 91 if(k == 1) { 92 test.changQueue(p, q); 93 } else if(k == 2) { 94 num[p].h = q; 95 } else if(k == 3) { 96 num[p].f = q; 97 } 98 result[i] = test.getResult(); 99 } 100 for(int i = 0;i < m;i++) 101 System.out.println(result[i]); 102 } 103 }
算法筆記_212:第七屆藍橋杯軟件類決賽真題(Java語言B組)
