MySQL基礎學習二
一,數據庫操作
主鍵
主鍵是索引的一種,並且是唯一性索引,且必須定義為primary key。一個表只有一個主鍵,主鍵可以由多列組成。
聲明主鍵的關鍵字為:primary key
簡單的一個聲明主鍵的示例:
create table score(sid int auto_increment primary key)engine=innodb default charset=utf8 primary key為聲明的關鍵字。
外鍵
如果一個實體的某個字段指向另一個實體的主鍵,就稱為外鍵。
被指向的實體,稱之為主實體(主表),也叫父實體(父表)。
負責指向的實體,稱之為從實體(從表),也叫子實體(子表)。
作用:用於約束處於關系內的實體。增加子表記錄的時候,是否有與之對應的父表記錄,如果主表沒有相關的記錄,從表不能插入。
外鍵示例代碼:
#創建被關聯的子表 create table class(cid int auto_increment primary key,clname char(20))engine=innodb default charset=utf8; #插入數據 insert into class(clname) values("三年級"),("一年級"),("四年級"),("二年級"); #創建主表(父表) create table student(sid int auto_increment primarykey,sname char(12), class_id int,constraint fk_id_class foreign key(class_id) references class(cid)) engine=innodb default charset=utf8; #constraint fk_id_class foreign key(class_id) references class(cid)關鍵詞,foreign key後跟父表列名,reference後加子表列名。 insert into student(sname,class_id) values("stu1"),("stu2"),("stu3");
外鍵變種:
外鍵與主鍵都有唯一索引,且都不能重復。區別就是主鍵不能為空,外鍵的唯一索引可以為空。
外鍵變種分為以下幾種關系:
一對多,一對一,多對多
1,一對一關系:
create table userinfo1( id int auto_increment primary key, name char(10), gender char(10), email varchar(64) )engine=innodb default charset=utf8; create table admin( id int not null auto_increment primary key, username varchar(64) not null, password VARCHAR(64) not null, user_id int not null, unique uq_u1 (user_id),#關鍵字,指定外鍵的一對一關系 CONSTRAINT fk_admin_u1 FOREIGN key (user_id) REFERENCES userinfo1(id) )engine=innodb default charset=utf8;
2,一對多關系
3,多對多關系
create table userinfo2( id int auto_increment primary key, name char(10), gender char(10), email varchar(64) )engine=innodb default charset=utf8; create table host( id int auto_increment primary key, hostname char(64) )engine=innodb default charset=utf8; create table user2host( id int auto_increment primary key, userid int not null, hostid int not null, unique uq_user_host (userid,hostid),#關鍵字,指定為多對多的關系語句 CONSTRAINT fk_u2h_user FOREIGN key (userid) REFERENCES userinfo2(id), CONSTRAINT fk_u2h_host FOREIGN key (hostid) REFERENCES host(id) )engine=innodb default charset=utf8;
數據表的操作:
插入,修改,選擇,刪除數據:
#一次插入多條數據的方式: insert into student(sname,class_id) values("stu1"),("stu2"),("stu3"); #修改表內數據 update student set sname="stu10" #操作顯示表數據 select sid,sname from student;#顯示學生表的id與學生名字 select sid,sname from student where sid>3;顯示表中sid大於3,的學生id與姓名 #刪除表數據 delete from student where id=1;#刪除表中id為1的數據
where條件語句
where:條件限制語句,在數據操作中需要對數據進行按條件篩選,就需要用到where語句。在使用時徐註意:
where函數條件後不允許加聚合函數條件
語法: where 條件表達式
條件表達式的運算符
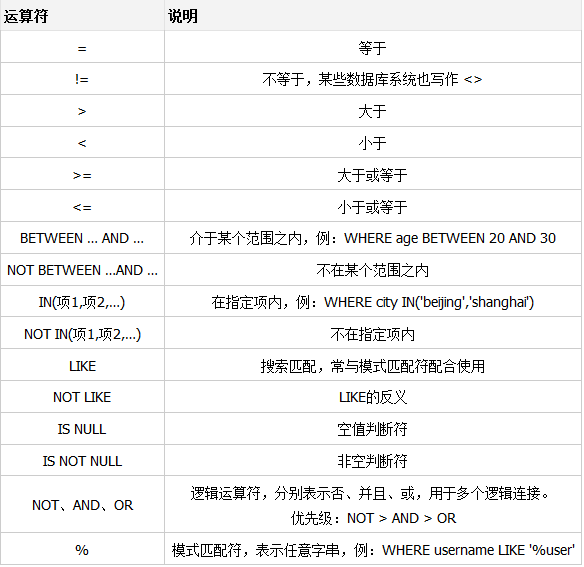
模糊匹配的關鍵字 like
模糊匹配補充 _下劃線 指的是該字符之後的一個任意數值,示例:where username like"a_"
自增數據操作
在數據表的會經常設置自增數據,自增數據是可以對其進行修改查看等操作的。由於mysql的步長是基於會話操作的,每次修改針對的是每一個會話而不是全局,如果需要對全局進行修改要是global
查看:
show session variables like ‘auto_inc%‘; +--------------------------+-------+ | Variable_name | Value | +--------------------------+-------+ | auto_increment_increment | 1 | | auto_increment_offset | 1 | +--------------------------+-------+ 2 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
修改自增步長:
set session auto_increment_increment=2; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) show session variables like ‘auto_inc%‘; +--------------------------+-------+ | Variable_name | Value | +--------------------------+-------+ | auto_increment_increment | 2 | | auto_increment_offset | 1 | +--------------------------+-------+ 2 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
全局查看:
全局查看是基於關鍵字global。
設置全局步長值:set global auto_increment_increment=2;
show global variables like ‘auto_inc%‘; +--------------------------+-------+ | Variable_name | Value | +--------------------------+-------+ | auto_increment_increment | 1 | | auto_increment_offset | 1 | +--------------------------+-------+ 2 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
MySQL基礎學習二
