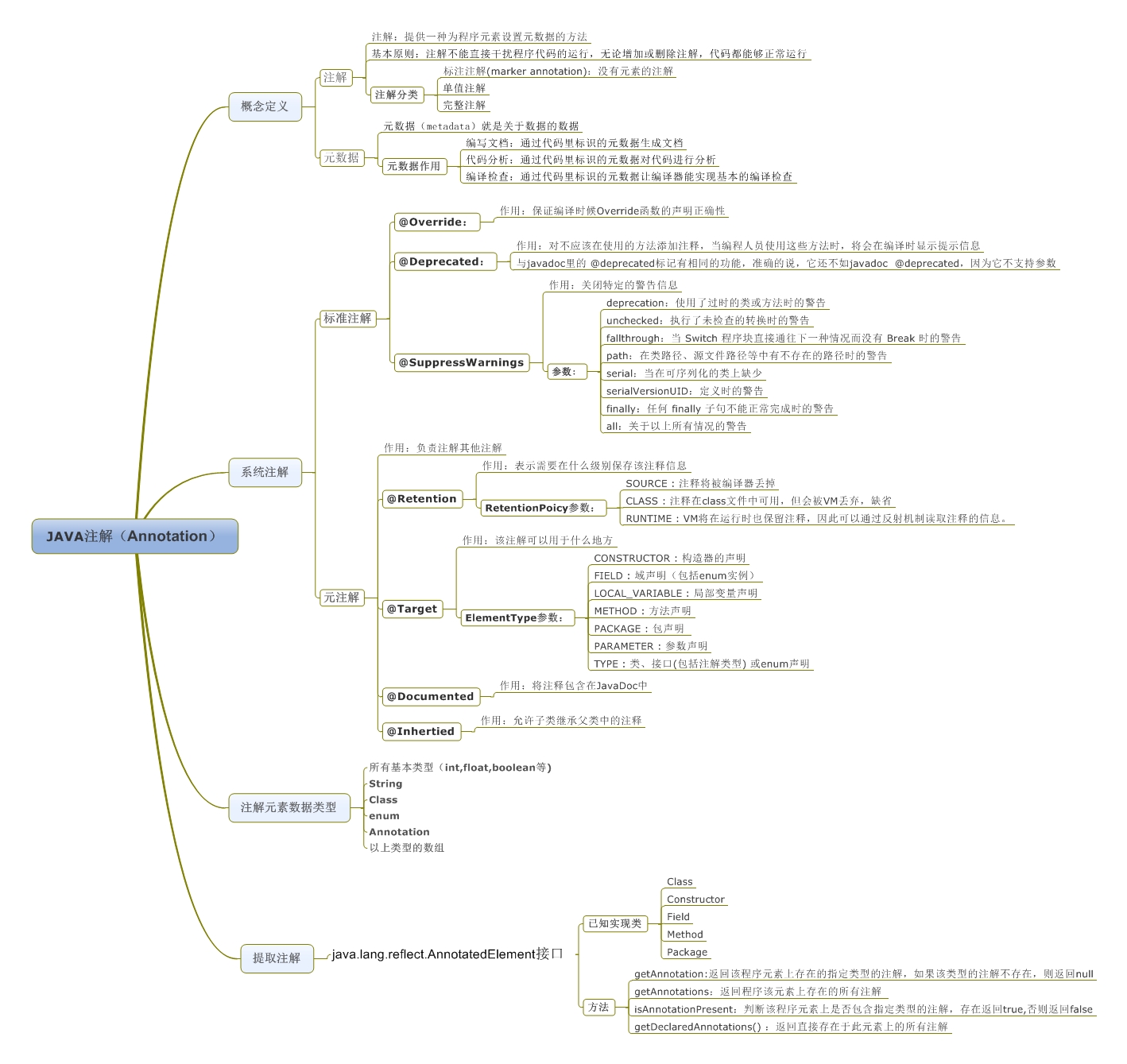
JAVA註解Annotation
從 JDK 5.0 開始, Java 增加了對元數據(MetaData) 的支持, 也就是 Annotation(註解)
Annotation 其實就是代碼裏的特殊標記, 這些標記可以在編譯, 類加載, 運行時被讀取, 並執行相應的處理. 通過使用 Annotation, 程序員可以在不改變原有邏輯的情況下, 在源文件中嵌入一些補充信息.
Annotation 可以像修飾符一樣被使用, 可用於修飾包,類, 構造器, 方法, 成員變量, 參數, 局部變量的聲明, 這些信息被保存在 Annotation 的 “name=value” 對中.
Annotation 能被用來為程序元素(類, 方法, 成員變量等) 設置元數據
三個基本的 Annotation:
@Override: 限定重寫父類方法, 該註釋只能用於方法
@Deprecated: 用於表示某個程序元素(類, 方法等)已過時
@SuppressWarnings: 抑制編譯器警告
JDK5.0提供了專門在註解上的註解類型,分別是:
1.Retention
2.Target
3.Documented
4.Inherited
@Retention: 只能用於修飾一個 Annotation 定義, 用於指定該 Annotation 可以保留多長時間, @Rentention 包含一個 RetentionPolicy 類型的成員變量, 使用 @Rentention 時必須為該 value 成員變量指定值:
RetentionPolicy.CLASS: 編譯器將把註釋記錄在 class 文件中. 當運行 Java 程序時, JVM 不會保留註 解。 這是默認值
RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME:編譯器將把註釋記錄在 class 文件中. 當運行 Java 程序時, JVM 會保留註釋. 程序可以通過反射獲取該註釋
@Target: 用於修飾 Annotation 定義, 用於指定被修飾的 Annotation 能用於修飾哪些程序元素. @Target 也包含一個名為 value 的成員變量.
@Documented:
定義為Documented的註解必須設置Retention值為RUNTIME。
@Inherited: 被它修飾的 Annotation 將具有繼承性.如果某個類使用了被 @Inherited 修飾的 Annotation, 則其子類將自動具有該註解
實際應用中,使用較少
註解處理器類庫(java.lang.reflect.AnnotatedElement):
Java使用Annotation接口來代表程序元素前面的註解,該接口是所有Annotation類型的父接口。除此之外,Java在java.lang.reflect 包下新增了AnnotatedElement接口,該接口代表程序中可以接受註解的程序元素,該接口主要有如下幾個實現類:
Class:類定義
Constructor:構造器定義
Field:累的成員變量定義
Method:類的方法定義
Package:類的包定義
java.lang.reflect 包下主要包含一些實現反射功能的工具類,實際上,java.lang.reflect
包所有提供的反射API擴充了讀取運行時Annotation信息的能力。當一個Annotation類型被定義為運行時的Annotation後,該註解才能是運行時可見,當class文件被裝載時被保存在class文件中的Annotation才會被虛擬機讀取。
AnnotatedElement
接口是所有程序元素(Class、Method和Constructor)的父接口,所以程序通過反射獲取了某個類的AnnotatedElement對象之後,程序就可以調用該對象的如下四個個方法來訪問Annotation信息:
方法1:<T extends Annotation> T getAnnotation(Class<T> annotationClass): 返回改程序元素上存在的、指定類型的註解,如果該類型註解不存在,則返回null。
方法2:Annotation[] getAnnotations():返回該程序元素上存在的所有註解。
方法3:boolean is AnnotationPresent(Class<?extends Annotation> annotationClass):判斷該程序元素上是否包含指定類型的註解,存在則返回true,否則返回false.
方法4:Annotation[]
getDeclaredAnnotations():返回直接存在於此元素上的所有註釋。與此接口中的其他方法不同,該方法將忽略繼承的註釋。(如果沒有註釋直接存在於此元素上,則返回長度為零的一個數組。)該方法的調用者可以隨意修改返回的數組;這不會對其他調用者返回的數組產生任何影響。
一個簡單的註解處理器:
/***********註解聲明***************//**
* 水果名稱註解
* @author yang
* [email protected](ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documentedpublic @interface FruitName {
String value() default "";
}/**
* 水果顏色註解
* @author yang
* [email protected](ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documentedpublic @interface FruitColor { /**
* 顏色枚舉
* @author peida
* */
public enum Color{ BULE,RED,GREEN};
/**
* 顏色屬性
* @return
*/
Color fruitColor() default Color.GREEN;
}/**
* 水果供應者註解
* @author yang
* [email protected](ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documentedpublic @interface FruitProvider { /**
* 供應商編號
* @return
*/
public int id() default -1;
/**
* 供應商名稱
* @return
*/
public String name() default "";
/**
* 供應商地址
* @return
*/
public String address() default "";
}/***********註解使用***************/public class Apple {
@FruitName("Apple") private String appleName;
@FruitColor(fruitColor=Color.RED) private String appleColor;
@FruitProvider(id=1,name="陜西紅富士集團",address="陜西省西安市延安路89號紅富士大廈") private String appleProvider;
public void setAppleColor(String appleColor) { this.appleColor = appleColor;
} public String getAppleColor() { return appleColor;
}
public void setAppleName(String appleName) { this.appleName = appleName;
} public String getAppleName() { return appleName;
}
public void setAppleProvider(String appleProvider) { this.appleProvider = appleProvider;
} public String getAppleProvider() { return appleProvider;
}
public void displayName(){
System.out.println("水果的名字是:蘋果");
}
}/***********註解處理器***************/
public class FruitInfoUtil {
public static void getFruitInfo(Class<?> clazz){
String strFruitName=" 水果名稱:";
String strFruitColor=" 水果顏色:";
String strFruitProvicer="供應商信息:";
Field[] fields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();
for(Field field :fields){ if(field.isAnnotationPresent(FruitName.class)){
FruitName fruitName = (FruitName) field.getAnnotation(FruitName.class);
strFruitName=strFruitName+fruitName.value();
System.out.println(strFruitName);
} else if(field.isAnnotationPresent(FruitColor.class)){
FruitColor fruitColor= (FruitColor) field.getAnnotation(FruitColor.class);
strFruitColor=strFruitColor+fruitColor.fruitColor().toString();
System.out.println(strFruitColor);
} else if(field.isAnnotationPresent(FruitProvider.class)){
FruitProvider fruitProvider= (FruitProvider) field.getAnnotation(FruitProvider.class);
strFruitProvicer=" 供應商編號:"+fruitProvider.id()+" 供應商名稱:"+fruitProvider.name()+" 供應商地址:"+fruitProvider.address();
System.out.println(strFruitProvicer);
}
}
}
}
/***********輸出結果***************/public class FruitRun {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
FruitInfoUtil.getFruitInfo(Apple.class);
}
}
====================================
水果名稱:Apple
水果顏色:RED
供應商編號:1 供應商名稱:陜西紅富士集團 供應商地址:陜西省西安市延安路89號紅富士大廈Java註解的基礎知識點(見下面導圖)基本都過了一遍,下一篇我們通過設計一個基於註解的簡單的ORM框架,來綜合應用和進一步加深對註解的各個知識點的理解和運用。
本文出自 “ciyo技術分享” 博客,請務必保留此出處http://ciyorecord.blog.51cto.com/6010867/1934218
JAVA註解Annotation
