varnish的了解與常用配置使用
Varnish是一款高性能的開源HTTP加速器及反向代理服務器。
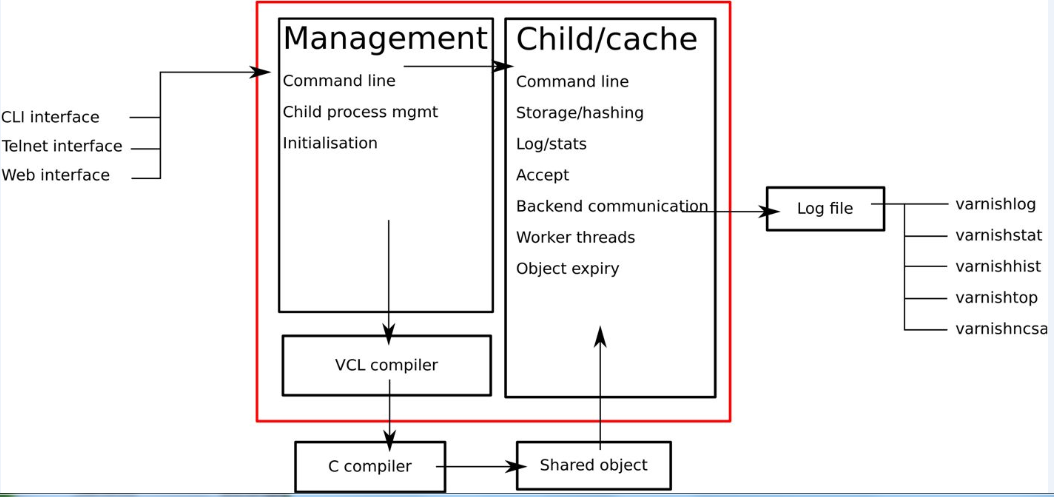
varnish架構圖:
Varnish 與一般服務器軟件類似,分為 master 進程和 child 進程。Master 進程讀入存儲配置文件,調用合適的存儲類型,然後創建 / 讀入相應大小的緩存文件,接著 master 初始化管理該存儲空間的結構體,然後 fork 並監控 child 進程。Child 進程在主線程的初始化的過程中,將前面打開的存儲文件整個 mmap 到內存中,此時創建並初始化空閑結構體,掛到存儲管理結構體,以待分配。Child 進程分配若幹線程進行工作,主要包括一些管理線程和很多 worker 線程。
接著,開始真正的工作,varnish 的某個負責接收新 HTTP 連接線程開始等待用戶,如果有新的 HTTP 連接過來,它總負責接收,然後喚醒某個等待中的線程,並把具體的處理過程交給它。Worker 線程讀入 HTTP 請求的 URI,查找已有的 object,如果命中則直接返回並回復用戶。如果沒有命中,則需要將所請求的內容,從後端服務器中取過來,存到緩存中,然後再回復。
分配緩存的過程是這樣的:它根據所讀到 object 的大小,創建相應大小的緩存文件。為了讀寫方便,程序會把每個 object 的大小變為最接近其大小的內存頁面倍數。然後從現有的空閑存儲結構體中查找,找到最合適的大小的空閑存儲塊,分配給它。如果空閑塊沒有用完,就把多余的內存另外組成一個空閑存儲塊,掛到管理結構體上。如果緩存已滿,就根據 LRU 機制,把最舊的 object 釋放掉。
釋放緩存的過程是這樣的:有一個超時線程,檢測緩存中所有 object 的生存期,如果超初設定的 TTL(Time To Live)沒有被訪問,就刪除之,並且釋放相應的結構體及存儲內存。註意釋放時會檢查該存儲內存塊前面或後面的空閑內存塊,如果前面或後面的空閑內存和該釋放內存是連續的,就將它們合並成更大一塊內存。
整個文件緩存的管理,沒有考慮文件與內存的關系,實際上是將所有的 object 都考慮是在內存中,如果系統內存不足,系統會自動將其換到 swap 空間,而不需要 varnish 程序去控制。
配置使用varnish
CentOS7上epel源上直接安裝使用:varnish-4.0.5
[[email protected] dylan]# yum install varnish epel源
[[email protected] dylan]# cd /etc/varnish/
[[email protected] varnish]# cp varnish.params{,.bak}
[[email protected] varnish]# systemctl start varnish.service
示例:
一臺web服務器安裝httpd作為後端服務器
[[email protected] ~]# vim /var/www/html/index.html
<h1> Backend Server 1</h1>
varnish主機上編輯:
[[email protected] varnish]# vim default.vcl
backend default {
.host = "192.168.0.150"; ###後端服務器地址
.port = "80"; ###端口
[[email protected] varnish]# systemctl reload varnish.service
舉幾個常用示例:
1、.測試緩存命中情況:
[[email protected] ~]# vim /etc/varnish/default.vcl
sub vcl_deliver {
# Happens when we have all the pieces we need, and are about to send the
# response to the client.
#
# You can do accounting or modifying the final object here.
if (obj.hits>0) { ###增加
set resp.http.X-Cache = "HIT";
} else {
set resp.http.X-Cache = "Miss";
}
}
sub vcl_deliver {
# Happens when we have all the pieces we need, and are about to send the
# response to the client.
#
# You can do accounting or modifying the final object here.
if (obj.hits>0) {
set resp.http.X-Cache = "HIT via" + " " + server.ip;
} else {
set resp.http.X-Cache = "Miss via" + " " + server.ip;
}
}
###使varnishadm工具來管理
[[email protected] ]# varnishadm -S /etc/varnish/secret -T 127.0.0.1:6082 ###varnishadm命令
vcl.load test1 default.vcl
200
VCL compiled.
varnish> vcl.use test1
200
VCL ‘test1‘ now active
2、緩存對象修剪
acl purgers { ###添加訪問控制 varnish4.0
"127.0.0.0"/8;
"192.168.0.0"/16;
}
sub vcl_recv {
# Happens before we check if we have this in cache already.
#
# Typically you clean up the request here, removing cookies you don‘t need,
# rewriting the request, etc.
if (req.url ~"^/test.html$") {
return(pass);
}
if (req.method == "PURGE"){
if (!client.ip ~ purgers){ ###ip不屬於定義端內的返回405錯誤
return(synth(405,"Purging not allow for" + client.ip));
}
return(purge);
}
}
sub vcl_purge {
return(synth(200,"Purged,")); ###修剪
}
管理端:
varnish> vcl.load test9 default.vcl ###重新配置
200
VCL compiled.
vcl.use test9 ###使用新配置
200
VCL ‘test9‘ now active
3、###設定多個後端主機
backend default {
.host = "192.168.0.150";
.port = "80";
}
backend appsrv { ###定義一個後端主機
.host = "192.168.0.113";
.port = "80";
}
sub vcl_recv {
# Happens before we check if we have this in cache already.
#
# Typically you clean up the request here, removing cookies you don‘t need,
# rewriting the request, etc.
if (req.url ~"(?i)\.php$") {
set req.backend_hint = appsrv;
} else {
set req.backend_hint = default;
}
}
vcl.load test10 default.vcl
200
VCL compiled.
vcl.load
varnish> vcl.use test10
200
VCL ‘test10‘ now active
4、設定負載均衡效果:
Directors:
import directors; ###首先import
backend websrv1 { ###定義兩個後端主機
.host = "192.168.0.150";
.port = "80";
}
backend websrv2 {
.host = "192.168.0.115";
.port = "80";
}
sub vcl_init {
new websrvs = directors.round_robin();
websrvs.add_backend(websrv1);
websrvs.add_backend(websrv2);
}
sub vcl_recv {
set req.backend_hint = websrvs.backend();
}
管理端使用:
varnish> vcl.load test13 default.vcl
200
VCL compiled.
vcl.use test13
200
VCL ‘test13‘ now active
5、健康狀態檢測:
backend websrv1 {
.host = "192.168.0.115";
.host = "80";
.prode = {
.url = "/";
.interval = 1s;
.window = 8;
.threshold = 5;
.timeout = 2s;
}
}
.request =
"GET /HTTP/1.1"
"Host: 192.168.0.115"
"connection:Close"
.expected_response=200;
完整性示例:
vcl 4.0;
import directors;
# Default backend definition. Set this to point to your content server.
backend websrv1 {
.host = "192.168.0.150";
.port = "80";
.probe = {
.url = "/";
.interval = 2s;
.window = 5;
.threshold = 4;
}
}
backend websrv2 {
.host = "192.168.0.115";
.port = "80";
.probe = {
.url = "/";
.interval = 2s;
.window = 5;
.threshold = 4;
}
}
sub vcl_init {
new websrvs = directors.round_robin();
websrvs.add_backend(websrv1);
websrvs.add_backend(websrv2);
}
sub vcl_recv {
# if (req.url ~"(?i)\.php$") {
# set req.backend_hint = appsrv;
# } else {
set req.backend_hint = websrvs.backend();
# }
if (req.url ~"^/login") {
return(pass);
}
if (req.method == "PURGE"){
if (!client.ip ~ purgers){
return(synth(405,"Purging not allow for" + client.ip));
}
return(purge);
}
}
sub vcl_purge {
return(synth(200,"Purged,"));
}
acl purgers {
"127.0.0.0"/8;
"192.168.0.0"/16;
}
sub vcl_backend_response {
if (beresp.http.cache-control !~ "s-masage") {
if (bereq.url ~ "(?i)\.jpg$") {
set beresp.ttl = 7200s;
unset beresp.http.Set-Cookie;
}
if (bereq.url ~ "(?i)\.css$"){
set beresp.ttl = 3600s;
unset beresp.http.Set-Cookie;
}
}
}
sub vcl_deliver {
if (obj.hits>0) {
set resp.http.X-Cache = "HIT via" + " " + server.ip;
} else {
set resp.http.X-Cache = "Miss via" + " " + server.ip;
}
# if (beresp.backend.name ~ "appsrv") {
# set resp.htttp.X-Server = "appsrv";
# }
}
varnish幾個常用的命令工具:
varnishadm
varnishtop
varish log entry ranking
varnishlog
varnishlog.service
varnishncsa
varnishncsa.service
varnishstat
Varnish Cache statistics
varnish的運行時參數: 配置文件中修改全局生效
[[email protected] ~]# vim /etc/varnish/varnish.params
DAEMON_OPTS="-p thread_pools=4" ###設置線程池為4
[[email protected] ~]# systemctl restart varnish.service ###不能隨便重啟,否則緩存全部失效
[[email protected] varnish]# varnishstat ###查看狀態
附:
變量
內鍵變量:
req.*:由客戶端發來的http請求相關
req.http.*:請求報文各首部
bereq.*:由varnish向backend主機發出的http請求
bere.http.*
beresp.*:由backend主機發來的http響應報文
resp.*: 由varnish響應給client的http響應報文
resp.http.*:響應報文各首部
obj.*:存儲在緩存空間的緩存對象屬性,只讀
client.*,server.*,storage.*:可用在所有的client side 的sub riutines中
自定義: set
常用的變量:
bereq:
bereq.http.HEADERS
bereq.request:請求方法
bereq.url:請求的url
bereq.proto:協議版本
bereq.backend:指明要調用的後端主機
beresp:
beresp.proto
beresp.status:響應的狀態碼
beresp.reason
beresp.backend.name
baresp.http.HEADERA:
beresp.ttl:後端服務器響應中的內容余下的生存時長
obj:
obj.hits:此對象從緩存中命中的次數;
obj.ttl:對象的ttl值
server:
server.ip
server.hostname
req.method:請求方法
req.url:請求的url
本文出自 “11290766” 博客,請務必保留此出處http://rylan.blog.51cto.com/11290766/1957126
varnish的了解與常用配置使用