有關IO流的其他常用流
操作基本數據類型的流、內存操作流、打印流、標準輸入流和標準的輸出流、隨機訪問流、合並流、序列化流/反序列化流、屬性集合類
一、操作基本數據類型的流
DataInputStream :數據輸入流
DataOutputStream:數據輸出流
可以操作一些基本數據類型
egg:
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("dos.txt"));
das.writeByte(10);
das.writeShort(100);
das.writeInt(1000);
das.writeLong(10000L);
das.writeFloat(12.34F);
das.writeDouble(12.56);
das.writeBoolean(true);
das.writeChar(‘A‘);
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream("das.txt"));
System.out.println(dis.readByte());
System.out.println(dis.readShort());
System.out.println(dis.readInt());
System.out.println(dis.readLong());
System.out.println(dis.readFloat());
System.out.println(dis.readDouble());
System.out.println(dis.readBoolean());
System.out.println(dis.readChar());
dos.close();
dis.close();
二、內存操作流
用來存儲內存中的臨時信息,程序結束,內存流消失
字節數組操作內存流:
ByteArrayInputStream
ByteArrayOutputStream
字符數組操作的內存流:
CharArrayReader
CharArrayWriter
字符串操作的內存流:
StringReader
StringWriter
egg:
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
baos.write("hello".getBytes());
byte[] bys = baos.toByteArray();
ByteArrayInputStream bais = new ByteArrayInputStream(bys);
int by=0;
while((by=bais.read())!= -1){
System.out.print((char)by);
}
該流的close方法沒有任何的操作,該流可以不用關閉
三、打印流(只能寫數據,不能讀數據)
1、字節打印流:PrintStream
構造方法:
printStream ps = System.out;
寫數據:
println()帶換行
print()
System.out.println();
2、字符打印流:PrintWriter
egg:
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter("pt.txt") ;
pw.write("hello");
pw.flush();
pw.close();
字符打印流的一個構造方法:可以進行自動刷新
public PrintWriter(Writer out, boolean autoFlush)第二個參數的值為:true則自動刷新
egg:
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(new FileWriter("pw2.txt"), true);
pw.println("hello"); //使用print()不換行寫入操作
pw.close();
四、標準輸入流和標準的輸出流
1、System類中的字段
public static final InputStream in 標準輸入流
InputStream in = System.in; 字節輸入流
public static final PrintStream out 標準輸出流
PrintStream out = System.out;:字節打印流
2、直接使用標準輸入流錄入數據
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new OutputStreamReader(System.in));
//使用裝換流將字節流裝換為字符流傳給字符緩沖流
System.out.println("請輸入一個字符串:");
String line = br.readLine(); //錄入數據
System.out.println(line);
br.close();
3、直接使用標準輸出流輸出數據
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new InputStreamWriter(System.out));
bw.write("hello");
bw.newLine();
bw.close();
五、隨機訪問流 —— RandomAccessFile(並不是實際意義的流)
類的實例支持對隨機訪問文件的讀取和寫入,融合了InputStream和OutputStream兩個類
1、構造方法:
public RandomAccessFile(String name,String mode) mode:常用的就 rw:既可以讀,也可以寫
egg:
RandomAccessFile raf = new RandomAccessFile("raf.txt","rw");
raf.writeByte(97);
raf.writeChar(‘A‘);
raf.writeUTF("中國");
System.out.println(raf.readByte());
System.out.println(raf.readChar());
System.out.println(raf.readUTF()); //讀取一個字符串
raf.close();
2、特殊方法:
public long getFilePointer(),返回此文件的偏移量
//到此文件開頭的偏移量(以字節為單位),在該位置發生下一個讀取或寫入操作。
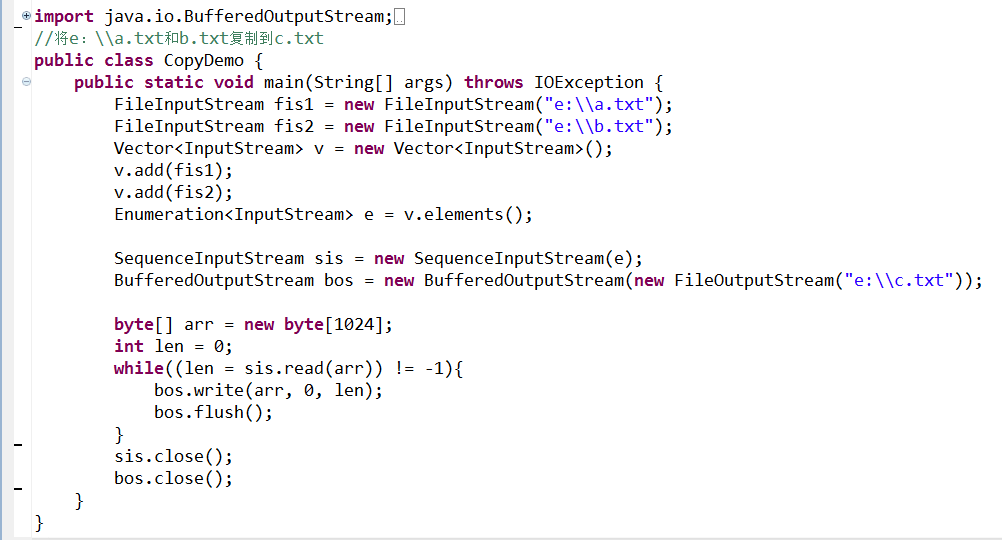
六、合並流 —— SequenceInputStream(只能合並輸入流)
1、構造方法:
public SequenceInputStream(InputStream s1,InputStream s2) 先讀取 s1,然後讀取 s2,將兩個輸入流合並
public SequenceInputStream(Enumeration<? extends InputStream> e)
//將多個輸入流對象添加到Vector集合,通過v.elements()方法產生Enumeration對象傳入合並流,使得多個輸入流合並
2、將e:\\a.txt和b.txt復制到c.txt
七、序列化流和反序列化流
1、概述
序列化流:ObjectOutputStream
將對象按照流的形式封裝成流數據:對象--->流數據
反序列化流:ObjectInputStream
將流數據又封裝成了一個對象: 流數據-->對象
2、實現方式:
類通過實現java.io.Serializable接口以啟用其序列化功能,未實現此接口的類將無法使其任何狀態序列化或反序列化。
Serializable接口中沒有字段,構造方法,成員方法,所有如果一個接口中沒有任何的方法或者他的字段,將這種接口叫標記接口!
1)該類實現Serializable接口
2)private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; //給當前類定義一個ID
重寫toString()方法
不然的話,在讀數據過程中如果中途對類有所修改,會報java.io.InvalidClassException異常
註意:如果在一個類中,有時候為了讓成員變量不被序列化,加一個關鍵字:transient
3)創建序列化流和反序列化流對象,創建需要序列化類的對象;
4)oos.writeObject(obj)寫
5)ois.readObject()讀
6)關閉所有的流
八、屬性集合類 —— Properties
1、概述:
Properties 類表示了一個持久的屬性集。Properties 可保存在流中或從流中加載
這個類是Hashtbale的子類,而Hashtable是Map下面的雙列集合,所以,Properties使用put()方法,添加元素
且,沒有泛型
2、特殊方法
public Object setProperty(String key,String value):和添加相關的
public Set<String> stringPropertyNames():獲取所有的鍵的集合
public String getProperty(String key):獲取指定的屬性集合中的鍵的值
public void load(Reader reader):將文本文件的數據讀取集合中
public void store(Writer writer, String comments):將集合中的數據保存到文本文件中
//comments:屬性列表的描述
有關IO流的其他常用流
