android界面設計之布局管理
談到android界面設計,各種布局樣式不得不提!傳統的布局方式有6種,我們會一一介紹。
在android studio2.2版本之後出現了一款超棒的布局方式,真正意義上的所見即所得,後面我們也會講到!
1.LinearLayout:線性布局:線性布局又有兩種,“垂直布局”和“水平布局”。
垂直布局每一行只能有一個控件(自己嵌套的不算);
水平布局只有一行,所有的控件依次從左向右排列;
linearLayout中有一個重要的屬性 android:layout_weight="",這個weight在垂直布局時,代表行距;水平的時候代表列寬;weight值越大就越大,當把所有控件的weight都設置為相同值,比如1的時候,這些控件會平分父類控件的區域。
舉個栗子:
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> 2 <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" 3 android:orientation="vertical" 4 android:layout_width="match_parent" 5 android:layout_height="match_parent"> 6 7 <Button 8 android:layout_width="match_parent" 9 android:layout_height="100dp" 10 android:text="button2" 11 android:textSize="60dp" 12 android:background="#1188aa" 13 android:enabled="false"/> 14 15 <Button 16 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 17 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 18 android:text="button1" 19 android:textSize="50dp" 20 android:enabled="false"/> 21 22 <TextView 23 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 24 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 25 android:text="textview1" 26 android:textSize="50dp" 27 android:textColor="#991111"/> 28 29 <TextView 30 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 31 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 32 android:text="textview2" 33 android:textSize="60dp" 34 android:textColor="#119911"/> 35 36 </LinearLayout>
以上代碼運行結果如下圖:
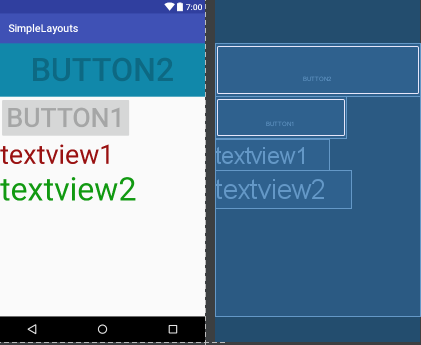
2.FrameLayout:幀布局:這個比較簡單,說白了就是在屏幕上定義一塊空白的區域(當然也可以是整個屏幕)。
在這個空白的區域中,所有的控件都是在區域的左上角排列的,也就是說你沒有辦法指定這個區域裏面控件的位置,後一個控件會一個接著一個的頂到左上角,這樣就會覆蓋前面的控件。
舉個栗子:
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> 2 <FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" 3 android:orientation="vertical" 4 android:layout_width="match_parent" 5 android:layout_height="match_parent"> 6 7 <Button 8 android:layout_width="match_parent" 9 android:layout_height="100dp" 10 android:text="button2" 11 android:textSize="60dp" 12 android:background="#1188aa" 13 android:enabled="false"/> 14 15 <Button 16 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 17 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 18 android:text="button1" 19 android:textSize="50dp" 20 android:enabled="false"/> 21 22 <TextView 23 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 24 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 25 android:text="textview1" 26 android:textSize="50dp" 27 android:textColor="#991111"/> 28 29 <TextView 30 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 31 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 32 android:text="textview2" 33 android:textSize="60dp" 34 android:textColor="#119911"/> 35 36 </FrameLayout>
以上代碼運行如下圖,細心的你可能會發現上述的button中有一個enable屬性,如果把這行代碼去掉,那麽button就會覆蓋textview,這與我們之前講的後一個組件會覆蓋前一個組件是相違背的,你問我為什麽,我也不知道,如知內情,望相告之:
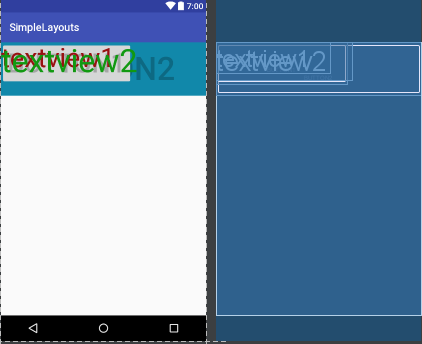
3.RelativeLayout:相對布局:相對布局可以理解為某一個元素為參照物,來定位的布局方式,這個稍微復雜一些,因為其屬性比較多,一個一個來看:
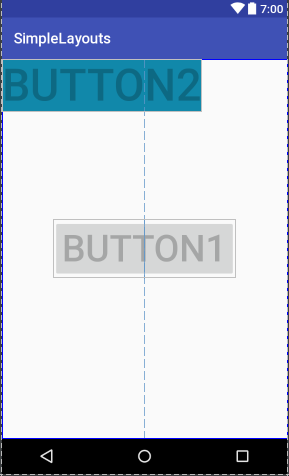
首先,我們定義兩個button,並且把btn1放在屏幕的最中間,如圖1,
我們在btn2中添加一行代碼:android:layout_below="@+id/btn1",如圖2,
把這行代碼換成:android:layout_alignBottom="@+id/btn1",如圖3,
再換一下:android:layout_alignParentBottom="true",如圖4,
再換一下:android:layout_marginRight="200dp",如圖5,連btn2的形狀都擠變形了,是不是很神奇,想要真正領悟,必須上代碼親自試探試探!
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> 2 <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" 3 android:layout_width="match_parent" 4 android:layout_height="match_parent"> 5 6 <Button 7 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 8 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 9 android:layout_centerInParent="true" 10 android:id="@+id/btn1" 11 android:text="button1" 12 android:textSize="50dp" 13 android:enabled="false"/> 14 15 <Button 16 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 17 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 18 android:id="@+id/btn2" 19 20 android:layout_marginRight="200dp" 21 22 android:text="button2" 23 android:textSize="60dp" 24 android:background="#1188aa" 25 android:enabled="false"/> 26 27 <!--<TextView 28 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 29 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 30 android:id="@+id/tv1" 31 android:text="textview1" 32 android:textSize="50dp" 33 android:textColor="#991111"/> 34 35 <TextView 36 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 37 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 38 android:id="@+id/tv2" 39 android:text="textview2" 40 android:textSize="60dp" 41 android:textColor="#119911"/>--> 42 43 </RelativeLayout>



4.AbsoluteLayout:絕對布局:這個也很簡單,主要屬性就兩個 layout_x 和 layout_y 分別定義 這個組件的絕對位置。 即,以屏幕左上角為(0,0)的坐標軸的x,y值,當向下或向右移動時,坐標值將變大。這個使用較少,因為其在不同設備上的顯示大相徑庭。但我還是舉例說明吧!
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> 2 <AbsoluteLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" 3 android:layout_width="match_parent" 4 android:layout_height="match_parent"> 5 6 <Button 7 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 8 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 9 android:id="@+id/btn1" 10 android:text="button1" 11 android:textSize="50dp" 12 13 android:layout_x="100dp" 14 android:layout_y="50dp"/> 15 16 <Button 17 android:layout_width="match_parent" 18 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 19 android:id="@+id/btn2" 20 android:text="button2" 21 android:textSize="50dp" 22 23 android:textColor="#ff1111" 24 25 android:layout_x="100dp" 26 android:layout_y="150dp"/> 27 28 29 30 </AbsoluteLayout>
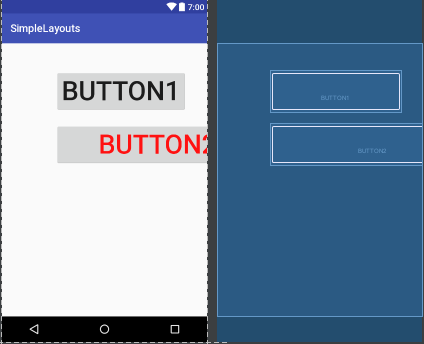
我們把btn2的寬度設置為填滿整個父控件,可以發現結果如上圖,看來,這個x和y針對的是控件的左上定點,並非控件中心點,這個需要註意。
5.TableLayout:表格布局:表格布局類似Html裏面的Table。每一個TableLayout裏面有表格行TableRow,TableRow裏面可以具體定義每一個元素。
表格由列和行組成許多的單元格。表格允許單元格為空。單元格不能跨列,這與HTML 中的不一樣。TabRow只論行,不論列(列自定義)。
舉例說明:
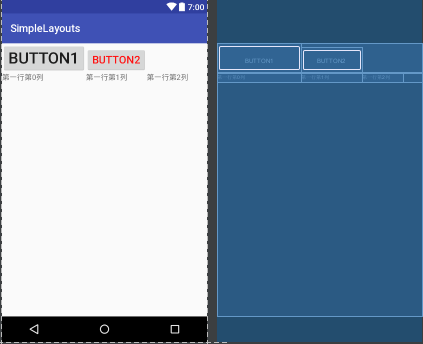
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> 2 <TableLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" 3 android:layout_width="match_parent" 4 android:layout_height="match_parent"> 5 6 <TableRow> 7 <Button 8 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 9 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 10 android:id="@+id/btn1" 11 android:text="button1" 12 android:textSize="30dp" 13 14 android:layout_x="100dp" 15 android:layout_y="50dp"/> 16 17 <Button 18 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 19 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 20 android:id="@+id/btn2" 21 android:text="button2" 22 android:textSize="20dp" 23 android:textColor="#ff1111" 24 android:layout_x="100dp" 25 android:layout_y="150dp"/> 26 27 </TableRow> 28 29 <TableRow> 30 31 <TextView android:text="第一行第0列" 32 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 33 android:layout_height="wrap_content"/> 34 <TextView android:text="第一行第1列" 35 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 36 android:layout_height="wrap_content"/> 37 <TextView android:text="第一行第2列" 38 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 39 android:layout_height="wrap_content"/> 40 41 </TableRow> 42 43 44 </TableLayout>
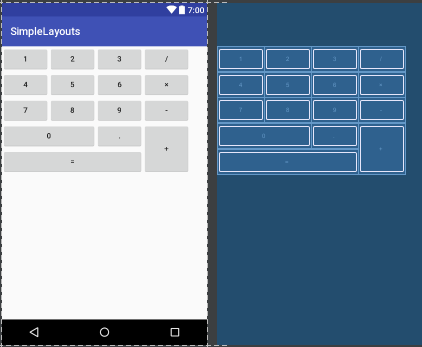
6.GridLayout:網格布局:網格布局是android4.0之後提出來的一種布局方式,使用它的理由有兩個:1,減少布局嵌套層次從而提高性能;2,對需要復雜對齊的布局,非他莫屬。不使用它的理由:由於太靈活導致學習難度比較大。在這裏就不詳細解釋了,大家可以參考文檔:http://www.jianshu.com/p/441d60be7d8a。
舉個栗子吧:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <GridLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:orientation="horizontal" android:rowCount="5" android:columnCount="4"> <Button android:id="@+id/one" android:text="1"/> <Button android:id="@+id/two" android:text="2"/> <Button android:id="@+id/three" android:text="3"/> <Button android:id="@+id/devide" android:text="/"/> <Button android:id="@+id/four" android:text="4"/> <Button android:id="@+id/five" android:text="5"/> <Button android:id="@+id/six" android:text="6"/> <Button android:id="@+id/multiply" android:text="×"/> <Button android:id="@+id/seven" android:text="7"/> <Button android:id="@+id/eight" android:text="8"/> <Button android:id="@+id/nine" android:text="9"/> <Button android:id="@+id/minus" android:text="-"/> <Button android:id="@+id/zero" android:layout_columnSpan="2" android:layout_gravity="fill" android:text="0"/> <Button android:id="@+id/point" android:text="."/> <Button android:id="@+id/plus" android:layout_rowSpan="2" android:layout_gravity="fill" android:text="+"/> <Button android:id="@+id/equal" android:layout_columnSpan="3" android:layout_gravity="fill" android:text="="/> </GridLayout>
7.ConstraintLayout:谷歌在2016年的IO大會上推出的一種新的布局方式—-ConstraintLayout,這局是一種約束型的布局方式。這絕對是你最應該了解的神器,有了它,天黑都不怕!這裏隆重獻上一個大神的作品,必須要讀,必須要讀,必須要讀啊!
這個講的非常清晰,我就不多廢話了:
Android新特性介紹,ConstraintLayout完全解析
android界面設計之布局管理
