爬了個爬(二)性能相關 及 深度優先與廣度優先
性能相關
在編寫爬蟲時,性能的消耗主要在IO請求中,當單進程單線程模式下請求URL時必然會引起等待,從而使得請求整體變慢。

import requests def fetch_async(url): response = requests.get(url) return response url_list = [‘http://www.github.com‘, ‘http://www.bing.com‘] for url in url_list: fetch_async(url) 1.同步執行1. 同步執行

from concurrent.futures import2. 多線程執行ThreadPoolExecutor import requests def fetch_async(url): response = requests.get(url) return response url_list = [‘http://www.github.com‘, ‘http://www.bing.com‘] pool = ThreadPoolExecutor(5) for url in url_list: pool.submit(fetch_async, url) pool.shutdown(wait=True)
 2.多線程+回調函數執行
2.多線程+回調函數執行
from concurrent.futures import ProcessPoolExecutor import requests def fetch_async(url): response = requests.get(url) return response url_list = [‘http://www.github.com‘, ‘http://www.bing.com‘] pool = ProcessPoolExecutor(5) for url in url_list: pool.submit(fetch_async, url) pool.shutdown(wait3.多進程執行=True)

from concurrent.futures import ProcessPoolExecutor import requests def fetch_async(url): response = requests.get(url) return response def callback(future): print(future.result()) url_list = [‘http://www.github.com‘, ‘http://www.bing.com‘] pool = ProcessPoolExecutor(5) for url in url_list: v = pool.submit(fetch_async, url) v.add_done_callback(callback) pool.shutdown(wait=True)3.多進程+回調函數執行
通過上述代碼均可以完成對請求性能的提高,對於多線程和多進行的缺點是在IO阻塞時會造成了線程和進程的浪費,所以異步IO回事首選:

import asyncio @asyncio.coroutine def func1(): print(‘before...func1......‘) yield from asyncio.sleep(5) print(‘end...func1......‘) tasks = [func1(), func1()] loop = asyncio.get_event_loop() loop.run_until_complete(asyncio.gather(*tasks)) loop.close()1.asyncio示例1

import asyncio @asyncio.coroutine def fetch_async(host, url=‘/‘): print(host, url) reader, writer = yield from asyncio.open_connection(host, 80) request_header_content = """GET %s HTTP/1.0\r\nHost: %s\r\n\r\n""" % (url, host,) request_header_content = bytes(request_header_content, encoding=‘utf-8‘) writer.write(request_header_content) yield from writer.drain() text = yield from reader.read() print(host, url, text) writer.close() tasks = [ fetch_async(‘www.cnblogs.com‘, ‘/wupeiqi/‘), fetch_async(‘dig.chouti.com‘, ‘/pic/show?nid=4073644713430508&lid=10273091‘) ] loop = asyncio.get_event_loop() results = loop.run_until_complete(asyncio.gather(*tasks)) loop.close()1.asyncio示例2

import aiohttp import asyncio @asyncio.coroutine def fetch_async(url): print(url) response = yield from aiohttp.request(‘GET‘, url) # data = yield from response.read() # print(url, data) print(url, response) response.close() tasks = [fetch_async(‘http://www.google.com/‘), fetch_async(‘http://www.chouti.com/‘)] event_loop = asyncio.get_event_loop() results = event_loop.run_until_complete(asyncio.gather(*tasks)) event_loop.close()2.asyncio + aiohttp

import asyncio import requests @asyncio.coroutine def fetch_async(func, *args): loop = asyncio.get_event_loop() future = loop.run_in_executor(None, func, *args) response = yield from future print(response.url, response.content) tasks = [ fetch_async(requests.get, ‘http://www.cnblogs.com/wupeiqi/‘), fetch_async(requests.get, ‘http://dig.chouti.com/pic/show?nid=4073644713430508&lid=10273091‘) ] loop = asyncio.get_event_loop() results = loop.run_until_complete(asyncio.gather(*tasks)) loop.close()3.asyncio + requests

import gevent import requests from gevent import monkey monkey.patch_all() def fetch_async(method, url, req_kwargs): print(method, url, req_kwargs) response = requests.request(method=method, url=url, **req_kwargs) print(response.url, response.content) # ##### 發送請求 ##### gevent.joinall([ gevent.spawn(fetch_async, method=‘get‘, url=‘https://www.python.org/‘, req_kwargs={}), gevent.spawn(fetch_async, method=‘get‘, url=‘https://www.yahoo.com/‘, req_kwargs={}), gevent.spawn(fetch_async, method=‘get‘, url=‘https://github.com/‘, req_kwargs={}), ]) # ##### 發送請求(協程池控制最大協程數量) ##### # from gevent.pool import Pool # pool = Pool(None) # gevent.joinall([ # pool.spawn(fetch_async, method=‘get‘, url=‘https://www.python.org/‘, req_kwargs={}), # pool.spawn(fetch_async, method=‘get‘, url=‘https://www.yahoo.com/‘, req_kwargs={}), # pool.spawn(fetch_async, method=‘get‘, url=‘https://www.github.com/‘, req_kwargs={}), # ])4.gevent + requests

import grequests request_list = [ grequests.get(‘http://httpbin.org/delay/1‘, timeout=0.001), grequests.get(‘http://fakedomain/‘), grequests.get(‘http://httpbin.org/status/500‘) ] # ##### 執行並獲取響應列表 ##### # response_list = grequests.map(request_list) # print(response_list) # ##### 執行並獲取響應列表(處理異常) ##### # def exception_handler(request, exception): # print(request,exception) # print("Request failed") # response_list = grequests.map(request_list, exception_handler=exception_handler) # print(response_list)5.grequests

from twisted.web.client import getPage, defer from twisted.internet import reactor def all_done(arg): reactor.stop() def callback(contents): print(contents) deferred_list = [] url_list = [‘http://www.bing.com‘, ‘http://www.baidu.com‘, ] for url in url_list: deferred = getPage(bytes(url, encoding=‘utf8‘)) deferred.addCallback(callback) deferred_list.append(deferred) dlist = defer.DeferredList(deferred_list) dlist.addBoth(all_done) reactor.run()6.Twisted示例

from tornado.httpclient import AsyncHTTPClient from tornado.httpclient import HTTPRequest from tornado import ioloop def handle_response(response): """ 處理返回值內容(需要維護計數器,來停止IO循環),調用 ioloop.IOLoop.current().stop() :param response: :return: """ if response.error: print("Error:", response.error) else: print(response.body) def func(): url_list = [ ‘http://www.baidu.com‘, ‘http://www.bing.com‘, ] for url in url_list: print(url) http_client = AsyncHTTPClient() http_client.fetch(HTTPRequest(url), handle_response) ioloop.IOLoop.current().add_callback(func) ioloop.IOLoop.current().start()7.Tornado

from twisted.internet import reactor from twisted.web.client import getPage import urllib.parse def one_done(arg): print(arg) reactor.stop() post_data = urllib.parse.urlencode({‘check_data‘: ‘adf‘}) post_data = bytes(post_data, encoding=‘utf8‘) headers = {b‘Content-Type‘: b‘application/x-www-form-urlencoded‘} response = getPage(bytes(‘http://dig.chouti.com/login‘, encoding=‘utf8‘), method=bytes(‘POST‘, encoding=‘utf8‘), postdata=post_data, cookies={}, headers=headers) response.addBoth(one_done) reactor.run()Twisted更多
深度優先與廣度優先
在爬蟲系統中,待抓取URL隊列是很重要的一部分,待抓取URL隊列中的URL以什麽樣的順序排隊列也是一個很重要的問題,因為這涉及到先抓取哪個頁面,後抓取哪個頁面。而決定這些URL排列順序的方法,叫做抓取策略。下面是常用的兩種策略:深度優先、廣度優先。
深度優先
深度優先 顧名思義就是 讓 網絡蜘蛛 盡量的在抓取網頁時 往網頁更深層次的挖掘進去 講究的是深度!也泛指: 網絡蜘蛛將會從起始頁開始,一個鏈接一個鏈接跟蹤下去,處理完這條線路之後再轉入下一個起始頁,繼續跟蹤鏈接!
深度優先搜索是一種在開發爬蟲早期使用較多的方法。它的目的是要達到被搜索結構的葉結點(即那些不包含任何超鏈的HTML文件) 。在一個HTML文件中,當一個超鏈被選擇後,被鏈接的HTML文件將執行深度優先搜索,即在搜索其余的超鏈結果之前必須先完整地搜索單獨的一條鏈。深度優先搜索沿著HTML文件上的超鏈走到不能再深入為止,然後返回到某一個HTML文件,再繼續選擇該HTML文件中的其他超鏈。當不再有其他超鏈可選擇時,說明搜索已經結束。優點是能遍歷一個Web 站點或深層嵌套的文檔集合;缺點是因為Web結構相當深,,有可能造成一旦進去,再也出不來的情況發生。
如圖所示:下面這張是 簡單化的網頁連接模型圖 其中A為起點 也就是蜘蛛索引的起點!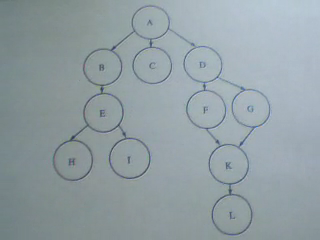
總共分了5條路徑 供蜘蛛爬行! 講究的是深度!
(下面這張是 經過優化的網頁連接模型圖! 也就是改進過的蜘蛛深度爬行策略圖!)
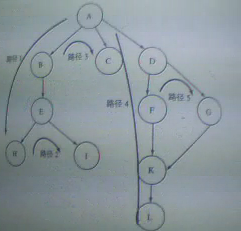
根據以上2個表格 我們可以得出以下結論:
圖1:
路徑1 ==> A --> B --> E --> H
路徑2 ==> A --> B --> E --> i
路徑3 ==> A --> C
路徑4 ==> A --> D --> F --> K --> L
路徑5 ==> A --> D --> G --> K --> L
經過優化後
圖2: (圖片已經幫大家標上方向了!)
路徑1 ==> A --> B --> E --> H
路徑2 ==> i
路徑3 ==> C
路徑4 ==> D --> F --> K --> L
路徑5 ==> G
廣度優先
整個的廣度優先爬蟲過程就是從一系列的種子節點開始,把這些網頁中的"子節點"(也就是超鏈接)提取出來,放入隊列中依次進行抓取。被處理過的鏈接需要放 入一張表(通常稱為Visited表)中。每次新處理一個鏈接之前,需要查看這個鏈接是否已經存在於Visited表中。如果存在,證明鏈接已經處理過, 跳過,不做處理,否則進行下一步處理。
初始的URL地址是爬蟲系統中提供的種子URL(一般在系統的配置文件中指定)。當解析這些種子URL所表示的網頁時,會產生新的URL(比如從頁面中的<a href= "http://www.cnblogs.com "中提取出http://www.cnblogs.com 這個鏈接)。然後,進行以下工作:
把解析出的鏈接和Visited表中的鏈接進行比較,若Visited表中不存在此鏈接,表示其未被訪問過。
把鏈接放入TODO表中。
處理完畢後,再次從TODO表中取得一條鏈接,直接放入Visited表中。
針對這個鏈接所表示的網頁,繼續上述過程。如此循環往復。
廣度優先遍歷是爬蟲中使用最廣泛的一種爬蟲策略,之所以使用廣度優先搜索策略,主要原因有三點:
重要的網頁往往離種子比較近,例如我們打開新聞網站的時候往往是最熱門的新聞,隨著不斷的深入沖浪,所看到的網頁的重要性越來越低。
萬維網的實際深度最多能達到17層,但到達某個網頁總存在一條很短的路徑。而廣度優先遍歷會以最快的速度到達這個網頁。
廣度優先有利於多爬蟲的合作抓取,多爬蟲合作通常先抓取站內鏈接,抓取的封閉性很強。
廣度相對深度對數據抓取更容易控制些! 對服務器的負栽相應也明顯減輕了許多! 爬蟲的分布式處理使速度明顯提高!
廣度優先策略圖(層爬行圖)
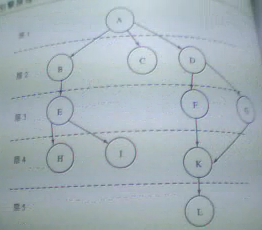
根據以上表格 我們可以得出以下結論路徑圖:
路徑1 ==> A
路徑2 ==> B --> C --> D
路徑3 ==> E --> F --> G
路徑4 ==> H --> i --> K
路徑5 ==> L
總結如下:
深度優先搜索策略
容易一根筋走到底,最後出不來。
廣度優先搜索策略
廣度優先搜索策略是指在抓取過程中,在完成當前層次的搜索後,才進行下一層次的搜索。該算法的設計和實現相對簡單。在目前為覆蓋盡可能多的網頁,一般使用廣度優先搜索方法。也有很多研究將廣度優先搜索策略應用於聚焦爬蟲中。其基本思想是認為與初始URL在一定鏈接距離內的網頁具有主題相關性的概率很大。另外一種方法是將廣度優先搜索與網頁過濾技術結合使用,先用廣度優先策略抓取網頁,再將其中無關的網頁過濾掉。這些方法的缺點在於,隨著抓取網頁的增多,大量的無關網頁將被下載並過濾,算法的效率將變低。
最佳優先搜索策略
最佳優先搜索策略按照一定的網頁分析算法,預測候選URL與目標網頁的相似度,或與主題的相關性,並選取評價最好的一個或幾個URL進行抓取。它只訪問經過網頁分析算法預測為“有用”的網頁。存在的一個問題是,在爬蟲抓取路徑上的很多相關網頁可能被忽略,因為最佳優先策略是一種局部最優搜索算法。 因此需要將最佳優先結合具體的應用進行改進,以跳出局部最優點。將在第4節中結合網頁分析算法作具體的討論。研究表明,這樣的閉環調整可以將無關網頁數量降低30%~90%。
爬了個爬(二)性能相關 及 深度優先與廣度優先

