MyBatis入門基礎(一)
閱讀目錄
- 一:對原生態JDBC問題的總結
- 二:MyBatis框架
- 三:mybatis入門程序
- 四:mybatis和Hibernate的本質區別與應用場景
- 五:小結
-
中文網址:http://www.mybatis.org/mybatis-3/zh/index.html
一:對原生態JDBC問題的總結
public static void main(String[] args) { Connection connection = null; PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null; ResultSet resultSet= null; try { //1、加載數據庫驅動 Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); //2、通過驅動管理類獲取數據庫鏈接 connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?characterEncoding=utf-8", "root", "root");//3、定義sql語句 ?表示占位符 String sql = "select * from user where username = ?"; //4、獲取預處理statement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); //5、設置參數,第一個參數為sql語句中參數的序號(從1開始),第二個參數為設置的參數值 preparedStatement.setString(1, "王五");//6、向數據庫發出sql執行查詢,查詢出結果集 resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery(); //7、遍歷查詢結果集 while(resultSet.next()){ User user System.out.println(resultSet.getString("id")+" "+resultSet.getString("username")); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ //8、釋放資源 if(resultSet!=null){ try { resultSet.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } if(preparedStatement!=null){ try { preparedStatement.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } if(connection!=null){ try { connection.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
出現的問題總結:
1.在代碼1中可以看出創建連接的時候存在硬編碼。(通過配置來解決)
2.在執行statement時存在硬編碼。(通過配置來解決)
3.頻繁的開啟和關閉數據庫連接,會造成數據庫性能下降。
數據庫連接池(全局配置文件)
二:MyBatis框架
1.MyBatis是什麽?(下載地址:https://github.com/mybatis/mybatis-3/releases)
MyBatis 本是apache的一個開源項目iBatis, 2010年這個項目由apache software foundation 遷移到了google code,並且改名為MyBatis,實質上Mybatis對ibatis進行一些改進。
MyBatis是一個優秀的持久層框架,它對jdbc的操作數據庫的過程進行封裝,使開發者只需要關註 SQL 本身,而不需要花費精力去處理例如註冊驅動、創建connection、創建statement、手動設置參數、結果集檢索等jdbc繁雜的過程代碼。
Mybatis通過xml或註解的方式將要執行的各種statement(statement、preparedStatemnt、CallableStatement)配置起來,並通過java對象和statement中的sql進行映射生成最終執行的sql語句,最後由mybatis框架執行sql並將結果映射成java對象並返回。
2.MyBatis架構圖
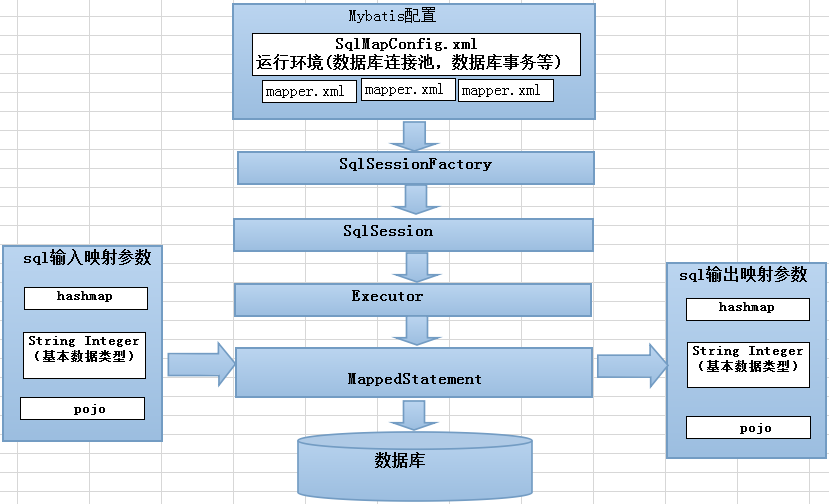
1、mybatis配置
SqlMapConfig.xml,此文件作為mybatis的全局配置文件,配置了mybatis的運行環境等信息。
mapper.xml文件即sql映射文件,文件中配置了操作數據庫的sql語句。此文件需要在SqlMapConfig.xml中加載。
2、通過mybatis環境等配置信息構造SqlSessionFactory即會話工廠
3、由會話工廠創建sqlSession即會話,操作數據庫需要通過sqlSession進行。
4、mybatis底層自定義了Executor執行器接口操作數據庫,Executor接口有兩個實現,一個是基本執行器、一個是緩存執行器。
5、Mapped Statement也是mybatis一個底層封裝對象,它包裝了mybatis配置信息及sql映射信息等。mapper.xml文件中一個sql對應一個Mapped Statement對象,sql的id即是Mapped statement的id。
6、Mapped Statement對sql執行輸入參數進行定義,包括HashMap、基本類型、pojo,Executor通過Mapped Statement在執行sql前將輸入的java對象映射至sql中,輸入參數映射就是jdbc編程中對preparedStatement設置參數。
7、Mapped Statement對sql執行輸出結果進行定義,包括HashMap、基本類型、pojo,Executor通過Mapped Statement在執行sql後將輸出結果映射至java對象中,輸出結果映射過程相當於jdbc編程中對結果的解析處理過程。
回到頂部三:mybatis入門程序
1.需求:(1).根據用戶id(主鍵)查詢用戶信息 (2).根據用戶名稱模糊查詢用戶信息(3).添加用戶 4).刪除用戶(5).更新用戶
2.環境:java環境:JDK1.7,eclipse,Mysql5.1
3.工程目錄結構

4.從mybatis的jar包結構可知mybatis用的是log4j記錄日誌,所以log4j.properties文件內容如下:

# Global logging configuration #在開發的環境下,日誌級別要設置成DEBUG,生產環境設置成info或error log4j.rootLogger=DEBUG, stdout # Console output... log4j.appender.stdout=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender log4j.appender.stdout.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout log4j.appender.stdout.layout.ConversionPattern=%5p [%t] - %m%n

5.SqlMapConfig.xml的配置文件內容

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<!-- 和spring整合後 environments配置將廢除-->
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<!-- 使用jdbc事務管理,事務控制由mybatis管理-->
<transactionManager type="JDBC" />
<!-- 數據庫連接池,由mybatis管理-->
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" />
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?characterEncoding=utf-8" />
<property name="username" value="root" />
<property name="password" value="root" />
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<!-- 加載映射文件 -->
<mappers>
<mapper resource="sqlmap/User.xml"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>

6.實體User.java內容
 View Code
View Code
7.映射文件User.xml的內容

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<!-- namespace命名空間,作用就是對sql進行分類化的管理,理解為sql隔離
註意:使用mapper代理開發時,namespace有特殊作用
-->
<mapper namespace="test">
<!-- 在映射文件中配置很多sql語句 -->
<!-- 需求:通過Id查詢用戶表的記錄 -->
<!-- 通過SELECT執行數據庫查詢
id:標識映射文件中的sql,稱為statement的id;
將sql語句封裝在mapperStatement的對象中,所以Id稱為Statement的id;
parameterType:指定輸入參數的類型,這裏指定int型
#{}:表示一個占位符;
#{id}:其中Id表示接收輸入的參數,參數名稱就是Id,如果輸入參數是簡單類型,#{}中的參數名可以任意,可以是value或者其它名稱;
resultType:指定sql輸出結果所映射的java對象類型,select指定resultType表示將單條記錄映射成java對象。
-->
<select id="findUserById" parameterType="int" resultType="com.mybatis.entity.User" >
select * from t_user where id=#{id}
</select>
<!-- 根據用戶名稱模糊查詢用戶信息,可能返回多條數據
resultType:指定的就是單條記錄所映射的java類型;
${}:表示拼接sql字符串,將接收到的參數內容不加任何修飾拼接在sql中.
使用${}拼接sql,可能會引起sql註入
${value}:接收輸入參數的內容,如果傳入的是簡單類型,${}中只能使用value
-->
<select id="findUserByName" parameterType="java.lang.String" resultType="com.mybatis.entity.User" >
select * from t_user where username LIKE ‘%${value}%‘
</select>
<!-- 添加用戶
parameterType:指定輸入的參數類型是pojo(包括用戶信息);
#{}中指定pojo的屬性名稱,接收到pojo對象的屬性值 ,mybatis通過OGNL(類似struts2的OGNL)獲取對象的屬性值
-->
<insert id="insertUser" parameterType="com.mybatis.entity.User" >
<!--
將insert插入的數據的主鍵返回到User對象中;
select last_insert_id():得到剛insert進去記錄的主鍵值,只適用於自增主鍵;
keyProperty:將查詢到的主鍵值,設置到parameterType指定的對象的那個屬性
order:select last_insert_id()執行順序,相對於insert語句來說它的執行順序。
resultType:指定select last_insert_id()的結果類型;
-->
<selectKey keyProperty="id" order="AFTER" resultType="java.lang.Integer">
select last_insert_id()
</selectKey>
<!--
使用mysql的uuid(),實現非自增主鍵的返回。
執行過程:通過uuid()得到主鍵,將主鍵設置到user對象的Id的屬性中,其次,在insert執行時,從user對象中取出Id屬性值;
<selectKey keyProperty="id" order="BEFORE" resultType="java.lang.String">
select uuid()
</selectKey>
insert into t_user (id,username,birthday,sex,address) values(#{id},#{username},#{birthday},#{sex},#{address})
-->
insert into t_user (username,birthday,sex,address) values(#{username},#{birthday},#{sex},#{address})
</insert>
<!-- 刪除用戶
根據ID刪除用戶,需要輸入Id值
-->
<delete id="deleteUser" parameterType="java.lang.Integer">
delete from t_user where id=#{id}
</delete>
<!-- 更新用戶
需要傳入用戶的Id和用戶的更新信息
parameterType:指定User對象,包括Id和用戶的更新信息,註意:Id是必須存在的
#{id}:從輸入的User對象中獲取Id的屬性值
-->
<update id="updateUser" parameterType="com.mybatis.entity.User">
update t_user set username=#{username},birthday=#{birthday},sex=#{sex},address=#{address}
where id=#{id}
</update>
</mapper>

8.測試程序MybatisService.java代碼

package com.mybatis.service;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;
import org.junit.Test;
import com.mybatis.entity.User;
/**
* @ClassName: MybatisService
* @Description: TODO(mybatis入門程序)
* @author warcaft
* @date 2015-6-27 下午4:49:49
*
*/
public class MybatisService {
// 根據Id查詢用戶信息,得到一條記錄結果
@Test
public void findUserByIdTest() {
// mybatis的配置文件
String resource = "SqlMapConfig.xml";
InputStream inputStream = null;
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
try {
inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
// 1.創建會話工場,傳入mybatis的配置文件信息
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder()
.build(inputStream);
// 2.通過工廠得到SqlSession
sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
// 3.通過sqlSession操作數據庫
// 第一個參數:映射文件中的statement的Id,等於namespace + "." + statement的id;
// 第二個參數:指定和映射文件中所匹配的parameterType類型的參數;
// sqlSession.selectOne結果是與映射文件所匹配的resultType類型的對象;
// selectOne:查詢一條結果
User user = sqlSession.selectOne("test.findUserById", 1);
System.out.println(user.toString());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (sqlSession != null) {
sqlSession.close();
}
if (inputStream != null) {
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
// 根據姓名模糊查詢用戶信息,得到一條或多條記錄結果
@Test
public void findUserByNameTest() {
// mybatis的配置文件
String resource = "SqlMapConfig.xml";
InputStream inputStream = null;
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
try {
inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
// 1.創建會話工場,傳入mybatis的配置文件信息
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder()
.build(inputStream);
// 2.通過工廠得到SqlSession
sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
// 3.通過sqlSession操作數據庫
// 第一個參數:映射文件中的statement的Id,等於namespace + "." + statement的id;
// 第二個參數:指定和映射文件中所匹配的parameterType類型的參數;
// sqlSession.selectOne結果是與映射文件所匹配的resultType類型的對象;
// list中的user和resultType類型一致
List<User> list = sqlSession.selectList("test.findUserByName", "小");
System.out.println(list);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (sqlSession != null) {
sqlSession.close();
}
if (inputStream != null) {
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
// 添加用戶
@Test
public void insertUserTest() {
// mybatis的配置文件
String resource = "SqlMapConfig.xml";
InputStream inputStream = null;
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
try {
inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
// 1.創建會話工場,傳入mybatis的配置文件信息
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder()
.build(inputStream);
// 2.通過工廠得到SqlSession
sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//插入用戶的對象
User user = new User();
user.setUsername("小紅");
user.setBirthday(new Date());
user.setSex("1");
user.setAddress("上海");
// 3.通過sqlSession操作數據庫
// 第一個參數:映射文件中的statement的Id,等於namespace + "." + statement的id;
// 第二個參數:指定和映射文件中所匹配的parameterType類型的參數;
// sqlSession.selectOne結果是與映射文件所匹配的resultType類型的對象;
sqlSession.insert("test.insertUser", user);
//執行提交事務
sqlSession.commit();
//項目中經常需要 獲取新增的用戶的主鍵
System.out.println(user.getId());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (sqlSession != null) {
sqlSession.close();
}
if (inputStream != null) {
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
// 根據Id刪除用戶
@Test
public void deleteUserTest() {
// mybatis的配置文件
String resource = "SqlMapConfig.xml";
InputStream inputStream = null;
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
try {
inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
// 1.創建會話工場,傳入mybatis的配置文件信息
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder()
.build(inputStream);
// 2.通過工廠得到SqlSession
sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
// 3.通過sqlSession操作數據庫
// 第一個參數:映射文件中的statement的Id,等於namespace + "." + statement的id;
// 第二個參數:指定和映射文件中所匹配的parameterType類型的參數;
// sqlSession.selectOne結果是與映射文件所匹配的resultType類型的對象;
//傳入Id,刪除用戶
sqlSession.delete("test.deleteUser", 7);
//執行提交事務
sqlSession.commit();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (sqlSession != null) {
sqlSession.close();
}
if (inputStream != null) {
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
// 根據Id更新用戶信息
@Test
public void updateUserTest() {
// mybatis的配置文件
String resource = "SqlMapConfig.xml";
InputStream inputStream = null;
SqlSession sqlSession = null;
try {
inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
// 1.創建會話工場,傳入mybatis的配置文件信息
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder()
.build(inputStream);
// 2.通過工廠得到SqlSession
sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//更新用戶的信息
User user = new User();
user.setId(2);
user.setUsername("小黑");
user.setBirthday(new Date());
user.setSex("2");
user.setAddress("上海");
// 3.通過sqlSession操作數據庫
// 第一個參數:映射文件中的statement的Id,等於namespace + "." + statement的id;
// 第二個參數:指定和映射文件中所匹配的parameterType類型的參數;
// sqlSession.selectOne結果是與映射文件所匹配的resultType類型的對象;
//更具Id更新用戶
sqlSession.update("test.updateUser", user);
//執行提交事務
sqlSession.commit();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (sqlSession != null) {
sqlSession.close();
}
if (inputStream != null) {
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}

9.數據庫所用sql腳本

CREATE TABLE t_user (
id INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
username VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL COMMENT ‘用戶名稱‘,
birthday DATE DEFAULT NULL COMMENT ‘生日‘,
sex CHAR(2) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT ‘性別‘,
address VARCHAR(256) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT ‘地址‘
);
INSERT INTO t_user (username,birthday,sex,address)
VALUES
(‘小A‘,‘2015-06-27‘,‘2‘,‘北京‘),
(‘小B‘,‘2015-06-27‘,‘2‘,‘北京‘),
(‘小C‘,‘2015-06-27‘,‘1‘,‘北京‘),
(‘小D‘,‘2015-06-27‘,‘2‘,‘北京‘);
 回到頂部
回到頂部
四:mybatis和Hibernate的本質區別與應用場景
hibernate:是一個標準ORM框架(對象關系映射),入門門檻較高的,不需要程序寫sql,sql語句自動生成了,對sql語句進行優化、修改比較困難的。
應用場景:
適用與需求變化不多的中小型項目,比如:後臺管理系統,erp、orm、oa。。
mybatis:專註是sql本身,需要程序員自己編寫sql語句,sql修改、優化比較方便。mybatis是一個不完全 的ORM框架,雖然程序員自己寫sql,mybatis 也可以實現映射(輸入映射、輸出映射)。
應用場景:
適用與需求變化較多的項目,比如:互聯網項目。
回到頂部五:小結
1.parameterType和resultType
parameterType:在映射文件中通過parameterType指定輸入 參數的類型。
resultType:在映射文件中通過resultType指定輸出結果的類型
2.#{}和${}
#{}表示一個占位符號,#{}接收輸入參數,類型可以是簡單類型,pojo、hashmap;
如果接收簡單類型,#{}中可以寫成value或其它名稱;
#{}接收pojo對象值,通過OGNL讀取對象中的屬性值,通過屬性.屬性.屬性...的方式獲取對象屬性值。
表示一個拼接符號,會引用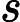
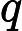
 註入,所以不建議使用表示一個拼接符號,會引用sql註入,所以不建議使用{};
註入,所以不建議使用表示一個拼接符號,會引用sql註入,所以不建議使用{};
${}接收輸入參數,類型可以是簡單類型,pojo、hashmap;
如果接收簡單類型,${}中只能寫成value;
${}接收pojo對象值,通過OGNL讀取對象中的屬性值,通過屬性.屬性.屬性...的方式獲取對象屬性值。
3.selectOne()和selectList()
selectOne表示查詢出一條記錄進行映射。如果使用selectOne可以實現使用selectList也可以實現(list中只有一個對象)。
selectList表示查詢出一個列表(多條記錄)進行映射。如果使用selectList查詢多條記錄,不能使用selectOne。
如果使用selectOne報錯: org.apache.ibatis.exceptions.TooManyResultsException: Expected one result (or null) to be returned by selectOne(), but found: 4
MyBatis入門基礎(一)
