Linux自學筆記——Centos7系統之systemd
回顧:
centos系統的啟動流程:POST àboot sequeue(BIOS)à bootloader(mbr) à kernel(ramdisk)àrootfs à/sbin/init
init:
centos5:sysv init
centos6:upstart
centos7:systemd
system的新特性:
系統引導時實現服務並行啟動;
按需激活進程;
系統狀態快照;
基於依賴關系定義服務控制邏輯;
核心概念:unit
unit由其相關配置文件進行標識、識別和配置;文件中主要包含了系統服務、監聽的socket、保存的快照以及其他與init相關的信息;這些配置文件主要保存在:
/usr/lib/systemd/system
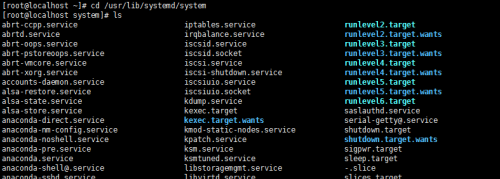
/run/systemd/system
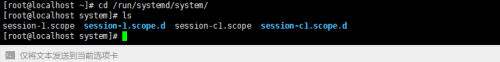
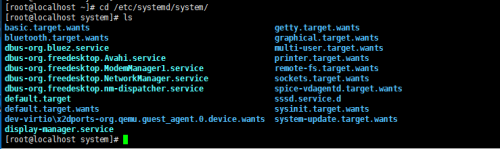
/etc/systemd/system
unit的常見類型:
service init:文件擴展名為.service,用於定義系統服務;
target unit:文件擴展名為.target,用於模擬實現“運行級別”;
device unit:.device,用於定義內核識別的設備;
mount unit:.mount,用於定義文件系統掛載點;
socket unit:.socket,用於標識進程間通信用到的socket文件;
snapshot unit:.snapshot,管理系統快照;
swap unit:.swap,用於標識swap設備;
automount unit :.automount,文件系統自動點設備;
path unit:.path,用於定義文件系統中的文件或目錄;
關鍵特性:
基於socket的激活機制:socket與程序分離;
基於bus的激活機制;
基於device的激活機制;
基於path的激活機制;
系統快照:保存各unit的當前狀態信息於持久存儲設備中;
向後兼容sysv init腳本;
/etc/init.d
不兼容:
Systemctl的命令時固定不變的;
非由systemd啟動的服務,systemctl無法與之通信;
管理系統服務:
Centos7:service類型的unit文件
systemctl命令:
- Control the systemd system and servicemanager
systemctl [OPTIONS...] COMMAND [NAME...]
啟動:service NAME start ==> systemctl startNAME.service
停止:service NAME stop ==> systemctl stopNAME.service
重啟:service NAME restart ==> systemctlrestart NAME.service
狀態:service NAME status ==> systemctlstatus NAME.service
Centos6:
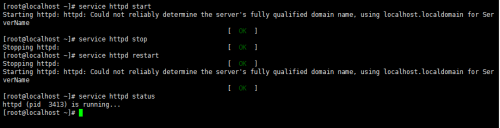
Centos7:
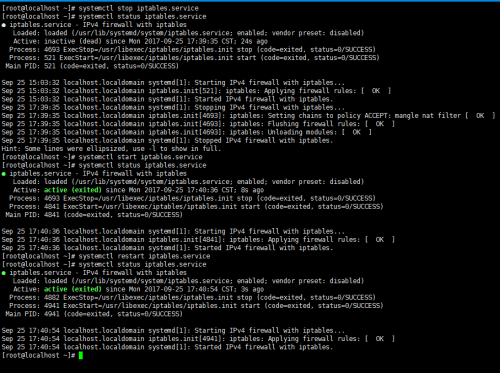
條件式重啟:service NAME condrestart ==> systemctl try-restart NAME.service
重載或重啟服務:systemctl reload-or-restart NAME.service
重載或條件式重啟服務:systemctl reload-or-try-restartNAME.service
查看某服務當前激活與否的狀態:systemctl is-activeNAME.service
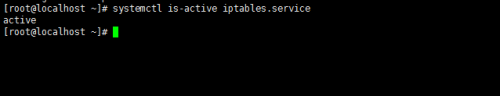
查看所有已激活的服務:systemctl list-units --typeservice
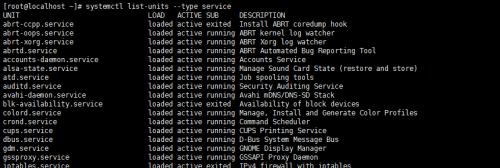
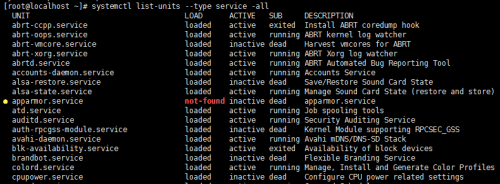
查看所有服務(已激活及未激活):chkconfig --list ==> systemctl list-units -t service--all
設置服務開機自啟:chkconfig NAME on ==> systemctl enable NAME.service
禁止服務開機自啟:chkconfig NAME off ==> systemctl diable NAME.service
查看某服務是否能開機自啟:chkconfig –list NAME ==>systemctl is-enabled NAME.service
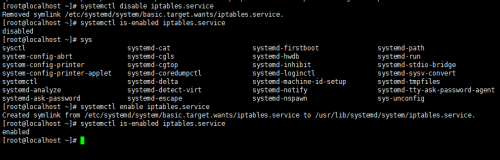
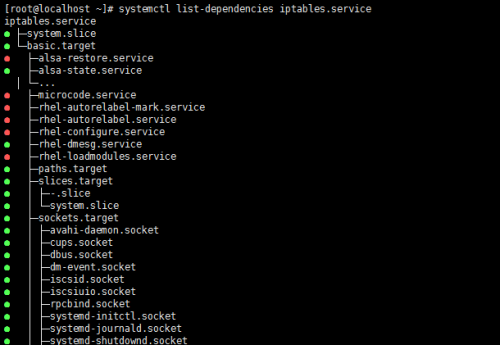
查看服務的依賴關系:systemctl list-dependenciesNAME.service
管理target units
運行級別:
0 ==> runlevel0.target,poweroff.target
1 ==> runlevel1.target,rescue.target
2 ==> runlevel2.target,multi-user.target
3 ==> runlevel3.target,multi-user.target
4 ==> runlevel4.target,multi-user.target
5 ==> runlevel5.target,graphical.target
7 ==> runlevel6.target,reboot.target
級別切換:init N ==> systemctl isolate NAME.target
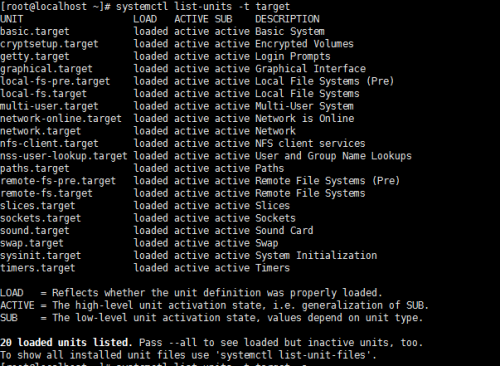
查看級別:runlevel ==> systemctl list-units–type target
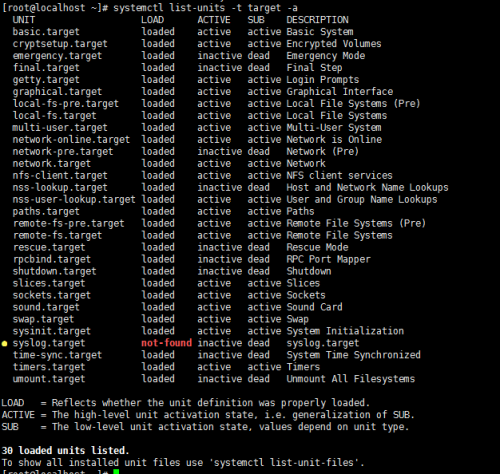
查看所有級別:systemctl list-units -t target –a
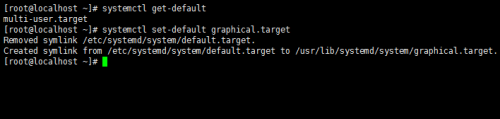
獲取默認運行級別:systemctl get-default
修改默認運行級別:systemctl set-default NAME.target
切換至緊急救援模式:systemctl rescue
切換至emergency模式:systemctlemergency
其它常用命令:
關機:systemctl halt,systemctlpoweroff
重啟:systemctl reboot
掛起:systemctl suspend
快照:systemctl hibernate
快照並掛起:systemctl hybrid-sleep
Serviceunit file:
文件通常由三部分組成:
[unit]:定義與unit類型無關的通用選項;用於提供unit的描述信息、unit行為及依賴關系等;
[service]:與特定類型相關的專用選項;此處為service類型;
[install]:定義由“systemctlenable”以及“systemctl disable”命令在實現服務啟用或禁用時用到的一些選項
Unit段的常用選項:
Description:描述信息;意義性描述;
After:定義unit的啟動順序;表示當前unit應該晚於哪些unit啟動;其功能與before相反;
Requires:依賴到的其它units;強依賴,被依賴的units無法激活時,當前的unit即無法激活;
Wants:依賴到的其它units;弱依賴;
Conflicts:定義units間的沖突關系;
Service段的常用選項:
Type:用於定義影響ExecStart及相關參數的功能的unit進程啟動類型;
類型:
simple:默認值,這個daemon主要由Execstart接的指令串來啟動,啟動後長駐於內存中;
forking:由ExecStart啟動的程序透過spawns延伸出其他子程序來作為此daemon的主要服務。
oneshot:與simple類似,不過這個程序在工作完畢後就結束了,不會常駐於內存之中;
dbus:與simple 類似,但這個damon必須要在取得一個D-bus的名稱後,才會繼續運作,因此通常也要同時設定BusNname才行
notify:
idle:
EnvironmentFile:環境配置文件;
ExecStart:指明啟動unit要運行的命令或腳本;ExeStartPre,ExecStartPost
Restart:
Install段的常用選項:
Alias:別名可使用systemctl command alias.service
RequiedBy:被哪些units所依賴;
WantedBy:被哪些units所依賴;
Note:對於新創建的unit文件或修改了的unit文件,要通知systemd重載配置文件;
#systemctl daemon-reload
Linux自學筆記——Centos7系統之systemd
