[轉] caffe激活層及參數
在激活層中,對輸入數據進行激活操作(實際上就是一種函數變換),是逐元素進行運算的。從bottom得到一個blob數據輸入,運算後,從top輸入一個blob數據。在運算過程中,沒有改變數據的大小,即輸入和輸出的數據大小是相等的。
輸入:n*c*h*w
輸出:n*c*h*w
常用的激活函數有sigmoid, tanh,relu等,下面分別介紹。
1、Sigmoid
對每個輸入數據,利用sigmoid函數執行操作。這種層設置比較簡單,沒有額外的參數。
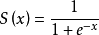
層類型:Sigmoid
示例:
layer {
name: "encode1neuron"
bottom: "encode1"
top: "encode1neuron"
type: "Sigmoid"
}2、ReLU / Rectified-Linear and Leaky-ReLU
ReLU是目前使用最多的激活函數,主要因為其收斂更快,並且能保持同樣效果。
標準的ReLU函數為max(x, 0),當x>0時,輸出x; 當x<=0時,輸出0
f(x)=max(x,0)
層類型:ReLU
可選參數:
negative_slope:默認為0. 對標準的ReLU函數進行變化,如果設置了這個值,那麽數據為負數時,就不再設置為0,而是用原始數據乘以negative_slope
layer {
name: "relu1"
type: "ReLU"
bottom: "pool1"
top: "pool1"
}RELU層支持in-place計算,這意味著bottom的輸出和輸入相同以避免內存的消耗。
3、TanH / Hyperbolic Tangent
利用雙曲正切函數對數據進行變換。
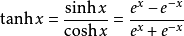
層類型:TanH
layer {
name: "layer"
bottom: "in"
top: "out"
type: "TanH"
}
4、Absolute Value
求每個輸入數據的絕對值。
f(x)=Abs(x)
層類型:AbsVal
layer {
name: "layer"
bottom: "in"
top: "out"
type: "AbsVal"
}5、Power
對每個輸入數據進行冪運算
f(x)= (shift + scale * x) ^ power
層類型:Power
可選參數:
power: 默認為1
scale: 默認為1
shift: 默認為0

layer {
name: "layer"
bottom: "in"
top: "out"
type: "Power"
power_param {
power: 2
scale: 1
shift: 0
}
}

6、BNLL
binomial normal log likelihood的簡稱
f(x)=log(1 + exp(x))
層類型:BNLL
layer {
name: "layer"
bottom: "in"
top: "out"
type: “BNLL”
}
原文:http://www.cnblogs.com/denny402/p/5072507.html#3652385
目前大多數模型都是使用 RELU 激活函數,此外RELU支持原址( in-place)計算, 即它的底層 blob 和頂層 blob 可以是同一個以節省內存開銷。
可以發現很多模型的RELU層內bottom和top為同一參數,但其他激活函數暫時不支持。
[轉] caffe激活層及參數
