04-String-動手動腦
一、.請運行以下示例代碼StringPool.java,查看輸出結果。如何解釋這樣的輸出結果?從中你能總結出什麽?
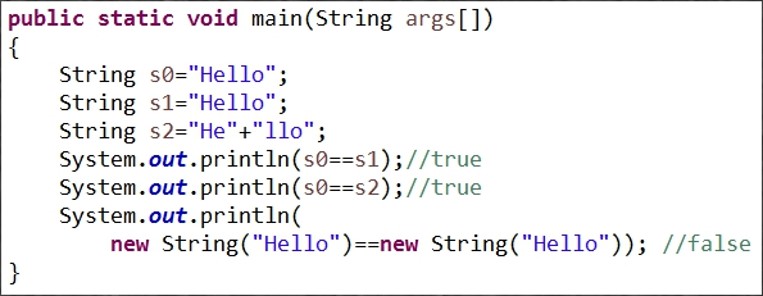
結果為:
結論:
結論:
1、在Java中,內容相同的字符常量只保存一份以節省內存,所以s0,s1,s2實際上引用的是同一個對象。
2、編譯器在編譯s2一句時,會去掉“+”號,直接把兩個字串連接起來得一個字串。這種優化工作由Java編譯器自動完成。
3、當直接使用new關鍵字創建字符串對象時,雖然值一致,但仍然是兩個獨立的對象。
二、請查看String.equals()方法的實現代碼,註意學習其實現方法。
1 public boolean equals(Object anObject) {2 if (this == anObject) { 3 return true; 4 } 5 if (anObject instanceof String) { 6 String anotherString = (String)anObject; 7 int n = count; 8 if (n == anotherString.count) { 9 char v1[] = value; 10 char v2[] = anotherString.value; 11int i = offset; 12 int j = anotherString.offset; 13 while (n-- != 0) { 14 if (v1[i++] != v2[j++]) 15 return false; 16 } 17 return true; 18 } 19 } 20 return false; 21 }
由代碼可知,這個函數首先判斷這兩個對象是否引用同一個字符串對象,如果是直接比較是否相同,如果不是,則比較兩個對象中的字符是否相等。而且比較的方式是比較單個字符。
三、整理String類的length()、charAt()、 getChars()、replace()、 toUpperCase()、 toLowerCase()、trim()、toCharArray()使用說明。
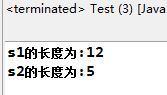
1.int length():返回字符串的長度。
1 public class Test { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 5 String s1 = new String("hello world!"); 6 7 String s2 = new String("hello"); 8 9 System.out.println("s1的長度為:"+s1.length()); 10 11 System.out.println("s2的長度為:"+s2.length()); 12 13 } 14 15 }
結果:
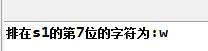
2. char charAt(int index):取字符串中的某一個字符,其中的參數index值得是字符串中序數。字符串的序數從0開始到length()-1。
1 public class Test { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 5 String s1 = new String("hello world!"); 6 7 System.out.println("排在s1的第7位的字符為:"+s1.charAt(6)); 8 9 } 10 11 }
結果:
3.void getChars(int srcBegin, int srcEnd, char dst[], int dstBegin):將字符從字符串復制到目標字符數組。
(1)srcBegin -- 字符串中要復制的第一個字符的索引。
(2)srcEnd -- 字符串中要復制的最後一個字符之後的索引。
(3)dst -- 目標數組。
(4)dstBegin -- 目標數組中的起始偏移量。
(5)無返回值,但會拋出IndexOutOfBoundsException異常
1 public class Test { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 5 String s1 = new String("hello world!"); 6 7 char s2[] = new char[10]; 8 9 s1.getChars(6, 12, s2, 0); 10 11 System.out.println(s2); 12 13 } 14 15 }
結果:
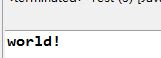
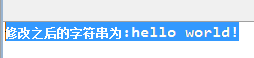
4.String replace(char oldChar,char newChar):將字符串中的所有oldChar替換成newChar
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { String s1 = new String("hello world!"); String s2 = s1.replace(‘o‘,‘a‘); System.out.println("修改之後的字符串為:"+s2); } }
結果:
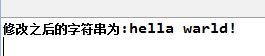
5.String toUpperCase():全部字符變為大寫,返回新字符串。
1 public class Test { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 5 String s1 = new String("hello world!"); 6 7 System.out.println("修改之後的字符串為:"+s1.toUpperCase()); 8 9 } 10 11 }
結果:
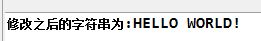
6.String toLowerCase():全部字符變為小寫,返回新字符串
1 public class Test { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 5 String s1 = new String("HELLO WORLD!"); 6 7 System.out.println("修改之後的字符串為:"+s1.toLowerCase()); 8 9 } 10 11 }
結果:
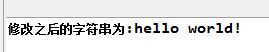
7.String trim():去掉字符串首尾的空格。
1 public class Test { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 5 String s1 = new String(" hello world! "); 6 7 System.out.println("修改之後的字符串為:"+s1.trim()); 8 9 } 10 11 }
結果:
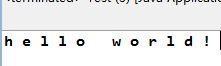
8.char [] toCharArray():將該String對象轉換成char數組。
1 public class Test { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 5 String s1 = new String("hello world!"); 6 7 char s2[] = new char[12]; 8 9 s2 = s1.toCharArray(); 10 11 for(int i = 0 ; i < 12 ; i ++){ 12 13 System.out.print(s2[i]+" "); 14 15 } 16 17 } 18 19 }
結果:
04-String-動手動腦
