Java學習lesson 12
*數組的高級排序
*冒泡排序
兩個兩個比較,大的往後
*選擇排序
從0索引開始,用它對應的元素一次和後面遏制進行比小的往前放,第一次比較完畢,最小值出現在了最小索引處,
*1)用0索引對應的元素依次和後面的索引對應的元素進行比較
比length.arr-1次
*二分查找;二分搜索法
*前提條件:數組必須是有序的(一個排好序的數組)
*思想:猜想中間的索引,這要可以將數組減半
*步驟:
1)定義最小索引,最大索引
2)計算中間索引
3)拿中間索引的元素和要查找的索引進行比較
相等:直接返回中間索引
不相等:
大了:左邊找
小了:右邊找
4)重新獲取最小索引,最大索引,計算中間索引
5)回到第三步
如果是一個亂序,不可以使用二分法;由於二分法會改變最初的索引找到的已經不是原來的你要查找的索引了;(使用基本查找就可以了)
*Arrays類
針對數組操作的工具類
*常用的幾個方法:
*public static String toString(int[] arr ):將任意數組義字符串形式顯示出來
*toString底層會對數組對象進行非空判斷
數組:當前對象為空,返回null
當前對象非空,但沒有數據,返回[];
當前數組有數據,創建字符串緩沖區,返回字符串緩沖區本身
*public static void sort(int arr[]):快速排序(給指定數組進行升序排序)
package arrays;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ArraysDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("請輸入一個字符串:");
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
//可以使用sc.next()但是一般你接受的是什麽類型就調用什麽類型的輸入方法
String str=sc.nextLine();
//將字符串轉換成字符數組
char[] ch=str.toCharArray();
//調用Arrays類中提供的sort方法sort方法內部會調用DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a)快速排序
Arrays.sort(ch);
//輸出時將數組要轉換回字符串輸出
System.out.println("排序後的字符串是:"+Arrays.toString(ch));
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
//調用自己寫的排序方法
sortArray(ch);
System.out.println("排序後的字符串是:"+Arrays.toString(ch));
}
public static void sortArray(char[] ch){
char temp=0;
for(int i=0;i<ch.length;i++){
for(int j=i+1;j<=ch.length-1;j++){
if(ch[j]<ch[i]){
temp=ch[i];
ch[i]=ch[j];
ch[j]=temp;
}
}
}
}
}
*public static int binarySearch(int[]arr,int key):二分查找
*如果找不到你要找的值,那麽返回-6或-1
package arrays;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class ArraysDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args){
int []arr={43,12,56,32,89,43,23};
System.out.println("最初的數組是:"+Arrays.toString(arr));
Arrays.sort(arr);
//註意:調用Arrays中的toString()方法將數組轉成字符串再輸出否則輸出的將是一個地址
System.out.println("排序後的數組是:"+Arrays.toString(arr));
//進行二分查找時由於是對一個有序數組進行查找,所以必須是一個排好序的數組,否則你要找的數的下標將不是原來的下標
//二分查找時如果找不到會返回-1,或-6;
System.out.println("查到的下標是排好序數組的下標:"+Arrays.binarySearch(arr, 3));
}
}//Arrays.binarySearch(arr, 3)

//Arrays.binarySearch(arr, 45)

//Arrays.binarySearch(arr, 43)

Java面向對象原則
實際開發中有對象存在,一定要給對象非空判斷
成員變量在堆內存,局部變量在棧內存
*System類
*該類有構造方法,所以字段和成員都用靜態修飾
*兩個字段 :
*Io流:設備和設備之間的數據傳輸(內存和硬盤上的傳輸)
in、out都和流有關
InputStream in=System.in;
常用方法:
*public static void gc():運行垃圾回收器
調用gc方法暗示了Java虛擬機回收未用對象,以便能夠快速的重用這些對象當前占用的內存,最終調用的就是重寫之後finalize()回收不用的對象
package system;
public class Student {
//成員變量私有,禁止在外部直接調用成員變量
private String name;
private int age ;
public Student() {
super();
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
//要以文本形式輸出當前變量必須重寫toString()方法,否則輸出的將是一個地址值
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]";
}
//重寫Object中的finalize()方法
@Override
protected void finalize() throws Throwable {
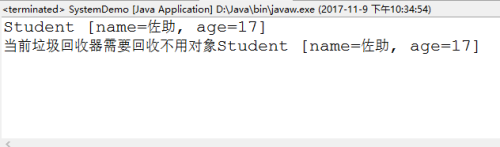
System.out.println("當前垃圾回收器需要回收不用對象"+this);
super.finalize();
}
package system;
public class SystemDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student st=new Student("佐助", 17) ;
System.out.println(st);
st=null ;
//當前Student沒有更多的引用
//啟動垃圾回收器
System.gc() ;//當前垃圾回收器需要回收不用對象
}
} 
* public static void exit(int status):終止當前正在運行的java虛擬機,參數用作狀態碼;根據慣例,非0的狀態碼表示異常終止
package system;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class SystemDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
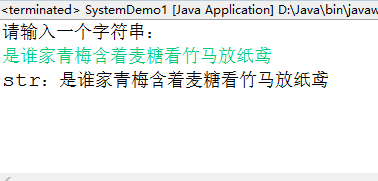
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("請輸入一個字符串:");
String str=sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("str:"+str);
//調用exit()方法
System.exit(0) ;
//退出JVM;所以exit()也可以退出循環
System.out.println("這句話不會輸出!!");
}
}
*public static long currrentTimeMillis ():返回當前系統毫秒值
單獨使用沒有意義,可以用於計算一個應用程序的毫秒值
package system;
public class SystemDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args){
//獲取當前系統時間毫秒值
long time=System.currentTimeMillis() ;//1510240353510
//單獨使用是沒有意義
System.out.println(time);
//一般用於計算某一個應用程序的耗時/毫秒
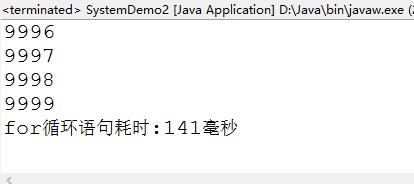
long start = System.currentTimeMillis() ;
for(int i=0;i<10000;i++){
System.out.println(i);
}
//計算上述循環所需要的時間
long end=System.currentTimeMillis() ;
System.out.println("for循環語句耗時:"+(end-start)+"毫秒");//前for循環語句共耗時:4628毫秒
}
}
* public static void arraycopy(Object src,int srcPos,Object dest int destPos,int length):
從指定源數組中復制一個數組,復制從指定的位置開始,到目標數組的指定位置結束。
package system;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class SystemDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//定義兩數組,靜態初始化
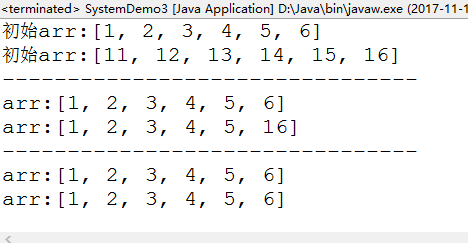
int []arr={1,2,3,4,5,6} ;
int []arr1={11,12,13,14,15,16} ;
System.out.println("初始arr:"+Arrays.toString(arr));
System.out.println("初始arr:"+Arrays.toString(arr1));
System.out.println("--------------------------------");
//復制數組;需要註意的是在Java中System.arraycopy(arr,start,arr1,start,end)
//都是不包括end的知道end-1
System.arraycopy(arr,0,arr1,0,5) ;
//以字符串形式輸出復制後的數組
System.out.println("arr:"+Arrays.toString(arr));
System.out.println("arr:"+Arrays.toString(arr1));
System.out.println("--------------------------------");
System.arraycopy(arr,0,arr1,0,6) ;
//輸出復制後的數組
System.out.println("arr:"+Arrays.toString(arr));
System.out.println("arr:"+Arrays.toString(arr1));
}
}
*BigDecimal類
對於浮點類型來說,他們的存儲和整形的存儲是不一樣的,是按照有效數字位來進行存儲的,浮點類型在計算的時候容易損失精度計算結果不精確,Java提供了這個類
*public static BigDecimal add(BigDecimal augend):加
*public static BigDecimal subtract(BigDecimal subtrachend):減
*public static BigDecimal multiply(BigDecimal multiplicand):乘
*public static Bigdecimal divide(BigDecimal divistor):除
*public BigDecimal divide(BigDecimal divisor,int scale,int roundingMode)
//參數1:商; 參數2:保留幾位小數; 參數3:舍入的一種模式:ROUND_HALF_UP
package bigdecimal;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
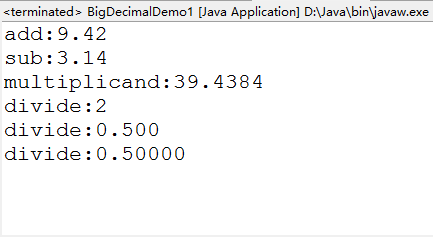
public class BigDecimalDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//創建BigDecimal對象
BigDecimal bd=new BigDecimal("6.28") ;
BigDecimal bd1=new BigDecimal("3.14") ;
//add(BigDecimal augend):加
System.out.println("add:"+bd.add(bd1));
//subtract(BigDecimal subtrahend):減
System.out.println("sub:"+bd.subtract(bd1));//0.68
//multiply(BigDecimal multiplicand):乘
System.out.println("multiplicand:"+bd.multiply(bd));
//divide(BigDecimal divisor):除
System.out.println("divide:"+bd.divide(bd1));
//divide(BigDecimal divisor,int scale,int roundingMode)
//參數1:商, 參數2:保留幾位小數,參數3:舍入的一種模式:ROUND_HALF_UP
System.out.println("divide:"+bd1.divide(bd, 3, BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP));
System.out.println("divide:"+bd1.divide(bd, 5, BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP));
}
}
*BigInteger類
用來計算超出Integer數據範圍的數據
* public BigInteger add(BigInteger val)
返回其值為 (this + val) 的 BigInteger。
*public BigInteger subtract(BigInteger val)
返回其值為 (this - val) 的 BigInteger。
*public BigInteger multiply(BigInteger val)
返回其值為 (this * val) 的 BigInteger。
*public BigInteger divide(BigInteger val)
返回其值為 (this / val) 的 BigInteger
* public BigInteger[] divideAndRemainder(BigInteger val)
返回包含 (this / val) 後跟 (this % val) 的兩個 BigInteger 的數組。
參數:
val - 此 BigInteger 要除以的值和計算所得的余數。
package biginteger;
import java.math.BigInteger;
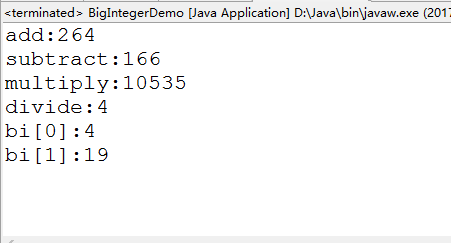
public class BigIntegerDemo {
public static void main(String[] args){
//創建對象
BigInteger bg=new BigInteger("215") ;
BigInteger bg1=new BigInteger("49") ;
//public BigInteger add(BigInteger val)
System.out.println("add:"+bg.add(bg1));
//public BigInteger subtract(BigInteger val)
System.out.println("subtract:"+bg.subtract(bg1));
//public BigInteger multiply(BigInteger val)
System.out.println("multiply:"+bg.multiply(bg1));
//public BigInteger divide(BigInteger val)
System.out.println("divide:"+bg.divide(bg1));
//返回的是數組第一個元素是商,第二個是余數
BigInteger[] bi=bg.divideAndRemainder(bg1) ;
System.out.println("bi[0]:"+bi[0]);
System.out.println("bi[1]:"+bi[1]);
}
}
*Calendar類
是一個抽象類,不能實例化,為特定瞬間與YEAR、MONTH、DAY_OF_MONTH、HOUR等日歷字段(常亮字段)之間的轉換提供一些方法
*實例化:靜態方法:public static Calender getInstans();//創建日歷類對象
Calendar c=Calendar.getInstance();
public int get(int field):返回所給定日歷字段的值
int year=c.get(calendar.YEAR)
*字段
*public static final int YEAR:表示日歷中 的年
*public static final int MONTH:月份:是0開始計算的
*public static final int DATE:和DAY_OF_MONTH是同義詞,表示月份中的某天
*成員方法
*public abstract voi add(int field,int amount):為給定日歷的字
添加(eg:+3)或者減去時間的偏移量(eg:-3)
*public final void set(int year,int month,int date):設置指定年月日字段
設置完要用get()去獲取
*Date類(導包:Ctrl+Shift+o)
日期類:精確到毫秒,表示特定的時間
兩個構造方法:
*public Date():表示分配的一個Date對象:無參,獲取當前系統的具體時間(常用)
Date d=new Date()
輸出:星期 月份 時間 ……Date日期格式
*public Date(long date):指定一個時間毫秒值和它1970-1-1 00:00:00有時間差
package date;
import java.util.Date;
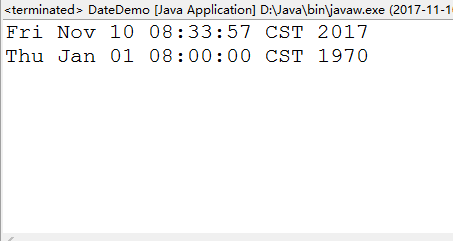
public class DateDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//創建對象:無參構造
Date date=new Date();
System.out.println(date);
//設置時間
long time=1000/60/60;
//指定一個時間毫秒值和1970-1-1 00:00:00有時間差
Date date1=new Date(time);
System.out.println(date1);
}
}
*兩個成員方法:
*public long getTime():獲取當前時間毫秒值
如果知道Date對象,可以通過getTime()獲取時間毫秒值
通過System也可以獲取當前系統的時間毫秒值
*有時候會叫Date對象------>String類型的日期的文本格式:格式化
或String類型的文本格式------->Date:解析
*public Date parse(String source):該方法會拋出異常,ParseException(解析時期異常)
要進行轉換必須使用中間橋梁DateFormat:時日期/時間格式化子類的抽象類
所以要通過SimpleDateFormat具體類實例化
SimpleDateFormat
Date對象------>String類型的日期的文本格式:格式化
Date d=new Date()
//創建SimpleDateFormat對象
SimpleDateFormat sdf=new SimpleDateFormat(shijianmoshi)
Date date=sdf.toString()
*構造方法
*public SimpleDateFormat();給定一個模式,是日期格式化
*public void setTime(long time):設定時間毫秒值
String類型的文本格式------->Date:解析
//一定要保證SimpleDateFormat中的StringPattern這個模式和當前所給字符串的文本格式必須一致
*創建SimpleDateFormat類的對象,用該對象解析String的日系的“文本格式”
package date;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Date;
public class DateDemo1 {
public static void main(String [] args) throws java.text.ParseException{
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("請輸入你的出生日期(yyyy年MM月dd日):");
String str=sc.nextLine();
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日") ;
Date date=sdf.parse(str);
long time=date.getTime();
long nowtime=System.currentTimeMillis();
long timecount=nowtime-time;
long day=timecount/1000/60/60/24;
System.out.println("你來到這個世界已經:"+day+"天了");
}
}*math類
*針對jdk5.0以後的新特性,靜態方法可以靜態導入
*常用成員方法
*public static int abs(int a):絕對值
*public static double ceil(double a):向上取整
*public static double floor(double a):向下取整
*public static double max(double a,double b):獲取最大值
*public static double min(double a,double b):獲取最小值
*public static double pow(double a,double b):a的b次冪
*public static double random():取值範圍:[0.0,1.0)
*public static long round(double a):四舍五入
*public static double sqrt(double a):一個數的正平方跟
package math;
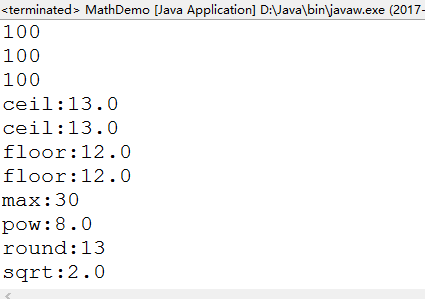
public class MathDemo {
public static void main (String[] args){
System.out.println(Math.abs(-100));
System.out.println(java.lang.Math.abs(-100));
System.out.println(java.lang.Math.abs(-100));
//public static double ceil(double a):向上取整
System.out.println("ceil:"+Math.ceil(12.34));
System.out.println("ceil:"+Math.ceil(12.54));
//public static double floor(double a):向下取整
System.out.println("floor:"+Math.floor(12.34));
System.out.println("floor:"+Math.floor(12.56));
// public static double max(double a,double b):獲取最大值
System.out.println("max:"+Math.max(Math.max(10,20),30));
//public static double pow(double a,double b):a的b次冪
System.out.println("pow:"+Math.pow(2, 3));
//public static long round(double a):四舍五入
System.out.println("round:"+Math.round(12.56));
//public static double sqrt(double a):一個數的正平方跟
System.out.println("sqrt:"+Math.sqrt(4));
}
}
Java學習lesson 12
