linux的shell基礎介紹(1)
8.1 shell介紹:器之間的交互
1、shell是一個命令解釋器,提供用戶和機器之間的交互
2、 支持特定語法,比如邏輯判斷、循環
3、每個用戶都可以有自己特定的shell
4、 CentOS7默認shell為bash(Bourne Agin Shell)
5、 還有zsh、ksh等
查看系統是否有安裝zsh、ksh,示例如下:
[root@aminglinux-01 ~]# yum list |grep zsh zsh.x86_64 5.0.2-25.el7 installed autojump-zsh.noarch 22.3.0-3.el7 epel zsh.x86_64 5.0.2-28.el7 base zsh-html.x86_64 5.0.2-28.el7 base zsh-lovers.noarch 0.9.0-1.el7 epel [root@aminglinux-01 ~]# yum list |grep ksh ksh.x86_64 20120801-34.el7 base mksh.x86_64 46-5.el7 base python-XStatic-Rickshaw.noarch 1.5.0.0-4.el7 epel python-moksha-common.noarch 1.2.3-2.el7 epel python-moksha-hub.noarch 1.5.3-2.el7 epel python-moksha-wsgi.noarch 1.2.2-2.el7 epel
8.2 命令歷史:
1、history命令 //查看之前使用的命令。
2、.bash_history //存儲使用過的命令文件,在root的家目錄下
3、最大1000條 //存儲使用命令的最大數
4、變量HISTSIZE
5、/etc/profile中修改
6、HISTTIMEFORMAT="%Y/%m/%d %H:%M:%S "
7、永久保存 chattr +a ~/.bash_history
8、!! //執行上一條命令
9、!n //n表示數字 比如:!176 這樣它就會執行命令歷史裏的176這條命令
10、!echo //echo表示你需要找命令歷史裏從下往上找以word開頭的第一條命令執行它。
示例如下:
[root@aminglinux-01 ~]# ls /root/.bash_history
/root/.bash_history
[root@aminglinux-01 ~]# cat /root/.bash_history
[root@aminglinux-01 ~]# history
1 ls -l /tmp/
2 ls -l
......
585 ls /root/.bash_history
586 cat /root/.bash_history
587 history
[root@aminglinux-01 ~]# echo $HISTSIZE
1000
[root@aminglinux-01 ~]# history -c //清空當前命令歷史記錄
[root@aminglinux-01 ~]# history
1 history
[root@aminglinux-01 ~]# cat .bash_history //查看是否清空了配置文件命令,沒有,只能清空當前命令歷史的。
ls -l /tmp/
ls -l
which rm註意:當前使用的命令並不會直接保存到.bash_history配置文件裏面去,只有當你退出終端的時候才會保存到配置文件裏。
更改命令歷史變量數值:
[root@aminglinux-01 ~]# vi /etc/profile //更改存儲命令變量,進入這個文件找到以下圖示位置更改
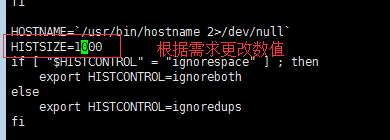
[root@aminglinux-01 ~]# echo $HISTSIZE //保存退出後查看變更並沒有生效
1000
[root@aminglinux-01 ~]# source /etc/profile //更改變量扣執行這條命令
[root@aminglinux-01 ~]# echo $HISTSIZE //完成更改
5000
[root@aminglinux-01 ~]# history
1 history
2 cat .bash_history
3 vi /etc/profile
4 echo $HISTSIZE
5 source /etc/profile
6 echo $HISTSIZE
7 history更改命令歷史格式:
[root@aminglinux-01 ~]# HISTTIMEFORMAT="%Y/%m/%d %H:%M:%S "
[root@aminglinux-01 ~]# echo $HISTTIMEFORMAT
%Y/%m/%d %H:%M:%S
[root@aminglinux-01 ~]# history
1 2017/11/14 16:45:35 history
2 2017/11/14 16:46:43 cat .bash_history
3 2017/11/14 17:59:55 vi /etc/profile
4 2017/11/14 18:04:45 echo $HISTSIZE
5 2017/11/14 18:05:12 source /etc/profile
6 2017/11/14 18:05:14 echo $HISTSIZE
7 2017/11/14 18:06:30 history
8 2017/11/14 18:07:10 HISTTIMEFORMAT="%Y/%m/%d %H:%M:%S "
9 2017/11/14 18:07:34 echo $HISTTIMEFORMAT
10 2017/11/14 18:07:57 history
[root@aminglinux-01 ~]# vim /etc/profile //如果想要保存如上history效果,就進入配置文件加上如下這條變量命令,保存退出。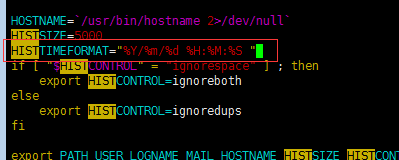
[root@aminglinux-01 ~]# source /etc/profile [root@aminglinux-01 ~]# echo $HISTTIMEFORMAT //這樣哪怕再開一個終端這也保存了。 %Y/%m/%d %H:%M:%S
為了讓命令歷史永久保存,不想讓其它人去破壞它,可以給它加一個特殊的權限。
[root@aminglinux-01 ~]# chattr +a ~/.bash_history //運行這條命令就可以。
註意:如果執行了這條命令後,你並沒有正常退出終端,就會導致保存的命令不全。
8.3 命令補全和別名:
1、tab鍵,敲一下,敲兩下
2、參數補全,安裝bash-completion
3、alias別名給命令重新起個名字
4、 各用戶都有自己配置別名的文件 ~/.bashrc //存放別名的路徑地址
5、ls /etc/profile.d/ //存放別名的路徑地址
6、 自定義的alias放到~/.bashrc //自定義後別名存放的地址
示例如下:
[root@aminglinux-01 ~]# systemctl restart network //使用tab補全這條命令參數 [root@aminglinux-01 ~]# yum install -y bash-completion //安裝這個庫 [root@aminglinux-01 ~]# reboot //重啟系統 [root@aminglinux-01 ~]# alias restartnet=‘systemctl restart network.service‘ //alias別名給命令重新命名 [root@aminglinux-01 ~]# restartnet //設置好的別名命令生效 [root@aminglinux-01 ~]# alias //查看已有的別名 alias cp=‘cp -i‘ alias egrep=‘egrep --color=auto‘ alias fgrep=‘fgrep --color=auto‘ alias grep=‘grep --color=auto‘ alias l.=‘ls -d .* --color=auto‘ alias ll=‘ls -l --color=auto‘ alias ls=‘ls --color=auto‘ alias mv=‘mv -i‘ alias restartnet=‘systemctl restart network.service‘ alias rm=‘rm -i‘ alias which=‘alias | /usr/bin/which --tty-only --read-alias --show-dot --show-tilde‘ [root@aminglinux-01 ~]# unalias restartnet //取消設置好的別名 [root@aminglinux-01 ~]# restartnet //別名命令失效 -bash: restartnet: 未找到命令
8.4 通配符:
1、ls *.txt //表示查找.txt通配文件
2、ls ?.txt //表示一個任意的字符
3、ls [0-9].txt //列出滿足條件範圍內的文件
4、ls {1,2}.txt //用花括號列出你需要的文件
示例如下:
[root@aminglinux-01 ~]# ls
111 1_heard.txt.bak 1.txt.bak 2.txt 456 aminglinux
123 1_sorft.txt.bak 234 3.txt aming2 anaconda-ks.cfg
[root@aminglinux-01 ~]# ls *.txt
2.txt 3.txt
[root@aminglinux-01 ~]# ls *txt
2.txt 3.txt
[root@aminglinux-01 ~]# ls *txt*
1_heard.txt.bak 1_sorft.txt.bak 1.txt.bak 2.txt 3.txt
[root@aminglinux-01 ~]# ls 1*
1_heard.txt.bak 1_sorft.txt.bak 1.txt.bak
111:
123:
[root@aminglinux-01 ~]# ls ?.txt
2.txt 3.txt
[root@aminglinux-01 ~]# touch 1.txt
[root@aminglinux-01 ~]# ls ?.txt
1.txt 2.txt 3.txt
[root@aminglinux-01 ~]# touch a.txt
[root@aminglinux-01 ~]# touch bb.txt
[root@aminglinux-01 ~]# ls ?.txt
1.txt 2.txt 3.txt a.txt
[root@aminglinux-01 ~]# ls [0-3].txt
1.txt 2.txt 3.txt
[root@aminglinux-01 ~]# ls [12].txt
1.txt 2.txt
[root@aminglinux-01 ~]# ls [23].txt
2.txt 3.txt
[root@aminglinux-01 ~]# ls {1,2}.txt
1.txt 2.txt8.5 輸入輸出重定向
1、cat 1.txt >2.txt //>它會把命令產生的正確信息輸出到指定文件裏去,刪除之前文件內容重寫。
2、cat 1.txt >> 2.txt //>>把前面命令輸出內容重定向追加到後面命令裏去,不刪除舊的。
3、ls aaa.txt 2> err //它會把命令產生的錯誤信息輸出到指定文件裏去
4、ls aaa.txt 2>> err // 錯誤信息輸出追加重定向
5、wc -l < 1.txt //查看一個文件的行數
示例如下:
[root@aminglinux-01 ~]# lsaaa //輸出一條錯誤信息 -bash: lsaaa: 未找到命令 [root@aminglinux-01 ~]# lsaaa 2> a.txt //保存一條信息到指定文件裏去 [root@aminglinux-01 ~]# cat a.txt //查看結果 -bash: lsaaa: 未找到命令 [root@aminglinux-01 ~]# lsaaa 2>> a.txt //追加一次錯誤信息到文件 [root@aminglinux-01 ~]# cat a.txt //查看結果 -bash: lsaaa: 未找到命令 -bash: lsaaa: 未找到命令 [root@aminglinux-01 ~]# ls [12].txt aaa.txt &> a.txt //&>結合正確錯誤信息重定向到一個文件裏去 [root@aminglinux-01 ~]# cat a.txt //查看結果 ls: 無法訪問aaa.txt: 沒有那個文件或目錄 1.txt 2.txt [root@aminglinux-01 ~]# ls [12].txt aaa.txt &>> a.txt //追加正確錯誤信息重定向 [root@aminglinux-01 ~]# cat a.txt ls: 無法訪問aaa.txt: 沒有那個文件或目錄 1.txt 2.txt ls: 無法訪問aaa.txt: 沒有那個文件或目錄 1.txt 2.txt [root@aminglinux-01 ~]# ls [12].txt aaa.txt > 1.txt 2>a.txt //既有正確也有錯誤的輸出,區分開來保存在指定的文件裏。 [root@aminglinux-01 ~]# cat 1.txt 1.txt 2.txt [root@aminglinux-01 ~]# cat a.txt ls: 無法訪問aaa.txt: 沒有那個文件或目錄
本文出自 “Gary博客” 博客,請務必保留此出處http://taoxie.blog.51cto.com/10245493/1982118
linux的shell基礎介紹(1)
