第1章 綜合練習
1.1 綜合練習一
A:鍵盤錄入3個學生信息(學號,姓名,年齡,居住地)存入集合,要求學生信息的學號不能重復
B:遍歷集合把每一個學生信息存入文本文件
C:每一個學生信息為一行數據,每行學生的學號,姓名,年齡和居住地在文件中均以逗號分隔
1.1.1 案例代碼一:
[AppleScript] 純文本查看 復制代碼
package com.itheima;
/*
- 標準的學生類
*/
public class Student {
//學號
private String id;
//姓名
private String name;
//年齡
private String age;
//居住地
private String address;public Student() {
}
public Student(String id, String name, String age, String address) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.address = address;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
}
public String getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(String age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
}
[AppleScript] 純文本查看 復制代碼
package com.itheima;[/align]
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Scanner;
/*
- 鍵盤錄入3個學生信息(學號,姓名,年齡,居住地)存入集合。然後遍歷集合把每一個學生信息存入文本文件(每一個學生信息為一行數據,自己定義分割標記)
- 分析:
- A:定義學生類
- B:創建集合對象
- C:寫方法實現鍵盤錄入學生信息,並把學生對象作為元素添加到集合
- D:創建輸出緩沖流對象
- E:遍歷集合,得到每一個學生信息,並把學生信息按照一定的格式寫入文本文件
- 舉例:heima001,向問天,30,北京
- F:釋放資源
*/
public class ArrayListToFileTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//創建集合對象
ArrayList<Student> array = new ArrayList<Student>();
//寫方法實現鍵盤錄入學生信息,並把學生對象作為元素添加到集合
addStudent(array);
addStudent(array);
addStudent(array);
//創建輸出緩沖流對象
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("array.txt"));
//遍歷集合,得到每一個學生信息,並把學生信息按照一定的格式寫入文本文件
for(int x=0; x<array.size(); x++) {
Student s = array.get(x);
//heima001,向問天,30,北京
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append(s.getId()).append(",").append(s.getName()).append(",").append(s.getAge()).append(",").append(s.getAddress());
bw.write(sb.toString());
bw.newLine();
bw.flush();
}
//釋放資源
bw.close();
}
//添加學生
public static void addStudent(ArrayList<Student> array) {
//創建鍵盤錄入對象
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
//為了讓id能夠被訪問到,我們就把id定義在了循環的外面
String id;
//為了讓代碼能夠回到這裏,用循環
while(true) {
System.out.println("請輸入學生學號:");
//String id = sc.nextLine();
id = sc.nextLine();
//判斷學號有沒有被人占用
//定義標記
boolean flag = false;
//遍歷集合,得到每一個學生
for(int x=0; x<array.size(); x++) {
Student s = array.get(x);
//獲取該學生的學號,和鍵盤錄入的學號進行比較
if(s.getId().equals(id)) {
flag = true; //說明學號被占用了
break;
}
}
if(flag) {
System.out.println("你輸入的學號已經被占用,請重新輸入");
}else {
break; //結束循環
}
}
System.out.println("請輸入學生姓名:");
String name = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("請輸入學生年齡:");
String age = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("請輸入學生居住地:");
String address = sc.nextLine();
//創建學生對象
Student s = new Student();
s.setId(id);
s.setName(name);
s.setAge(age);
s.setAddress(address);
//把學生對象作為元素添加到集合
array.add(s);
//給出提示
System.out.println("添加學生成功");
}
}
1.2 綜合練習二:
把上一案例的array.txt文本文件中的學生信息讀取出來存儲到集合中,然後遍歷集合,在控制臺輸出
1.2.1 案例代碼二:
[AppleScript] 純文本查看 復制代碼
package com.itheima;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
/*
- 把上一題的文本文件中的學生信息讀取出來存儲到集合中,然後遍歷集合,在控制臺輸出
- 分析:
- A:定義學生類
- B:創建輸入緩沖流對象
- C:創建集合對象
- D:讀取文件數據,並把數據按照一定的格式進行分割賦值給學生對象,然後把學生對象作為元素存儲到集合
- heima001,向問天,30,北京
- E:釋放資源
- F:遍歷集合
*/
public class FileToArrayListTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//創建輸入緩沖流對象
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("array.txt"));
//創建集合對象
ArrayList<Student> array = new ArrayList<Student>();
//讀取文件數據,並把數據按照一定的格式進行分割賦值給學生對象,然後把學生對象作為元素存儲到集合
String line;
while((line=br.readLine())!=null) {
//分割字符串
String[] strArray = line.split(",");
//創建學生對象並賦值
Student s = new Student();
s.setId(strArray[0]);
s.setName(strArray[1]);
s.setAge(strArray[2]);
s.setAddress(strArray[3]);
//把學生對象作為元素存儲到集合
array.add(s);
}
//釋放資源
br.close();
//遍歷集合
System.out.println("學號\t\t姓名\t年齡\t居住地");
for(int x=0; x<array.size(); x++) {
Student s = array.get(x);
System.out.println(s.getId()+"\t"+s.getName()+"\t"+s.getAge()+"\t"+s.getAddress());
}
}
}
[AppleScript] 純文本查看 復制代碼
package com.itheima;[/align]
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
/*
- 把上一題的文本文件中的學生信息讀取出來存儲到集合中,然後遍歷集合,在控制臺輸出
- 分析:
- A:定義學生類
- B:創建輸入緩沖流對象
- C:創建集合對象
- D:讀取文件數據,並把數據按照一定的格式進行分割賦值給學生對象,然後把學生對象作為元素存儲到集合
- heima001,向問天,30,北京
- E:釋放資源
- F:遍歷集合
*/
public class FileToArrayListTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//創建輸入緩沖流對象
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("array.txt"));
//創建集合對象
ArrayList<Student> array = new ArrayList<Student>();
//讀取文件數據,並把數據按照一定的格式進行分割賦值給學生對象,然後把學生對象作為元素存儲到集合
String line;
while((line=br.readLine())!=null) {
//分割字符串
String[] strArray = line.split(",");
//創建學生對象並賦值
Student s = new Student();
s.setId(strArray[0]);
s.setName(strArray[1]);
s.setAge(strArray[2]);
s.setAddress(strArray[3]);
//把學生對象作為元素存儲到集合
array.add(s);
}
//釋放資源
br.close();
//遍歷集合
System.out.println("學號\t\t姓名\t年齡\t居住地");
for(int x=0; x<array.size(); x++) {
Student s = array.get(x);
System.out.println(s.getId()+"\t"+s.getName()+"\t"+s.getAge()+"\t"+s.getAddress());
}
}
}
1.3 綜合案例三:
學生管理系統IO版:
A:在第九天學生管理系統案例的基礎上,添加新需求
B:查看所有的學生的數據需要從students.txt(提供好的)中讀取出來
C:增刪改都需要先從students.txt中讀出學生的數據然後再把改後的學生數據重新寫回students.txt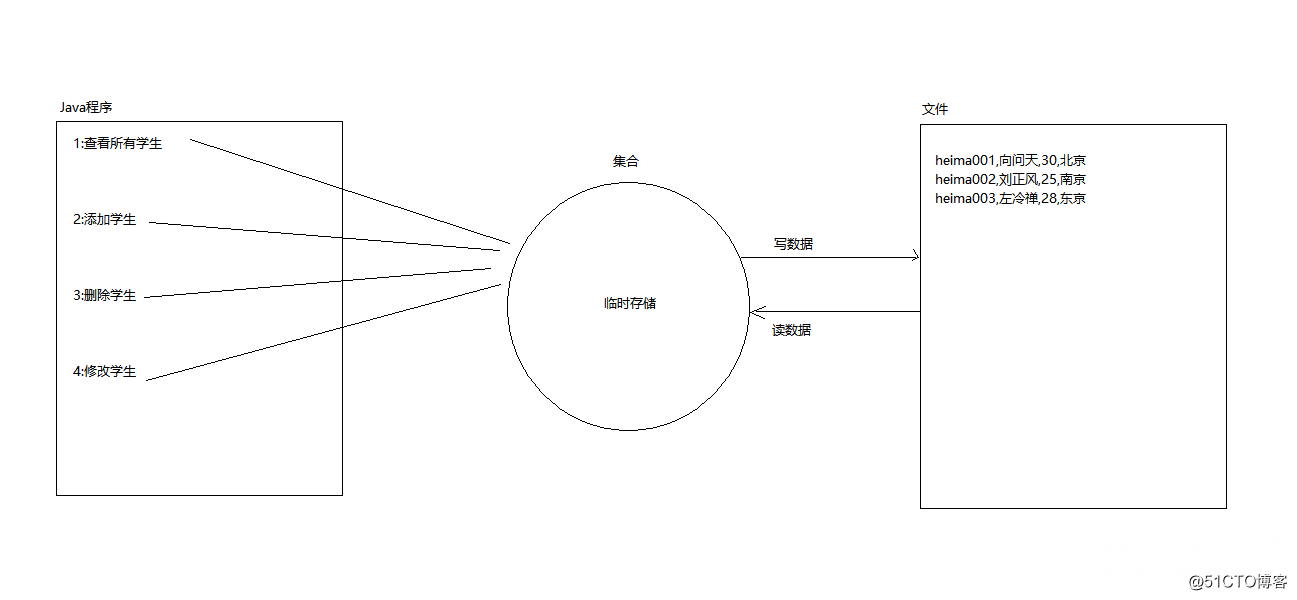
1.3.1 原有的集合版學生管理系統:
1.3.1.1 案例代碼三:
[AppleScript] 純文本查看 復制代碼
package com.itheima;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Scanner;
/*
- 這是我的學生管理系統的主類
- 步驟如下:
- A:定義學生類
- B:學生管理系統的主界面的代碼編寫
- C:學生管理系統的查看所有學生的代碼編寫
- D:學生管理系統的添加學生的代碼編寫
- E:學生管理系統的刪除學生的代碼編寫
- F:學生管理系統的修改學生的代碼編寫
*/
public class StudentManagerTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//創建集合對象,用於存儲學生數據
ArrayList<Student> array = new ArrayList<Student>();
//為了讓程序能夠回到這裏來,我們使用循環
while(true) {
//這是學生管理系統的主界面
System.out.println("--------歡迎來到學生管理系統--------");
System.out.println("1 查看所有學生");
System.out.println("2 添加學生");
System.out.println("3 刪除學生");
System.out.println("4 修改學生");
System.out.println("5 退出");
System.out.println("請輸入你的選擇:");
//創建鍵盤錄入對象
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String choiceString = sc.nextLine();
//用switch語句實現選擇
switch(choiceString) {
case "1":
//查看所有學生
findAllStudent(array);
break;
case "2":
//添加學生
addStudent(array);
break;
case "3":
//刪除學生
deleteStudent(array);
break;
case "4":
//修改學生
updateStudent(array);
break;
case "5":
//退出
//System.out.println("謝謝你的使用");
//break;
default:
System.out.println("謝謝你的使用");
System.exit(0); //JVM退出
break;
}
}
}
//修改學生
public static void updateStudent(ArrayList<Student> array) {
//修改學生的思路:鍵盤錄入一個學號,到集合中去查找,看是否有學生使用的是該學號,如果有就修改該學生
//創建鍵盤錄入對象
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("請輸入你要修改的學生的學號:");
String id = sc.nextLine();
//定義一個索引
int index = -1;
//遍歷集合
for(int x=0; x<array.size(); x++) {
//獲取每一個學生對象
Student s = array.get(x);
//拿學生對象的學號和鍵盤錄入的學號進行比較
if(s.getId().equals(id)) {
index = x;
break;
}
}
if(index == -1) {
System.out.println("不好意思,你要修改的學號對應的學生信息不存在,請回去重新你的選擇");
}else {
System.out.println("請輸入學生新姓名:");
String name = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("請輸入學生新年齡:");
String age = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("請輸入學生新居住地:");
String address = sc.nextLine();
//創建學生對象
Student s = new Student();
s.setId(id);
s.setName(name);
s.setAge(age);
s.setAddress(address);
//修改集合中的學生對象
array.set(index, s);
//給出提示
System.out.println("修改學生成功");
}
}
//刪除學生
public static void deleteStudent(ArrayList<Student> array) {
//刪除學生的思路:鍵盤錄入一個學號,到集合中去查找,看是否有學生使用的是該學號,如果有就刪除該學生
//創建鍵盤錄入對象
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("請輸入你要刪除的學生的學號:");
String id = sc.nextLine();
//定義一個索引
int index = -1;
//遍歷集合
for(int x=0; x<array.size(); x++) {
//獲取到每一個學生對象
Student s = array.get(x);
//拿這個學生對象的學號和鍵盤錄入的學號進行比較
if(s.getId().equals(id)) {
index = x;
break;
}
}
if(index == -1) {
System.out.println("不好意思,你要刪除的學號對應的學生信息不存在,請回去重新你的選擇");
}else {
array.remove(index);
System.out.println("刪除學生成功");
}
}
//添加學生
public static void addStudent(ArrayList<Student> array) {
//創建鍵盤錄入對象
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
//為了讓id能夠被訪問到,我們就把id定義在了循環的外面
String id;
//為了讓代碼能夠回到這裏,用循環
while(true) {
System.out.println("請輸入學生學號:");
//String id = sc.nextLine();
id = sc.nextLine();
//判斷學號有沒有被人占用
//定義標記
boolean flag = false;
//遍歷集合,得到每一個學生
for(int x=0; x<array.size(); x++) {
Student s = array.get(x);
//獲取該學生的學號,和鍵盤錄入的學號進行比較
if(s.getId().equals(id)) {
flag = true; //說明學號被占用了
break;
}
}
if(flag) {
System.out.println("你輸入的學號已經被占用,請重新輸入");
}else {
break; //結束循環
}
}
System.out.println("請輸入學生姓名:");
String name = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("請輸入學生年齡:");
String age = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("請輸入學生居住地:");
String address = sc.nextLine();
//創建學生對象
Student s = new Student();
s.setId(id);
s.setName(name);
s.setAge(age);
s.setAddress(address);
//把學生對象作為元素添加到集合
array.add(s);
//給出提示
System.out.println("添加學生成功");
}
//查看所有學生
public static void findAllStudent(ArrayList<Student> array) {
//首先來判斷集合中是否有數據,如果沒有數據,就給出提示,並讓該方法不繼續往下執行
if(array.size() == 0) {
System.out.println("不好意思,目前沒有學生信息可供查詢,請回去重新選擇你的操作");
return;
}
//\t 其實就是一個tab鍵的位置
System.out.println("學號\t\t姓名\t年齡\t居住地");
for(int x=0; x<array.size(); x++) {
Student s = array.get(x);
System.out.println(s.getId()+"\t"+s.getName()+"\t"+s.getAge()+"\t"+s.getAddress());
}
}
}
1.3.2 對文本文件進行讀寫操作:
1.3.2.1 案例代碼四:
public static void readData(String fileName,ArrayList<Student> array):從fileName的文件中讀取學生的數據,並把學生的數據封裝到array集合中
public static void writeData(String fileName,ArrayList<Student> array):
將array中的每個元素中包含的數據寫入到fileName的文件中
[AppleScript] 純文本查看 復制代碼
// 從文件中讀數據到集合
public static void readData(String fileName, ArrayList<Student> array)
throws IOException {
// 創建輸入緩沖流對象
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(fileName));
String line;
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
String[] datas = line.split(",");
Student s = new Student();
s.setId(datas[0]);
s.setName(datas[1]);
s.setAge(datas[2]);
s.setAddress(datas[3]);
array.add(s);
}
br.close();
}
// 把集合中的數據寫入文件
public static void writeData(String fileName, ArrayList<Student> array)
throws IOException {
// 創建輸出緩沖流對象
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(fileName));
for (int x = 0; x < array.size(); x++) {
Student s = array.get(x);
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append(s.getId()).append(",").append(s.getName()).append(",")
.append(s.getAge()).append(",").append(s.getAddress());
bw.write(sb.toString());
bw.newLine();
bw.flush();
}
bw.close();
}
1.3.3 增刪改查功能調用讀寫文件方法:
1.3.3.1 案例代碼五:
[AppleScript] 純文本查看 復制代碼
package com.itheima;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Scanner;
/*
- 這是我的學生管理系統的主類
- 步驟如下:
- A:定義學生類
- B:學生管理系統的主界面的代碼編寫
- C:學生管理系統的查看所有學生的代碼編寫
- D:學生管理系統的添加學生的代碼編寫
- E:學生管理系統的刪除學生的代碼編寫
- F:學生管理系統的修改學生的代碼編寫
*/
public class StudentManagerTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
//定義文件路徑
String fileName = "students.txt";
//為了讓程序能夠回到這裏來,我們使用循環
while(true) {
//這是學生管理系統的主界面
System.out.println("--------歡迎來到學生管理系統--------");
System.out.println("1 查看所有學生");
System.out.println("2 添加學生");
System.out.println("3 刪除學生");
System.out.println("4 修改學生");
System.out.println("5 退出");
System.out.println("請輸入你的選擇:");
//創建鍵盤錄入對象
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String choiceString = sc.nextLine();
//用switch語句實現選擇
switch(choiceString) {
case "1":
//查看所有學生
findAllStudent(fileName);
break;
case "2":
//添加學生
addStudent(fileName);
break;
case "3":
//刪除學生
deleteStudent(fileName);
break;
case "4":
//修改學生
updateStudent(fileName);
break;
case "5":
default:
System.out.println("謝謝你的使用");
System.exit(0); //JVM退出
break;
}
}
}
// 從文件中讀數據到集合
public static void readData(String fileName, ArrayList<Student> array)
throws IOException {
// 創建輸入緩沖流對象
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(fileName));
String line;
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
String[] datas = line.split(",");
Student s = new Student();
s.setId(datas[0]);
s.setName(datas[1]);
s.setAge(datas[2]);
s.setAddress(datas[3]);
array.add(s);
}
br.close();
}
// 把集合中的數據寫入文件
public static void writeData(String fileName, ArrayList<Student> array)
throws IOException {
// 創建輸出緩沖流對象
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(fileName));
for (int x = 0; x < array.size(); x++) {
Student s = array.get(x);
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append(s.getId()).append(",").append(s.getName()).append(",")
.append(s.getAge()).append(",").append(s.getAddress());
bw.write(sb.toString());
bw.newLine();
bw.flush();
}
bw.close();
}
//修改學生
public static void updateStudent(String fileName) throws IOException {
//創建集合對象
ArrayList<Student> array = new ArrayList<Student>();
//從文件中把數據讀取到集合中
readData(fileName, array);
//修改學生的思路:鍵盤錄入一個學號,到集合中去查找,看是否有學生使用的是該學號,如果有就修改該學生
//創建鍵盤錄入對象
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("請輸入你要修改的學生的學號:");
String id = sc.nextLine();
//定義一個索引
int index = -1;
//遍歷集合
for(int x=0; x<array.size(); x++) {
//獲取每一個學生對象
Student s = array.get(x);
//拿學生對象的學號和鍵盤錄入的學號進行比較
if(s.getId().equals(id)) {
index = x;
break;
}
}
if(index == -1) {
System.out.println("不好意思,你要修改的學號對應的學生信息不存在,請回去重新你的選擇");
}else {
System.out.println("請輸入學生新姓名:");
String name = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("請輸入學生新年齡:");
String age = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("請輸入學生新居住地:");
String address = sc.nextLine();
//創建學生對象
Student s = new Student();
s.setId(id);
s.setName(name);
s.setAge(age);
s.setAddress(address);
//修改集合中的學生對象
array.set(index, s);
//把集合中的數據重新寫回到文件
writeData(fileName, array);
//給出提示
System.out.println("修改學生成功");
}
}
//刪除學生
public static void deleteStudent(String fileName) throws IOException {
//創建集合對象
ArrayList<Student> array = new ArrayList<Student>();
//從文件中把數據讀取到集合中
readData(fileName, array);
//刪除學生的思路:鍵盤錄入一個學號,到集合中去查找,看是否有學生使用的是該學號,如果有就刪除該學生
//創建鍵盤錄入對象
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("請輸入你要刪除的學生的學號:");
String id = sc.nextLine();
//我們必須給出學號不存在的時候的提示
//定義一個索引
int index = -1;
//遍歷集合
for(int x=0; x<array.size(); x++) {
//獲取到每一個學生對象
Student s = array.get(x);
//拿這個學生對象的學號和鍵盤錄入的學號進行比較
if(s.getId().equals(id)) {
index = x;
break;
}
}
if(index == -1) {
System.out.println("不好意思,你要刪除的學號對應的學生信息不存在,請回去重新你的選擇");
}else {
array.remove(index);
//把集合中的數據重新寫回到文件
writeData(fileName, array);
System.out.println("刪除學生成功");
}
}
//添加學生
public static void addStudent(String fileName) throws IOException {
//創建集合對象
ArrayList<Student> array = new ArrayList<Student>();
//從文件中把數據讀取到集合中
readData(fileName, array);
//創建鍵盤錄入對象
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
//為了讓id能夠被訪問到,我們就把id定義在了循環的外面
String id;
//為了讓代碼能夠回到這裏,用循環
while(true) {
System.out.println("請輸入學生學號:");
//String id = sc.nextLine();
id = sc.nextLine();
//判斷學號有沒有被人占用
//定義標記
boolean flag = false;
//遍歷集合,得到每一個學生
for(int x=0; x<array.size(); x++) {
Student s = array.get(x);
//獲取該學生的學號,和鍵盤錄入的學號進行比較
if(s.getId().equals(id)) {
flag = true; //說明學號被占用了
break;
}
}
if(flag) {
System.out.println("你輸入的學號已經被占用,請重新輸入");
}else {
break; //結束循環
}
}
System.out.println("請輸入學生姓名:");
String name = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("請輸入學生年齡:");
String age = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("請輸入學生居住地:");
String address = sc.nextLine();
//創建學生對象
Student s = new Student();
s.setId(id);
s.setName(name);
s.setAge(age);
s.setAddress(address);
//把學生對象作為元素添加到集合
array.add(s);
//把集合中的數據重新寫回到文件
writeData(fileName, array);
//給出提示
System.out.println("添加學生成功");
}
//查看所有學生
public static void findAllStudent(String fileName) throws IOException {
//創建集合對象
ArrayList<Student> array = new ArrayList<Student>();
//從文件中把數據讀取到集合中
readData(fileName, array);
//首先來判斷集合中是否有數據,如果沒有數據,就給出提示,並讓該方法不繼續往下執行
if(array.size() == 0) {
System.out.println("不好意思,目前沒有學生信息可供查詢,請回去重新選擇你的操作");
return;
}
//\t 其實就是一個tab鍵的位置
System.out.println("學號\t\t姓名\t年齡\t居住地");
for(int x=0; x<array.size(); x++) {
Student s = array.get(x);
System.out.println(s.getId()+"\t"+s.getName()+"\t"+s.getAge()+"\t"+s.getAddress());
}
}
}
第1章 綜合練習
