MySQL半一致性讀原理解析-從源碼角度解析
A type of read operation used for UPDATE statements, that is a combination of read committed and consistent read. When an UPDATE statement examines a row that is already locked, InnoDB returns the latest committed version to MySQL so that MySQL can determine whether the row matches the WHERE condition of the UPDATE. If the row matches (must be updated), MySQL reads the row again, and this time InnoDB either locks it or waits for a lock on it. This type of read operation can only happen when the transaction has the read committed isolation level, or when the innodb_locks_unsafe_for_binlog option is enabled.
就是發生在update語句中。在RC隔離級別或者innodb_locks_unsafe_for_binlog被設置為true,並發時,如果update的記錄發生鎖等待,那麽返回該記錄的prev 版本(在返回前會將鎖等待的這個lock從trx中刪除掉),到mysql層進行where判斷,是否滿足條件。如果滿足where條件,那麽再次進入innodb層,真正加鎖或者發生鎖等待。
這樣做的好處是:減少同一行記錄的鎖沖突及鎖等待;無並發沖突時,直接讀取最新版本加鎖,有沖突時,不加鎖,讀取prev版本不需要鎖等待。
缺點:非沖突串行話策略,對於binlog來說是不安全的。只能發生在RC隔離級別和innodb_lock_unsafe_for_binlog下。
2、原理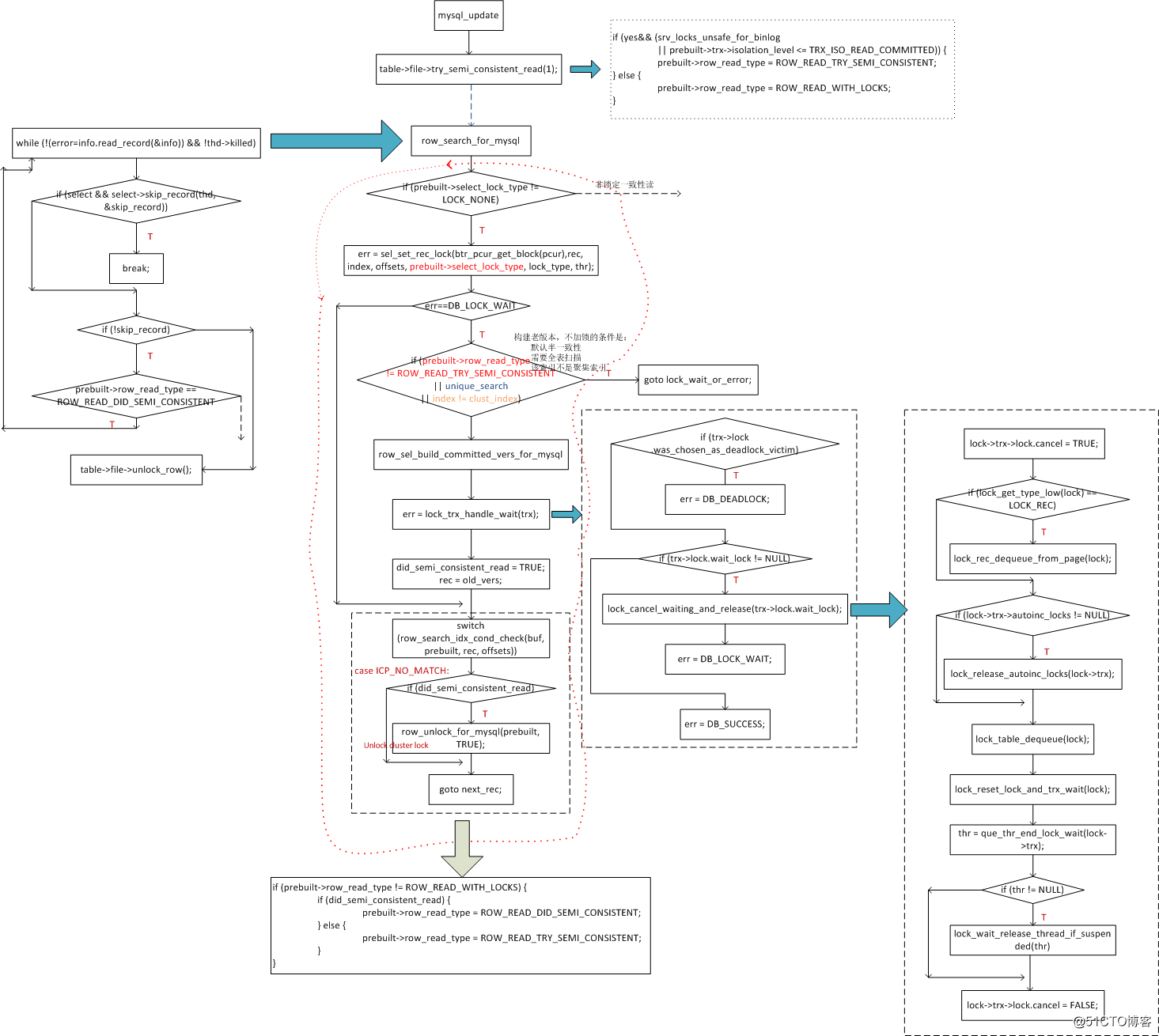
3、講解
1)半一致性讀需要mysql層和innodb層配合使用。
2)mysql_update函數中,默認都會調用try_semi_consistent_read在RC或innodb_lock_unsafe_for_binlog下加上試圖半一致性讀標簽:prebuilt->row_read_type = ROW_READ_TRY_SEMI_CONSISTENT。真正執行半一致性讀是由innodb層決定。
3)半一致性讀的條件:該記錄發生鎖等待;必須是全表掃描 && 該索引是二級索引
4)半一致性讀時,構建prev版本,然後調用函數lock_trx_handle_wait將鎖等待從trx中刪除。
5)返回prev rec前,會將置成半一致性讀標簽:prebuilt->row_read_type = ROW_READ_DID_SEMI_CONSISTENT
6)返回到mysql層,會進行where判斷。如果匹配,那麽會再次進入innodb層,由於prebuilt->row_read_type == ROW_READ_DID_SEMI_CONSISTENT,此時不再走半一致性讀判斷的流程,直接進入加鎖或鎖等待。
5)這裏update有個優化:innodb層如果執行計劃是索引下推,那麽判斷where條件是否匹配會提前。若不匹配則提前調用函數row_unlock_for_mysql釋放聚集索引上的鎖
6)另外一個優化:返回mysql層後,判斷where不匹配,則會調用unlock_row函數釋放鎖。註:這裏update在innodb層沒有發生鎖沖突,成功加上了鎖。即沒有半一致性讀
MySQL半一致性讀原理解析-從源碼角度解析
