題解:UVa1025 A Spy in the Metro
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-05-12
cit %d mat png a10 direct 發現 TP 最小 pdf
原題鏈接
題目大意
給出一張無向圖圖,求該圖的最小瓶頸生成樹。
無向圖的瓶頸生成樹:無向圖\(G\)的一顆瓶頸生成樹是這樣的一顆生成樹:它最大的邊權值在\(G\)的所有生成樹中是最小的。瓶頸生成樹的值為\(T\)中最大權值邊的權。
該圖建立在坐標系中, 給出每個點的坐標。任意兩點之間都有邊,邊權即為兩點間的距離。
題解
由於只關心生成樹的最大值,我們可以將邊從小到大排序,依次加入(若構成環則不加入),直到構成一顆生成樹。
相信你已經發現了:這不就是Kruskal算法嗎?
於是,我們得出結論:無向圖的最小生成樹一定是瓶頸生成樹。
如果你仍然感到懷疑,那麽我們再用反證法證明:
假設存在一張無向圖的最小生成樹\(T\)
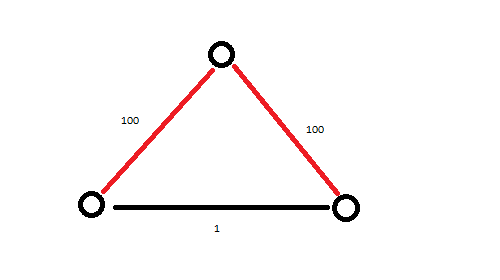
順便提一句,無向圖瓶頸生成樹一定是最小生成樹嗎?
看一看下圖就知道了:
由於本題是稠密圖,最好用Prim解決(然而懶到家的我還是用了Kruskal)。
聽說有一種復雜度更優的算法叫Camerini‘s algorithm(然而我並不會),如果有大神會的話也可以教導我一下。
代碼
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 5005;
struct City
{
double x, y;//註意是小數(開float似乎也行)
} city[maxn];
struct Edge
{
int from, to;
double dist;
bool 題解:UVa1025 A Spy in the Metro
