DNA sequence(映射+BFS)
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-07-30
amp vector number else 而是 sent images modern problems
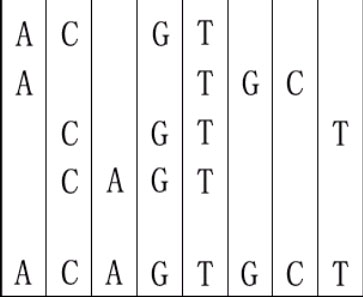
For example, given "ACGT","ATGC","CGTT" and "CAGT", you can make a sequence in the following way. It is the shortest but may be not the only one.
Problem Description
The twenty-first century is a biology-technology developing century. We know that a gene is made of DNA. The nucleotide bases from which DNA is built are A(adenine), C(cytosine), G(guanine), and T(thymine). Finding the longest common subsequence between DNA/Protein sequences is one of the basic problems in modern computational molecular biology. But this problem is a little different. Given several DNA sequences, you are asked to make a shortest sequence from them so that each of the given sequence is the subsequence of it.For example, given "ACGT","ATGC","CGTT" and "CAGT", you can make a sequence in the following way. It is the shortest but may be not the only one.

Input
The first line is the test case number t. Then t test cases follow. In each case, the first line is an integer n ( 1<=n<=8 ) represents number of the DNA sequences. The following k lines contain the k sequences, one per line. Assuming that the length of any sequence is between 1 and 5.Output
SampleInput
1 4 ACGT ATGC CGTT CAGT
SampleOutput
8
題意就是給你幾個DNA序列,要求找到一個序列,使得所有序列都是它的子序列(不一定連續)。
直接搜MLE、TLE、RE,所以不能直接搜索,一般處理這種序列問題,都是把序列映射到整數或其他便於處理的東西上。題目還說了每個DNA的序列長度不會超過5,所以我們可以按位處理映射到一個整數上,而且題目只需要我們輸出最短的序列長度,所以我們也不必去映射字符,映射長度便夠了。
最多8個字符,每個字符1-5長度,所以最大數為6^8。好為什麽是6^8,不明明是5^8麽,這個我暫時先不解釋,我加在了代碼註釋裏。
代碼:
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <string> 3 #include <cstdio> 4 #include <cstdlib> 5 #include <sstream> 6 #include <iomanip> 7 #include <map> 8 #include <stack> 9 #include <deque> 10 #include <queue> 11 #include <vector> 12 #include <set> 13 #include <list> 14 #include <cstring> 15 #include <cctype> 16 #include <algorithm> 17 #include <iterator> 18 #include <cmath> 19 #include <bitset> 20 #include <ctime> 21 #include <fstream> 22 #include <limits.h> 23 #include <numeric> 24 25 using namespace std; 26 27 #define F first 28 #define S second 29 #define mian main 30 #define ture true 31 32 #define MAXN 1000000+5 33 #define MOD 1000000007 34 #define PI (acos(-1.0)) 35 #define EPS 1e-6 36 #define MMT(s) memset(s, 0, sizeof s) 37 typedef unsigned long long ull; 38 typedef long long ll; 39 typedef double db; 40 typedef long double ldb; 41 typedef stringstream sstm; 42 const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; 43 44 int t,n; 45 map<int,int>vis; 46 char s[10][10]; //保存序列 47 int len[10]; //保存每個序列的長度 48 int p[10] = {1,6,36,216,1296,7776,46656,279936,1679616,10077696}; //6的k次方表 49 char temp[4]={‘A‘,‘C‘,‘G‘,‘T‘}; 50 51 struct node{ 52 int step; //長度 53 int st; //也就是映射數 54 node(){} 55 node(int _step, int _st):step(_step),st(_st){} 56 }; 57 58 int bfs(int res){ 59 vis.clear(); 60 queue<node>q; 61 q.push(node(0,0)); 62 vis[0] = 1; 63 while(!q.empty()){ 64 node nxt,k = q.front(); 65 q.pop(); 66 if(k.st == res){ //當映射等於結果時 返回長度 67 return k.step; 68 } 69 for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++){ 70 nxt.st = 0; 71 nxt.step = k.step+1; 72 int tp = k.st; 73 for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++){ 74 int x = tp%6; //得到位數 75 tp /= 6; 76 if(x == len[j] || s[j][x+1] != temp[i]){ //判斷字符是否匹配 77 nxt.st += x*p[j-1]; 78 } 79 else{ 80 nxt.st += (x+1)*p[j-1]; 81 } 82 } 83 if(vis[nxt.st] == 0){ //標記是否已經搜過 84 q.push(nxt); 85 vis[nxt.st] = 1; 86 } 87 } 88 } 89 } 90 91 int main(){ 92 ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false); 93 cout.tie(0); 94 cin.tie(0); 95 cin>>t; 96 while(t--){ 97 cin>>n; 98 int res = 0; 99 for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){ //因為數組從0開始計數,但我們映射以及後面操作都是基於位置,所以從1開始 100 cin>>s[i]+1; //同理從一開始 101 len[i] = strlen(s[i]+1); 102 res += len[i]*p[i-1]; //這也就是為什麽是6^8,因為我們是從1開始有5個狀態而不是0 103 } 104 cout << bfs(res) <<endl; 105 } 106 return 0; 107 }
所以這題你非要從0位置搞,弄5^8確實沒錯,也可以做出來,但是操作會繁瑣很多,還不如從方便的角度多加一個長度。
這道題的難度就是不知道怎麽入手,即使知道轉換處理也不知道該如何轉換以及如何搜索,這裏我們避免了去從字符開始搜索,而是直接基於長度搜。
值得一提的是,我問了隊友後,他們表示這道題做法很多,還可以用IDA*算法或者啟發式搜索,甚至不用搜索用AC自動機加矩陣也可以做。但這些做法都是基於字符去搜索的,也不能說誰好誰壞,只是我們的思維就不一樣了,很多題目其實都不止一種解法,多想想,很有用的。至於其他做法我也就懶得做了(其實是不會23333)
DNA sequence(映射+BFS)
