神經網絡優化算法如何選擇Adam,SGD
之前在tensorflow上和caffe上都折騰過CNN用來做視頻處理,在學習tensorflow例子的時候代碼裏面給的優化方案默認很多情況下都是直接用的AdamOptimizer優化算法,如下:
optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=lr).minimize(cost)- 1
但是在使用caffe時solver裏面一般都用的SGD+momentum,如下:
base_lr: 0.0001
momentum: 0.9
weight_decay: 0.0005
lr_policy: "step"- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
加上最近看了一篇文章:The Marginal Value of Adaptive Gradient Methods
in Machine Learning文章鏈接,文中也探討了在自適應優化算法:AdaGrad, RMSProp, and Adam和SGD算法性能之間的比較和選擇,因此在此搬一下結論和感想。
Abstract
經過本文的實驗,得出最重要的結論是:
We observe that the solutions found by adaptive methods generalize worse (often significantly worse) than SGD, even when these solutions have better training performance. These
results suggest that practitioners should reconsider the use of adaptive methods to train neural
networks - 1
- 2
- 3
翻譯一下就是自適應優化算法通常都會得到比SGD算法性能更差(經常是差很多)的結果,盡管自適應優化算法在訓練時會表現的比較好,因此使用者在使用自適應優化算法時需要慎重考慮!(終於知道為啥CVPR的paper全都用的SGD了,而不是用理論上最diao的Adam)
Introduction
作者繼續給了幹貨結論:
Our experiments reveal three primary findings.
First,
with the same amount of hyperparameter tuning, SGD and SGD with momentum outperform
adaptive methods on the development/test set across all evaluated models and tasks. This is
true even when the adaptive methods achieve the same training loss or lower than non-adaptive
methods. Second, adaptive methods often display faster initial progress on the training set, but
their performance quickly plateaus on the development/test set. Third, the same amount of tuning
was required for all methods, including adaptive methods. This challenges the conventional wisdom
that adaptive methods require less tuning. - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
翻譯:
1:用相同數量的超參數來調參,SGD和SGD +momentum 方法性能在測試集上的額誤差好於所有的自適應優化算法,盡管有時自適應優化算法在訓練集上的loss更小,但是他們在測試集上的loss卻依然比SGD方法高,
2:自適應優化算法 在訓練前期階段在訓練集上收斂的更快,但是在測試集上這種有點遇到了瓶頸。
3:所有方法需要的叠代次數相同,這就和約定俗成的默認自適應優化算法 需要更少的叠代次數的結論相悖!
Conclusion
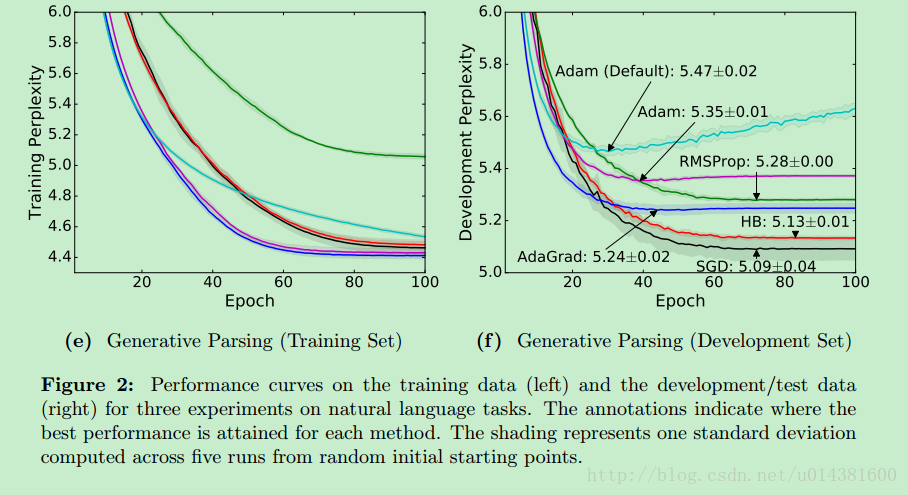
貼幾張作者做的實驗結果圖:
可以看到SGD在訓練前期loss下降並不是最快的,但是在test set上的Perplexity 困惑度(這裏寫鏈接內容)是最小的。
在tensorflow中使用SGD算法:(參考)
# global_step
training_iters=len(data_config[‘train_label‘])
global_step=training_iters*model_config[‘n_epoch‘]
decay_steps=training_iters*1
#global_step = tf.Variable(0, name = ‘global_step‘, trainable=False)
lr=tf.train.exponential_decay(learning_rate=model_config[‘learning_rate‘],
global_step=global_step, decay_steps=decay_steps, decay_rate=0.1, staircase=False, name=None)
optimizer=tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(lr).minimize(cost,var_list=network.all_params)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
神經網絡優化算法如何選擇Adam,SGD