HDU 1890 - Robotic Sort - [splay][區間反轉+刪除根節點]
題目鏈接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1890
Time Limit: 6000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Problem Description Somewhere deep in the Czech Technical University buildings, there are laboratories for examining mechanical and electrical properties of various materials. In one of yesterday’s presentations, you have seen how was one of the laboratories changed into a new multimedia lab. But there are still others, serving to their original purposes.In this task, you are to write software for a robot that handles samples in such a laboratory. Imagine there are material samples lined up on a running belt. The samples have different heights, which may cause troubles to the next processing unit. To eliminate such troubles, we need to sort the samples by their height into the ascending order.
Reordering is done by a mechanical robot arm, which is able to pick up any number of consecutive samples and turn them round, such that their mutual order is reversed. In other words, one robot operation can reverse the order of samples on positions between A and B.
A possible way to sort the samples is to find the position of the smallest one (P1) and reverse the order between positions 1 and P1, which causes the smallest sample to become first. Then we find the second one on position P and reverse the order between 2 and P2. Then the third sample is located etc.
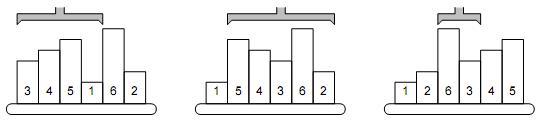
The picture shows a simple example of 6 samples. The smallest one is on the 4th position, therefore, the robot arm reverses the first 4 samples. The second smallest sample is the last one, so the next robot operation will reverse the order of five samples on positions 2–6. The third step will be to reverse the samples 3–4, etc.
Your task is to find the correct sequence of reversal operations that will sort the samples using the above algorithm. If there are more samples with the same height, their mutual order must be preserved: the one that was given first in the initial order must be placed before the others in the final order too. Input
The last scenario is followed by a line containing zero. Output
Each Pi must be an integer (1 ≤ Pi ≤ N ) giving the position of the i-th sample just before the i-th reversal operation.
Note that if a sample is already on its correct position Pi , you should output the number Pi anyway, indicating that the “interval between Pi and Pi ” (a single sample) should be reversed. Sample Input 6 3 4 5 1 6 2 4 3 3 2 1 0 Sample Output 4 6 4 5 6 6 4 2 4 4
題意:
給出一個n,給出n個樣品的高度,
給出一種根據高度排序的算法,其第 i 次操作:找到第 i 小的那個數的位置為Pi,將整個區間[i,Pi]反轉,這樣一來第 i 小的數就在位置 i 上;從 i 等於 1 到 n 循環這樣的操作。
現在要求你給出每次操作的Pi。
題解:
伸展樹1~n建樹,把每個節點key值等於節點的編號(即key[x] = x),同時使得中序遍歷伸展樹得到的序列為1~n,
以題目中兩個樣例為例,建成的樹應為如下圖:

 (註意,圖中節點內的數字,既是節點編號,也是key值,即key[3] = 3,key[1] = 1,key[5] = 5……)
(註意,圖中節點內的數字,既是節點編號,也是key值,即key[3] = 3,key[1] = 1,key[5] = 5……)
我們此時的伸展樹維護的是n個樣品的編號(編號為1~n);
將n個樣品按輸入順序編號,再按照first高度second編號進行升序排序,那麽新的順序,就是題目中所描述的排序算法中的每次操作的順序,
這樣,按新的順序依次枚舉n個樣品,對於第 i 個樣品,其編號為sample[i].id,
我們此時就要去伸展樹中尋找某個節點x,其key[x] = sample[i].id;而我們要求的Pi,就是比這個節點小的節點個數加1;
根據上面反復提到的,key[x] = x,所以我們其實就是把節點x = sample[i].id伸展到根,然後求其左子樹內節點個數,再加1,
同時,因為需要區間翻轉,所以我們可以翻轉左子樹,並且刪除根節點,相當於翻轉了[i,Pi],
由於我們不斷的刪除節點,因此實際答案就應該是左子樹內節點個數 + 1 + (i - 1)。
AC代碼:
#include<bits/stdc++.h> #define Key_value ch[ch[root][1]][0] using namespace std; const int maxn=1e5+10; int n; struct Sample { int h; int id; }sample[maxn]; bool cmp(Sample a,Sample b) { if(a.h==b.h) return a.id<b.id; else return a.h<b.h; } /******************************** splay - st ********************************/ int root,nodecnt; int par[maxn],ch[maxn][2]; int key[maxn],size[maxn]; bool rev[maxn]; void NewNode(int &x,int p,int k) { x=k; par[x]=p; ch[x][0]=ch[x][1]=0; key[x]=k; size[x]=1; rev[x]=0; } void Update_Rev(int x) { if(x==0) return; rev[x]=!rev[x]; } void Pushup(int x) { size[x]=size[ch[x][0]]+size[ch[x][1]]+1; } void Pushdown(int x) { if(rev[x]) { swap(ch[x][0],ch[x][1]); rev[ch[x][0]]^=1; rev[ch[x][1]]^=1; rev[x]=0; } } void Rotate(int x,int type) //旋轉,0為左旋zag,1為右旋zig { int y=par[x]; Pushdown(y); Pushdown(x); //先把y的標記向下傳遞,再把x的標記往下傳遞 ch[y][!type]=ch[x][type]; par[ch[x][type]]=y; if(par[y]) ch[par[y]][(ch[par[y]][1]==y)]=x; par[x]=par[y]; ch[x][type]=y; par[y]=x; Pushup(y); Pushup(x); } void Splay(int x,int goal) { Pushdown(x); while(par[x]!=goal) { if(par[par[x]]==goal) { Pushdown(par[x]); Pushdown(x); Rotate(x,ch[par[x]][0]==x); //左孩子zig,有孩子zag } else { Pushdown(par[par[x]]); Pushdown(par[x]); Pushdown(x); int y=par[x]; int type=(ch[par[y]][0]==y); //type=0,y是右孩子;type=1,y是左孩子 if(ch[y][type]==x) { Rotate(x,!type); Rotate(x,type); } else { Rotate(y,type); Rotate(x,type); } } } if(goal==0) root=x; } int Get_Kth(int x,int k) //得到第k個節點 { Pushdown(x); int t=size[ch[x][0]]+1; if(t==k) return x; if(t>k) return Get_Kth(ch[x][0],k); else return Get_Kth(ch[x][1],k-t); } int Get_Min(int x) { Pushdown(x); while(ch[x][0]) { x=ch[x][0]; Pushdown(x); } return x; } int Get_Max(int x) { Pushdown(x); while(ch[x][1]) { x=ch[x][1]; Pushdown(x); } return x; } void Build(int &x,int l,int r,int par) { if(l>r) return; int mid=(l+r)/2; NewNode(x,par,mid); Build(ch[x][0],l,mid-1,x); Build(ch[x][1],mid+1,r,x); Pushup(x); } void Init() { root=nodecnt=0; ch[root][0]=ch[root][1]=size[root]=key[root]=par[root]=rev[root]=0; Build(root,1,n,0); } void Del() { if(ch[root][0]==0 && ch[root][1]==0) root=0; else if(ch[root][0]==0) { par[ch[root][1]]=0; root=ch[root][1]; } else if(ch[root][1]==0) { par[ch[root][0]]=0; root=ch[root][0]; } else { int pre=Get_Max(ch[root][0]); int nxt=Get_Min(ch[root][1]); Splay(pre,0); Splay(nxt,root); par[Key_value]=0; Key_value=0; Pushup(ch[root][1]); Pushup(root); } } /******************************** splay - ed ********************************/ int main() { while(scanf("%d",&n) && n!=0) { Init(); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { scanf("%d",&sample[i].h); sample[i].id=i; } sort(sample+1,sample+n+1,cmp); for(int i=1;i<n;i++) { Splay(sample[i].id,0); printf("%d ",i+size[ch[root][0]]); Update_Rev(ch[root][0]); Del(); } printf("%d\n",n); } }
HDU 1890 - Robotic Sort - [splay][區間反轉+刪除根節點]
