APUE 檔案IO
檔案 IO
記錄書中的重要知識和思考實踐部分
Unix 每個檔案都對應一個檔案描述符(file descriptor),為一個非負整數,一個檔案可以有多個fd, 後面所有與檔案(裝置,套接字等)有關操作都是圍繞這個fd來的。
在shell中 < > 都為重定向符號,前者為重定向輸入,後者為輸出。
檔案的開啟
#include <fcntl.h> int open(const char *path, int flags, ... /* mode_t mode */); int openat(int fd, const char *path, int flags, ... /* mode_t mode */);
O_RDONLY, O_WRONLY, O_RDWR, O_EXEC, O_SEARCH 這五個引數(flags)是必須的,另外可選的引數裡面 O_CLOEXEC 與 FD_CLOEXEC 都是在 exec() 函式中關閉檔案描述符的標誌,這個後面會看到。
檔案偏移量
#include <unistd.h>
int lseek(fd, off_t off, int wheren);我們使用 lseek 函式的時候,比如lseek(fd, 10, SEEK_END); 這樣會導致檔案的偏移量增加而檔案的大小仍然不變,
但是當再使用 write 函式向檔案中寫入資料時,直接給個例子更好理解, 檔案 foo 中原有資料為123。
int fd;
if ((fd = open("./foo", O_RDWR)) < 0)
err_sys("open error for foo");
lseek(fd, 2, SEEK_END);
write(fd, "zxh", 3);
$ od -c foo
0000000 1 2 3 \0 \0 z x h
0000010可以看到產生兩個\0,產生了空洞檔案。
使用以下的方式得到當前的檔案偏移量。
off_t off;
off = lseek(fd, 0, SEEK_END); // off 為當前的檔案偏移量,在上例中為 5原子操作
操作是不可中斷的,如 read write 系統呼叫,可能讀取或者寫入的資料少於我們要的數量,但是在函式呼叫這個事件上要麼直接成功要麼直接失敗。
新檔案的讀寫可以使用 open 函式的 O_CREAT 標誌來建立再讀寫,此為原子操作;
還有一種方式是使用 creat 函式建立檔案後再用 open 開啟,這裡有兩個呼叫,當進行程序切換時候,其他程序對此檔案進行處理,產生意向不到的錯誤。
上面是檔案的建立操作,還有檔案描述符的複製操作, 也是如此,對於單程序的效果是一樣的,但是在多程序的時候就
dup2(fd, fd2);
等效於
close(fd2);
fcntl(fd, F_DUPFD, fd2);函式 fcntl
可以改變檔案的屬性,算的上是個雜貨箱吧。
函式原型
#include <fcntl.h>
int fcntl(int fd, int cmd, ... /* arg */);功能:
- 複製一個已有的描述符(cmd = F_DUPFD 或 F_DUPFD_CLOEXEC)
- 獲取/設定檔案描述符標誌(cmd = F_GETFD 或 F_SETFD)
- 獲取/設定檔案狀態標誌(cmd = F_GETFL 或 F_SETFL)
- F_GETFL 只能用遮蔽字O_ACCMODE取得存取方式位
- F_SETFL 更改的標誌只有 O_APPEND,O_NONBLOCK,O_SYNC 和 O_ASYNC
- 獲取/設定非同步IO所有權(cmd = F_GETOWN 或 F_SETOWN)
- 獲取/設定記錄鎖(cmd = F_GETLK、F_SETLK 或 F_SETLKW)
函式的返回值依賴引數而定,所有失敗都是返回 -1,除特定引數,如下:
- F_DUPFD、F_DUPFD_CLOEXEC,返回新的檔案描述符,FD_CLOEXEC標誌被清除
- F_GETFD, 返回檔案描述符標誌,當前只定義了一個 FD_CLOEXEC
- F_GETFL,返回檔案狀態標誌,O_RDONLY等
- F_GETOWN,返回一個程序組ID
成功返回 0。
設定檔案描述符標誌(FD_CLOEXEC)和檔案狀態標誌可用如下函式
int set_cloexec(int fd)
{
int val = fcntl(fd, F_GETFD, 0);
val |= FD_CLOEXEC;
return fcntl(fd, F_SETFD, val);
}
int set_fl(int fd, int flags)
{
int val = fcntl(fd, F_GETFL, 0);
val |= flags;
return fcntl(fd, F_SETFL, val);
}檔案描述符標誌 FD_CLOEXEC
在前面提到,open 函式用使用 O_CLOEXEC 標誌會是開啟的檔案描述符在exec開啟的程序中關閉,可以達到程序間的檔案隔離的效果。
#ifdef _CLOEXEC
open("./foo", O_CLOEXEC | O_RDWR);
#else
open("./file.hole", O_RDWR);
#endif
execl("./rdwr", "rdwr", "10000", NULL);
執行execl後進程是 rdwr,在編譯命令裡面加入 -D_CLOEXEC 選項來看變化
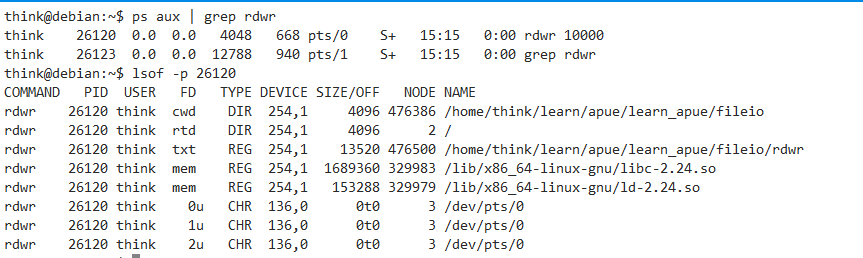
可以發現沒有佔用foo,不加入-D_CLOEXEC

這樣也存在一個問題,在另外一個程序裡關閉了檔案描述符,就須注意當前程序後面不能再對檔案進行操作了。
上面是 open 函式,我們同樣可以用fcntl來改變檔案的描述符標誌,直接呼叫上面的 set_cloexec(fd) 也可以達到這個效果;
5 #include <fcntl.h>
6 #include "apue.h"
7
8 // int fcntl(int fd, int cmd, ... /* int arg */);
9
10 // F_DUPFD F_DUPFD_CLOEXEC
11 // return new fd.
12 int dupfd(int fd) {
13 printf("fcntl_dup: %d\n", fd);
14 int new_fd = fcntl(fd, F_DUPFD, 4); // new_fd 應該是 fd + 1
15 if (new_fd < 0)
16 err_sys("fcntl F_DUPFD error\n");
17 printf("F_DUPFD: %d\n", new_fd);
18 return new_fd;
19 }
20
21 // F_GETFD
22 int getfd(int fd) {
23 int val = fcntl(fd, F_GETFD);
24 if (val < 0)
25 err_sys("fcntl F_GETFD error");
26 printf("getfd %d\n", val);
27 if (val & FD_CLOEXEC) // 這裡 0,所以只會走 30 行的
28 printf("getfd FD_CLOEXEC\n");
29 else
30 printf("getfd not FD_CLOEXEC\n");
31
32 close(val);
33 return val;
34 }
35
36 // F_SETFD
37 int setfd(int fd) {
38 int val = set_cloexec(fd);
39 printf("setfd %d\n", val);
40 // execl("./rdwr", "rdwr", "123", NULL);
41 return val;
42 }
43
44 void setfl(int fd, int flags) {
45 set_fl(fd, flags);
46 }
47
48 int getfl(int fd) {
49 int val;
50 if ((val = fcntl(fd, F_GETFL)) < 0)
51 err_sys("fcntl F_GETFL error");
52
53 switch (val & O_ACCMODE) {
54 case O_RDONLY:
55 printf("read only\n");
56 break;
57 case O_WRONLY:
58 printf("write only\n");
59 break;
60 case O_RDWR:
61 printf("read write\n");
62 break;
63 default:
64 err_dump("unkown access mode");
65 }
66 if (val & O_APPEND)
67 printf(", append");
68 if (val & O_NONBLOCK)
69 printf(", nonblocking");
70 if (val & O_SYNC)
71 printf(", synchronous writes");
72 return val;
73 };
74
75 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
76 int fd;
77
78 if ((fd = open("./foo", O_RDWR | O_CREAT)) < 0)
79 err_sys("open error");
80 dupfd(fd);
81 getfd(fd);
82 setfd(fd);
83 getfl(fd);
84 // setfl(fd, O_APPEND); // 從檔案為開始操作
85 if (write(fd, "jinpi", 5) < 0)
86 err_sys("write error");
87 }
