Android框架原始碼解析之(二)OKhttp
原始碼在:https://github.com/square/okhttp
包實在是太多了,OKhttp核心在這塊https://github.com/square/okhttp/tree/master/okhttp
直接匯入Android Studio中即可。
基本使用:
//1、建立OkHttpClient
OkHttpClient mOkHttpClient = new OkHttpClient();
//2、建立Request
final Request request = new Request.Builder()
.url("https://www.jianshu.com/u/b4e69e85aef6" 原始碼解析:
1、建立OkHttpClient
//OkHttpClient.java
public OkHttpClient() {
this(new Builder()); 通過建造者模式為我們設定預設的OKhttpClient
2、建立Request
//Request.java
Request(Builder builder) {
//請求的url
this.url = builder.url;
//請求的方式
this.method = builder.method;
//請求頭
this.headers = builder.headers.build();
//請求體
this.body = builder.body;
this.tags = Util.immutableMap(builder.tags);
}
//具體的設定我就不貼了,可以看出通過建造者模式建立Request
public Builder newBuilder() {
return new Builder(this);
}
public Request build() {
if (url == null) throw new IllegalStateException("url == null");
return new Request(this);
}
通過建造者模式建立Request
3、建立Call
Call call = mOkHttpClient.newCall(request);原始碼:
@Override public Call newCall(Request request) {
return RealCall.newRealCall(this, request, false /* for web socket */);
}可以看出,呼叫了RealCall.newRealCall方法,繼續往下看
static RealCall newRealCall(OkHttpClient client, Request originalRequest, boolean forWebSocket) {
// Safely publish the Call instance to the EventListener.
RealCall call = new RealCall(client, originalRequest, forWebSocket);
call.eventListener = client.eventListenerFactory().create(call);
return call;
}實際上是建立了RealCall物件
4、執行RealCall.enqueue方法,非同步請求
@Override public void enqueue(Callback responseCallback) {
synchronized (this) {
//為保證執行緒安全,若已經執行,丟擲IllegalStateException
if (executed) throw new IllegalStateException("Already Executed");
executed = true;
}
captureCallStackTrace();
eventListener.callStart(this);
//重點在這裡
client.dispatcher().enqueue(new AsyncCall(responseCallback));
}可以看出最終的請求是dispatcher來完成的
看一下同步請求程式碼:
@Override public Response execute() throws IOException {
synchronized (this) {
if (executed) throw new IllegalStateException("Already Executed");
executed = true;
}
captureCallStackTrace();
eventListener.callStart(this);
try {
//同步請求
client.dispatcher().executed(this);
Response result = getResponseWithInterceptorChain();
if (result == null) throw new IOException("Canceled");
return result;
} catch (IOException e) {
eventListener.callFailed(this, e);
throw e;
} finally {
client.dispatcher().finished(this);
}
}在這裡可以看出
非同步請求呼叫了dispatcher().enqueue
同步請求呼叫了dispatcher().executed
接下來分析dispatcher
5、Dispatcher
Dispatcher主要用於控制併發的請求,主要維護了以下變數
//最大併發請求數
private int maxRequests = 64;
//每個主機的最大請求數
private int maxRequestsPerHost = 5;
private @Nullable Runnable idleCallback;
/** Executes calls. Created lazily. */
//消費者執行緒池
private @Nullable ExecutorService executorService;
/** Ready async calls in the order they'll be run. */
//將要執行的非同步請求佇列
private final Deque<AsyncCall> readyAsyncCalls = new ArrayDeque<>();
/** Running asynchronous calls. Includes canceled calls that haven't finished yet. */
//正在執行的非同步請求佇列
private final Deque<AsyncCall> runningAsyncCalls = new ArrayDeque<>();
/** Running synchronous calls. Includes canceled calls that haven't finished yet. */
//正在執行的同步請求佇列
private final Deque<RealCall> runningSyncCalls = new ArrayDeque<>();接下來看看Dispatche的構造方法
public Dispatcher(ExecutorService executorService) {
this.executorService = executorService;
}
public Dispatcher() {
}
public synchronized ExecutorService executorService() {
if (executorService == null) {
//如果使用者沒有設定自己的執行緒池,自OKhttp初始化預設的執行緒池
executorService = new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 60, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>(), Util.threadFactory("OkHttp Dispatcher", false));
}
return executorService;
}Dispatcher有兩個構造方法,可以使用自己的執行緒池。如果沒有設定自己的執行緒池,則會設定預設的執行緒池。這個執行緒池類類似於CachedThreadPool,比較適合執行大量的耗時比較少的任務。
接下來看看Dispatcher的同步執行方法
/** Used by {@code Call#execute} to signal it is in-flight. */
synchronized void executed(RealCall call) {
//將請求新增到同步執行佇列
runningSyncCalls.add(call);
}Dispatcher的非同步執行方法
synchronized void enqueue(AsyncCall call) {
/*當正在執行的非同步請求佇列中的數量小於64並且正在執行的請求主機數小於5時
把請求新增到runningAsyncCalls
否則,將請求新增到readyAsyncCalls
*/
if (runningAsyncCalls.size() < maxRequests && runningCallsForHost(call) < maxRequestsPerHost) {
runningAsyncCalls.add(call);
executorService().execute(call);
} else {
readyAsyncCalls.add(call);
}
}接下來呼叫executorService().execute(call);,實際呼叫的是AsyncCall的execute方法,接下來分析
6、AsyncCal的execute方法
AsyncCall是RealCall的內部類,其內部也實現了execute方法,如下:
@Override protected void execute() {
boolean signalledCallback = false;
try {
//在這塊實現了網路請求,並返回Response
Response response = getResponseWithInterceptorChain();
if (retryAndFollowUpInterceptor.isCanceled()) {
signalledCallback = true;
responseCallback.onFailure(RealCall.this, new IOException("Canceled"));
} else {
signalledCallback = true;
responseCallback.onResponse(RealCall.this, response);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
if (signalledCallback) {
// Do not signal the callback twice!
Platform.get().log(INFO, "Callback failure for " + toLoggableString(), e);
} else {
eventListener.callFailed(RealCall.this, e);
responseCallback.onFailure(RealCall.this, e);
}
} finally {
client.dispatcher().finished(this);
}
}
}可以看出,網路請求操作在Response response = getResponseWithInterceptorChain();中執行
下面分析getResponseWithInterceptorChain()
7、RealCall.getResponseWithInterceptorChain()
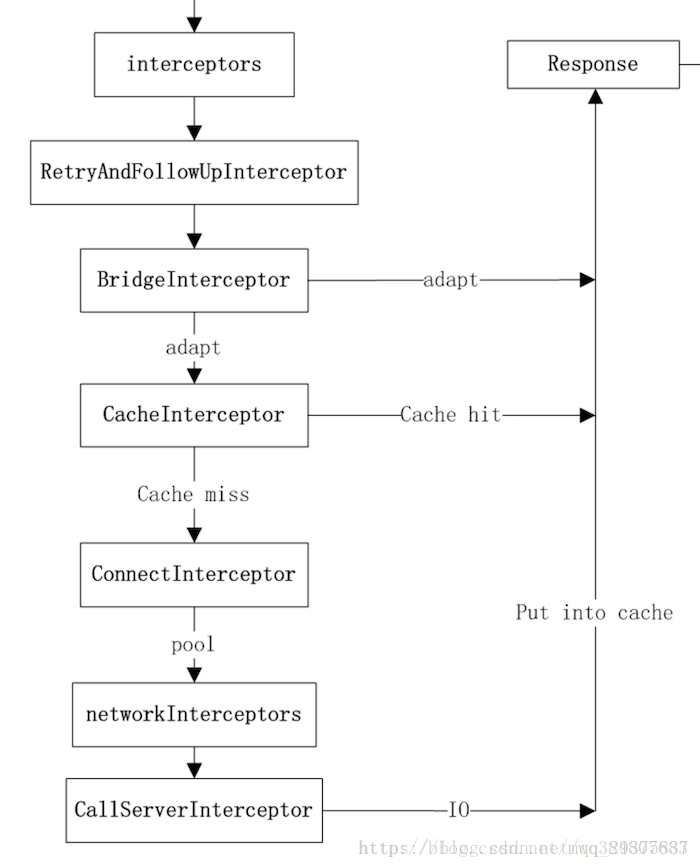
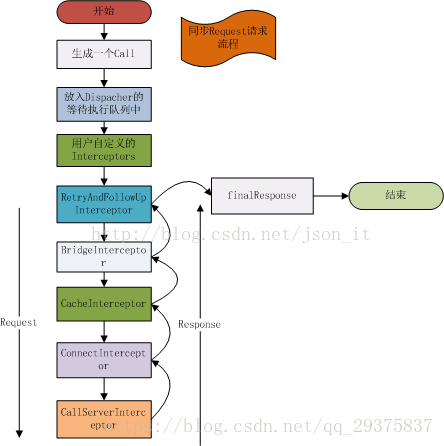
Response getResponseWithInterceptorChain() throws IOException {
// Build a full stack of interceptors.
//新增各種Interceptor
List<Interceptor> interceptors = new ArrayList<>();
interceptors.addAll(client.interceptors());
interceptors.add(retryAndFollowUpInterceptor);
interceptors.add(new BridgeInterceptor(client.cookieJar()));
interceptors.add(new CacheInterceptor(client.internalCache()));
interceptors.add(new ConnectInterceptor(client));
if (!forWebSocket) {
interceptors.addAll(client.networkInterceptors());
}
interceptors.add(new CallServerInterceptor(forWebSocket));
Interceptor.Chain chain = new RealInterceptorChain(interceptors, null, null, null, 0,
originalRequest, this, eventListener, client.connectTimeoutMillis(),
client.readTimeoutMillis(), client.writeTimeoutMillis());
return chain.proceed(originalRequest);
}可以看出建立了RealInterceptorChain它是一個攔截器鏈,這個類也是RealCall的內部類,接下來執行它的proceed方法
public Response proceed(Request request, StreamAllocation streamAllocation, HttpCodec httpCodec,
RealConnection connection) throws IOException {
if (index >= interceptors.size()) throw new AssertionError();
calls++;
// If we already have a stream, confirm that the incoming request will use it.
if (this.httpCodec != null && !this.connection.supportsUrl(request.url())) {
throw new IllegalStateException("network interceptor " + interceptors.get(index - 1)
+ " must retain the same host and port");
}
// If we already have a stream, confirm that this is the only call to chain.proceed().
if (this.httpCodec != null && calls > 1) {
throw new IllegalStateException("network interceptor " + interceptors.get(index - 1)
+ " must call proceed() exactly once");
}
// Call the next interceptor in the chain.
//從攔截器中取出攔截器
RealInterceptorChain next = new RealInterceptorChain(interceptors, streamAllocation, httpCodec,
connection, index + 1, request, call, eventListener, connectTimeout, readTimeout,
writeTimeout);
Interceptor interceptor = interceptors.get(index);
Response response = interceptor.intercept(next);
// Confirm that the next interceptor made its required call to chain.proceed().
if (httpCodec != null && index + 1 < interceptors.size() && next.calls != 1) {
throw new IllegalStateException("network interceptor " + interceptor
+ " must call proceed() exactly once");
}
// Confirm that the intercepted response isn't null.
if (response == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("interceptor " + interceptor + " returned null");
}
if (response.body() == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"interceptor " + interceptor + " returned a response with no body");
}
return response;
}攔截器的作用
來自官網的英文原文:
Interceptors are a powerful mechanism that can monitor, rewrite, and retry calls.
意思大概是,攔截器是一個強有力的機制,,它可以實現網路監聽、請求以及響應重寫、請求失敗重試等功能。
這裡不做過多分析,具體詳情可以看看這篇文章
https://blog.csdn.net/lepaitianshi/article/details/72457928
具體的網路請求已經在攔截器中實現
* CacheInterceptor實現快取管理*
@Override public Response intercept(Chain chain) throws IOException {
Response cacheCandidate = cache != null
? cache.get(chain.request())
: null;
long now = System.currentTimeMillis();
CacheStrategy strategy = new CacheStrategy.Factory(now, chain.request(), cacheCandidate).get();
//網路請求
Request networkRequest = strategy.networkRequest;
//快取響應
Response cacheResponse = strategy.cacheResponse;
if (cache != null) {
//記錄當前請求是網路發起還是快取發起
cache.trackResponse(strategy);
}
if (cacheCandidate != null && cacheResponse == null) {
closeQuietly(cacheCandidate.body()); // The cache candidate wasn't applicable. Close it.
}
// If we're forbidden from using the network and the cache is insufficient, fail.
//不進行網路請求,並且快取不存在,則返回504錯誤
if (networkRequest == null && cacheResponse == null) {
return new Response.Builder()
.request(chain.request())
.protocol(Protocol.HTTP_1_1)
.code(504)
.message("Unsatisfiable Request (only-if-cached)")
.body(Util.EMPTY_RESPONSE)
.sentRequestAtMillis(-1L)
.receivedResponseAtMillis(System.currentTimeMillis())
.build();
}
// If we don't need the network, we're done.
//如果不進行網路請求,而且快取可用,則直接返回快取
if (networkRequest == null) {
return cacheResponse.newBuilder()
.cacheResponse(stripBody(cacheResponse))
.build();
}
//請求網路
Response networkResponse = null;
try {
networkResponse = chain.proceed(networkRequest);
} finally {
// If we're crashing on I/O or otherwise, don't leak the cache body.
if (networkResponse == null && cacheCandidate != null) {
closeQuietly(cacheCandidate.body());
}
}
// If we have a cache response too, then we're doing a conditional get.
//如果存在快取,並且伺服器沒有修改資料(networkResponse.code() == HTTP_NOT_MODIFIED),則返回快取
if (cacheResponse != null) {
if (networkResponse.code() == HTTP_NOT_MODIFIED) {
Response response = cacheResponse.newBuilder()
.headers(combine(cacheResponse.headers(), networkResponse.headers()))
.sentRequestAtMillis(networkResponse.sentRequestAtMillis())
.receivedResponseAtMillis(networkResponse.receivedResponseAtMillis())
.cacheResponse(stripBody(cacheResponse))
.networkResponse(stripBody(networkResponse))
.build();
networkResponse.body().close();
// Update the cache after combining headers but before stripping the
// Content-Encoding header (as performed by initContentStream()).
cache.trackConditionalCacheHit();
cache.update(cacheResponse, response);
return response;
} else {
closeQuietly(cacheResponse.body());
}
}
//f否則進行網路請求
Response response = networkResponse.newBuilder()
.cacheResponse(stripBody(cacheResponse))
.networkResponse(stripBody(networkResponse))
.build();
if (cache != null) {
if (HttpHeaders.hasBody(response) && CacheStrategy.isCacheable(response, networkRequest)) {
// Offer this request to the cache.
CacheRequest cacheRequest = cache.put(response);
return cacheWritingResponse(cacheRequest, response);
}
if (HttpMethod.invalidatesCache(networkRequest.method())) {
try {
cache.remove(networkRequest);
} catch (IOException ignored) {
// The cache cannot be written.
}
}
}
return response;
}如果快取存在而且沒有過期(伺服器返回資料為304),則返回響應,否則請求網路
這裡的快取均基於Map,key是請求中url的md5,value是檔案中查詢到的快取,頁面置換基於LRU演算法。
至此原始碼就分析到這,主要是攔截器鏈起作用,具體的話,可以看看這篇文章
https://blog.csdn.net/lepaitianshi/article/details/72457928