屬性動畫之Animator API基本使用
上一篇中我們簡單的介紹瞭如何使用檢視動畫Animation API的基本使用,今天就來介紹一下功能更為強大的屬性動畫Animator API的基本使用,首先我們來看一看Animator的繼承結構:
Animator
public abstract class Animator extends Object implements Cloneable
| java.lang.Object | |
| ↳ | android.animation.Animator |
| Known direct subclasses |
| Known indirect subclasses |
上面是官方API給出的解答,下面是我簡單繪製的關係圖:
其中,使用最多的就是ObjectAnimator以及ObjectAnimator配合AnimatorSet使用,下面就來看一看具體的用法。
1,ObjectAnimator基本使用
1.1 建立方法
(1)通過它的靜態工廠類獲取,比如:
ObjectAnimator animator1= (ObjectAnimator) ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(imageView,"alpha",1,0,1);(2)通過資原始檔配合AnimatorInflater獲取,比如:
ObjectAnimator animator9= (ObjectAnimator) AnimatorInflater.loadAnimator(this,R.animator.animator1);1.2 動畫屬性引數
和檢視動畫類似,這裡分的更加細緻了,主要有以下幾個:
- alpha
ObjectAnimator animator1= (ObjectAnimator) ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(imageView,"alpha",1,0,1); - scaleX
ObjectAnimator animator2= (ObjectAnimator) ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(imageView,"scaleX",1,0,1); - scaleY
ObjectAnimator animator3= (ObjectAnimator) ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(imageView,"scaleY",1,0,1); - rotationX
ObjectAnimator animator4= (ObjectAnimator) ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(imageView,"rotationX",0,180,0); - rotationY
ObjectAnimator animator5= (ObjectAnimator) ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(imageView,"rotationY",0,240,0); - rotation
ObjectAnimator animator6= (ObjectAnimator) ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(imageView,"rotation",0,360,0); - translationX
ObjectAnimator animator7= (ObjectAnimator) ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(imageView,"translationX",10,100,200,400); - translationY
ObjectAnimator animator8= (ObjectAnimator) ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(imageView,"translationY",10,100,200,400);
上面的屬性都是預設自帶的屬性,我們也可以通過自定義屬性的方式來新增新的屬性,比如給一個ImageView物件新增寬度屬性,首先需要定義各一個包裝類WrapperView,在其中實現getXXX和setXXX即可(該部分程式碼直接源於《Android群英傳》):
package com.hfut.operationanimator;
import android.widget.ImageView;
/**
* author:why
* created on: 2018/9/8 23:18
* description:
*/
public class WrapperView {
ImageView mImageView;
public WrapperView(ImageView imageView){
this.mImageView=imageView;
}
public int getWidth(){
return mImageView.getLayoutParams().width;
}
public void setWidth(int width){
mImageView.getLayoutParams().width=width;
mImageView.requestLayout();
}
}
應用(自定義width屬性):
WrapperView wrapperView=new WrapperView(imageView); ObjectAnimator objectAnimator10=ObjectAnimator.ofInt(wrapperView,"width",100);
1.3 ObjectAnimator示例
下面就來看一下ObjectAnimator配合AnimatorSet的示例:
activity_main.xml程式碼:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context="com.hfut.operationanimator.MainActivity">
<Button
android:id="@+id/control_text_button"
android:text="文字動畫"
android:onClick="textAnimator"
android:textSize="30sp"
android:layout_marginTop="20dp"
app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
<ImageView
android:layout_marginTop="45px"
android:id="@+id/test_image"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@id/control_text_button"
android:src="@mipmap/image"
app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent"
android:layout_width="500dp"
android:layout_height="420dp" />
</android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout>
MainActivity程式碼:
package com.hfut.operationanimator;
import android.animation.Animator;
import android.animation.AnimatorInflater;
import android.animation.AnimatorListenerAdapter;
import android.animation.AnimatorSet;
import android.animation.ObjectAnimator;
import android.animation.ValueAnimator;
import android.os.Handler;
import android.os.Message;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.ImageView;
import android.widget.TextView;
import android.widget.Toast;
/**
* @author why
* @date 2018-9-6 20:55:46
*/
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private static final String TAG = "MainActivity";
TextView textView;
ImageView imageView;
// Handler handler=new Handler(){
// @Override
// public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
// Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this,"透明度在0.3左右了,開始同步旋轉",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
// //animator2.start();
// ObjectAnimator animator3= (ObjectAnimator) ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(imageView,"alpha",0.3f,1);
// ObjectAnimator animator2=(ObjectAnimator) ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(imageView,"rotation",0,90);
// animator2.addListener(new AnimatorListenerAdapter() {
// @Override
// public void onAnimationCancel(Animator animation) {
// super.onAnimationCancel(animation);
// }
//
// @Override
// public void onAnimationStart(Animator animation) {
// super.onAnimationStart(animation);
// }
//
// @Override
// public void onAnimationEnd(Animator animation) {
// super.onAnimationEnd(animation);
// Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this,"動畫結束,好好欣賞妹子吧",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
// }
// });
// animator2.setDuration(4000);
// animator3.setDuration(4000);
// AnimatorSet animatorSet=new AnimatorSet();
// animatorSet.playTogether(animator2,animator3);
// animatorSet.start();
// }
// };
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
imageView=findViewById(R.id.test_image);
imageView.setImageDrawable(getResources().getDrawable(R.mipmap.image));
}
public void textAnimator(View view){
//
ObjectAnimator animator1= (ObjectAnimator) ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(imageView,"alpha",0,1);
ObjectAnimator animator2= (ObjectAnimator) ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(imageView,"scaleX",1,0,1);
ObjectAnimator animator3= (ObjectAnimator) ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(imageView,"scaleY",1,0,1);
ObjectAnimator animator4= (ObjectAnimator) ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(imageView,"rotationX",0,180,0);
ObjectAnimator animator5= (ObjectAnimator) ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(imageView,"rotationY",0,240,0);
ObjectAnimator animator6= (ObjectAnimator) ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(imageView,"rotation",0,450);
ObjectAnimator animator7= (ObjectAnimator) ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(imageView,"translationX",imageView.getX()-45,100);
ObjectAnimator animator8= (ObjectAnimator) ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(imageView,"translationY",imageView.getY(),300);
ObjectAnimator animator9= (ObjectAnimator) ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(imageView,"translationX",100,10);
ObjectAnimator animator10= (ObjectAnimator) ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(imageView,"scaleX",1,1.2f);
ObjectAnimator animator11= (ObjectAnimator) ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(imageView,"scaleY",1,1.2f);
ObjectAnimator animator12= (ObjectAnimator) ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(imageView,"translationY",300,200);
// ObjectAnimator animator9= (ObjectAnimator) AnimatorInflater.loadAnimator(this,R.animator.animator1);
animator1.setDuration(1000);
animator1.start();
animator2.setDuration(1000);
animator2.setStartDelay(300);
animator3.setDuration(1000);
animator3.setStartDelay(300);
animator4.setDuration(1000);
animator4.setStartDelay(300);
animator5.setDuration(1000);
animator5.setStartDelay(300);
animator6.setDuration(1000);
animator6.setStartDelay(300);
animator7.setDuration(1000);
animator7.setStartDelay(300);
animator8.setDuration(1000);
animator8.setStartDelay(300);
animator9.setDuration(2000);
animator9.setStartDelay(300);
animator10.setDuration(2000);
animator10.setStartDelay(300);
animator11.setDuration(2000);
animator11.setStartDelay(300);
animator12.setDuration(2000);
animator12.setStartDelay(300);
AnimatorSet animatorSet1=new AnimatorSet();
animatorSet1.playTogether(animator10,animator11,animator12);
AnimatorSet set=new AnimatorSet();
set.playSequentially(animator1,animator2,animator3,animator4,animator5,animator6,animator7,animator8,animator9,animatorSet1);
//set.playSequentially(animator1,animator2,animator3,animator4,animator5,animator6,animator7,animator8,animator9,animator10,animator11);
set.start();
// WrapperView wrapperView=new WrapperView(imageView);
// ObjectAnimator objectAnimator10=ObjectAnimator.ofInt(wrapperView,"width",100);
// final ValueAnimator valueAnimator=ValueAnimator.ofFloat(0,1.0f);
// // valueAnimator.setTarget(imageView);
// valueAnimator.setDuration(6000);
// valueAnimator.addUpdateListener(new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() {
// @Override
// public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator animation) {
// float endAlpha= (float) animation.getAnimatedValue();
// Log.d(TAG, "onAnimationUpdate: "+endAlpha);
// if(endAlpha>=0.29f&&endAlpha<=0.31f){
// valueAnimator.cancel();
// //Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this,"透明度在0.5左右了",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
// Message message=new Message();
// handler.sendMessage(message);
// }
// }
// });
// valueAnimator.start();
}
}
上面的程式碼注意幾點:
(1)每一個Animator可以單獨作用到一個View上
(2)多個Animator可以通過ANimatorSet作用到View上
(3)AnimatorSet中可以巢狀AnimatorSet
(4)AnimatorSet中新增的多個動畫有以上兩種播放模式(不考慮引數型別):
- set.playTogether()
- set.playSequentially()
(5)AnimatorSet播放動畫時長可以自己設定,也可以通過其新增的動畫自己設定,比如:
AnimatorSet set=new AnimatorSet(); set.setDuration(2000);
也可以通過上例中來設定。
2 ,ValueAnimator基本使用
2.1 基礎理解
從最開始的繼承關係圖可以看出,它是ObjectAnimator的父類,它本身不產生任何動畫效果,但是我們可以通過它實現對我們動畫更加精確的控制,這裡面我們可以通過對其新增更新監聽實時獲取動畫的相關引數數值,從而實現對動畫的精確控制,下面我就來提一個需求:
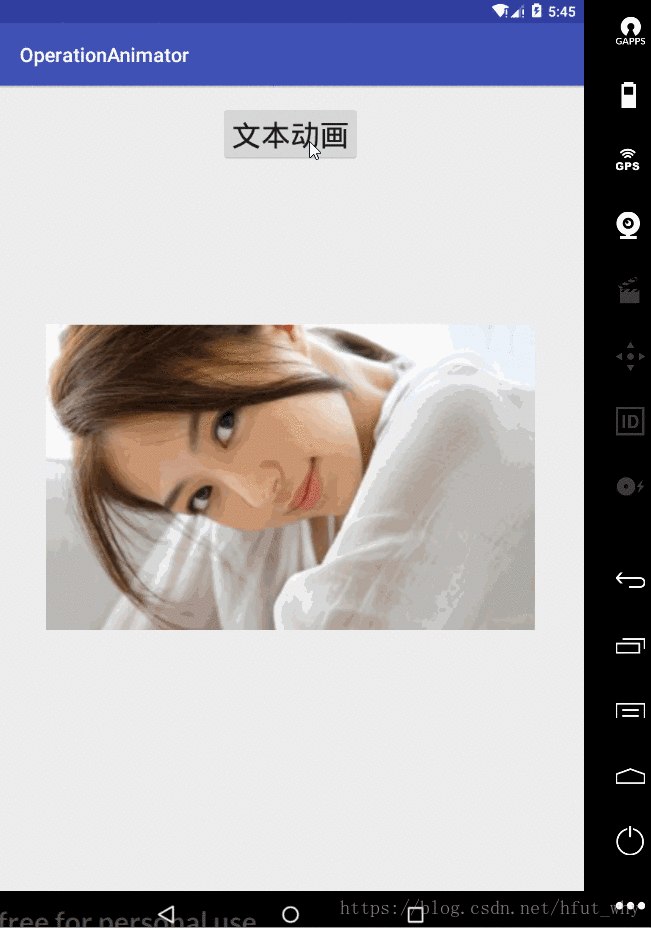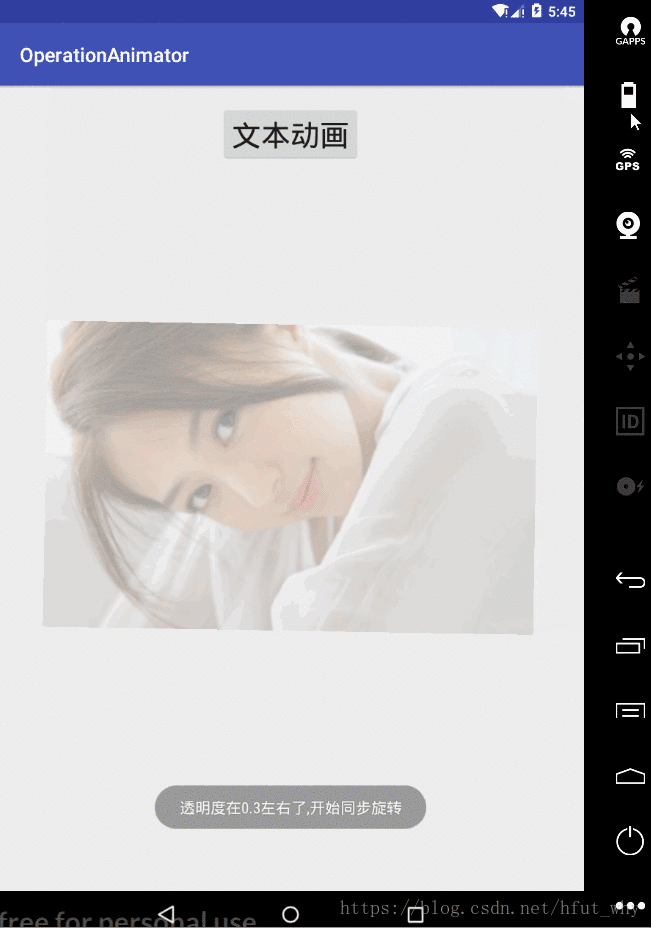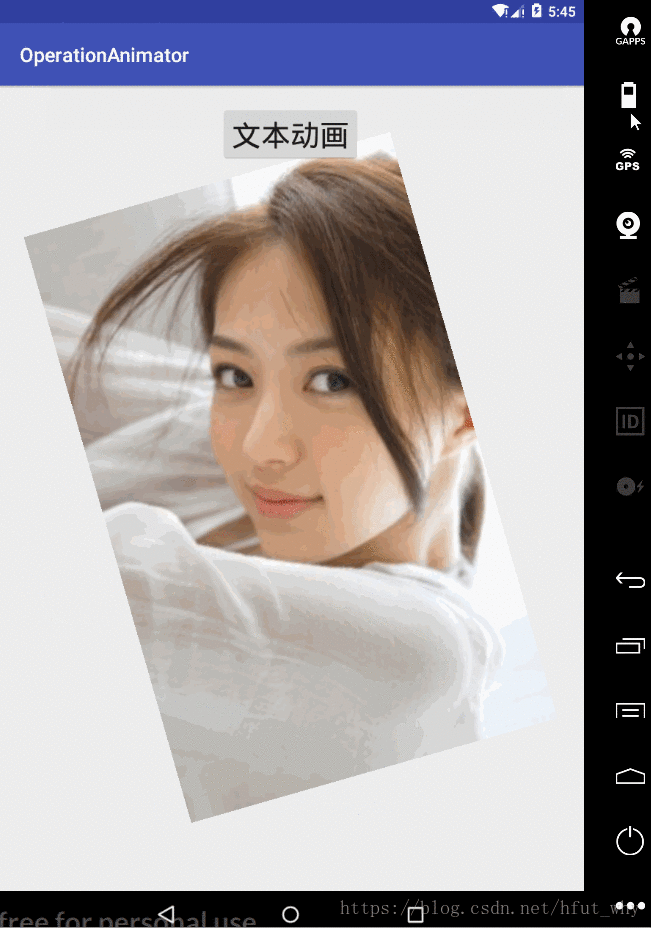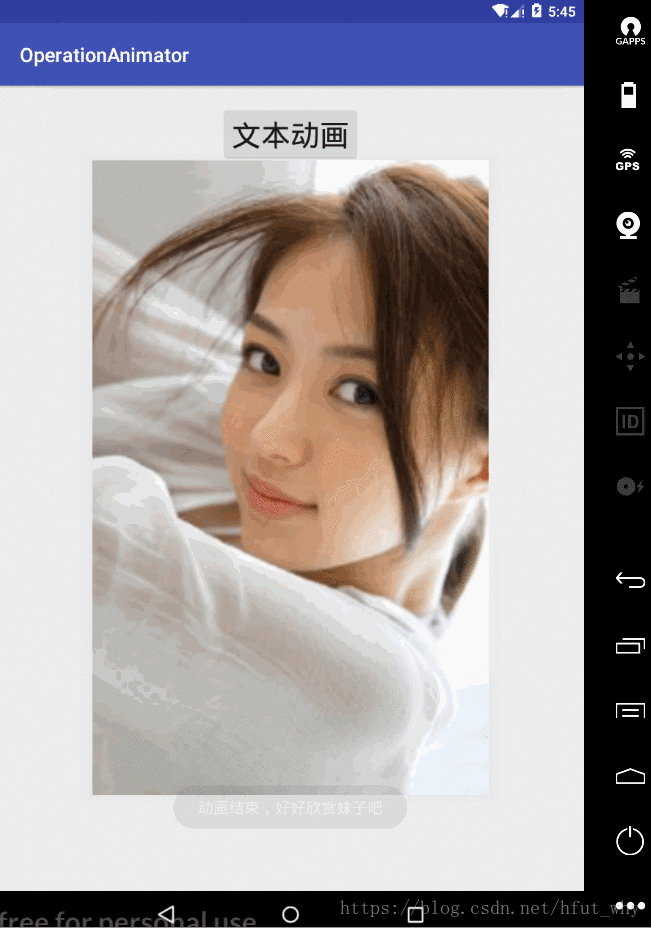
實現當一個View 的透明度在0.3的時候開啟同步旋轉放大動畫?下面就來看看具體實現
2.2 示例實現
效果圖如下:
activity_main.xml程式碼:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context="com.hfut.operationanimator.MainActivity">
<Button
android:id="@+id/control_text_button"
android:text="文字動畫"
android:onClick="textAnimator"
android:textSize="30sp"
android:layout_marginTop="20dp"
app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
<ImageView
android:layout_marginTop="150px"
android:id="@+id/test_image"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@id/control_text_button"
android:src="@mipmap/image"
app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent"
android:layout_width="500dp"
android:layout_height="420dp" />
</android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout>
Mainactivity程式碼:
package com.hfut.operationanimator;
import android.animation.Animator;
import android.animation.AnimatorInflater;
import android.animation.AnimatorListenerAdapter;
import android.animation.AnimatorSet;
import android.animation.ObjectAnimator;
import android.animation.ValueAnimator;
import android.os.Handler;
import android.os.Message;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.ImageView;
import android.widget.TextView;
import android.widget.Toast;
/**
* @author why
* @date 2018-9-6 20:55:46
*/
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private static final String TAG = "MainActivity";
ImageView imageView;
Handler handler=new Handler(){
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this,"透明度在0.3左右了,開始同步旋轉",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
//animator2.start();
ObjectAnimator animator1=(ObjectAnimator) ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(imageView,"scaleX",1,1.3f);
ObjectAnimator animator2=(ObjectAnimator) ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(imageView,"scaleY",1,1.3f);
ObjectAnimator animator3=(ObjectAnimator) ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(imageView,"rotation",0,90);
animator2.addListener(new AnimatorListenerAdapter() {
@Override
public void onAnimationCancel(Animator animation) {
super.onAnimationCancel(animation);
}
@Override
public void onAnimationStart(Animator animation) {
super.onAnimationStart(animation);
}
@Override
public void onAnimationEnd(Animator animation) {
super.onAnimationEnd(animation);
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this,"動畫結束,好好欣賞妹子吧",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
});
animator1.setDuration(5000);
animator2.setDuration(5000);
animator3.setDuration(5000);
AnimatorSet animatorSet=new AnimatorSet();
animatorSet.playTogether(animator1,animator2,animator3);
animatorSet.start();
}
};
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
imageView=findViewById(R.id.test_image);
imageView.setImageDrawable(getResources().getDrawable(R.mipmap.image));
}
public void textAnimator(View view){
//
// ObjectAnimator animator1= (ObjectAnimator) ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(imageView,"alpha",0,1);
// ObjectAnimator animator2= (ObjectAnimator) ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(imageView,"scaleX",1,0,1);
// ObjectAnimator animator3= (ObjectAnimator) ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(imageView,"scaleY",1,0,1);
// ObjectAnimator animator4= (ObjectAnimator) ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(imageView,"rotationX",0,180,0);
// ObjectAnimator animator5= (ObjectAnimator) ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(imageView,"rotationY",0,240,0);
// ObjectAnimator animator6= (ObjectAnimator) ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(imageView,"rotation",0,450);
// ObjectAnimator animator7= (ObjectAnimator) ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(imageView,"translationX",imageView.getX()-45,100);
// ObjectAnimator animator8= (ObjectAnimator) ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(imageView,"translationY",imageView.getY(),300);
//
// ObjectAnimator animator9= (ObjectAnimator) ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(imageView,"translationX",100,10);
// ObjectAnimator animator10= (ObjectAnimator) ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(imageView,"scaleX",1,1.2f);
// ObjectAnimator animator11= (ObjectAnimator) ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(imageView,"scaleY",1,1.2f);
// ObjectAnimator animator12= (ObjectAnimator) ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(imageView,"translationY",300,200);
//
//
// // ObjectAnimator animator9= (ObjectAnimator) AnimatorInflater.loadAnimator(this,R.animator.animator1);
//
// animator1.setDuration(1000);
// animator1.start();
//
// animator2.setDuration(1000);
// animator2.setStartDelay(300);
//
// animator3.setDuration(1000);
// animator3.setStartDelay(300);
//
// animator4.setDuration(1000);
// animator4.setStartDelay(300);
//
// animator5.setDuration(1000);
// animator5.setStartDelay(300);
//
// animator6.setDuration(1000);
// animator6.setStartDelay(300);
//
// animator7.setDuration(1000);
// animator7.setStartDelay(300);
//
// animator8.setDuration(1000);
// animator8.setStartDelay(300);
//
// animator9.setDuration(2000);
// animator9.setStartDelay(300);
// animator10.setDuration(2000);
// animator10.setStartDelay(300);
// animator11.setDuration(2000);
// animator11.setStartDelay(300);
// animator12.setDuration(2000);
// animator12.setStartDelay(300);
//
// AnimatorSet animatorSet1=new AnimatorSet();
// animatorSet1.playTogether(animator10,animator11,animator12);
// AnimatorSet set=new AnimatorSet();
//set.setDuration(2000);
//set.playSequentially(animator1,animator2,animator3,animator4,animator5,animator6,animator7,animator8,animator9,animatorSet1);
//set.playSequentially(animator1,animator2,animator3,animator4,animator5,animator6,animator7,animator8,animator9,animator10,animator11);
//set.start();
// WrapperView wrapperView=new WrapperView(imageView);
// ObjectAnimator objectAnimator10=ObjectAnimator.ofInt(wrapperView,"width",100);
ObjectAnimator animator3= (ObjectAnimator) ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(imageView,"alpha",0,1);
animator3.setDuration(8000);
animator3.start();
final ValueAnimator valueAnimator=ValueAnimator.ofFloat(0,1.0f);
// valueAnimator.setTarget(imageView);
valueAnimator.setDuration(8000);
valueAnimator.addUpdateListener(new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator animation) {
float processAlpha= (float) animation.getAnimatedValue();
Log.d(TAG, "onAnimationUpdate: "+processAlpha);
if(processAlpha>=0.29f&&processAlpha<=0.31f){
valueAnimator.cancel();
//Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this,"透明度在0.5左右了",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
Message message=new Message();
handler.sendMessage(message);
}
}
});
valueAnimator.start();
}
}
下面是日誌資訊:
可見,此API可以實時獲取動畫屬性值,可以幫助我們做更為精確的控制。
3, PropertyValuesHolder的基本使用
其功能和AnimatorSet中的playTogether()介面類似,用於定義一個View多個動畫同時播放,下面給出簡單的演示程式碼,效果示例就不完整寫了:
PropertyValuesHolder valuesHolder1=PropertyValuesHolder.ofFloat("scaleX",1,1.1f);
PropertyValuesHolder valuesHolder2=PropertyValuesHolder.ofFloat("scaleY",1,1.1f);
PropertyValuesHolder valuesHolder3=PropertyValuesHolder.ofFloat("alpha",0.5f,1.0f);
ObjectAnimator.ofPropertyValuesHolder(imageView,valuesHolder1,valuesHolder2,valuesHolder3).setDuration(3000).start();
4,xml實現屬性動畫
4.1 單個屬性動畫實現
這個在上面已經介紹過了
4.2 多個屬性動畫實現
說到這裡,我們就需要先看一下官方API了:
【
從api 23開始,可以使用PropertyValuesHolder和Keyframe在資原始檔中建立更復雜的動畫。使用PropertyValuesHolders允許Animator並行地動畫幾個屬性,如本示例所示:
<objectAnimator xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:duration="1000"
android:repeatCount="1"
android:repeatMode="reverse">
<propertyValuesHolder
android:propertyName="x"
android:valueTo="400" />
<propertyValuesHolder
android:propertyName="y"
android:valueTo="200" />
</objectAnimator>
使用關鍵幀允許動畫遵循更復雜的路徑從開始到結束值。請注意,您可以為每個關鍵幀指定顯式小數值(從0到1),以確定動畫在總體持續時間內何時應該達到該值。或者,您可以離開分數,關鍵幀將在整個持續時間內平均分佈。此外,當動畫器啟動時,沒有值的關鍵幀將從目標物件中派生出它的值,就像只指定一個值的動畫師一樣。此外,還可以指定一個可選的內插器。內插器將應用於內插器設定的關鍵幀與前一個關鍵幀之間的間隔上。如果沒有提供內插器,則預設AccelerateDecelerateInterpolator會被使用。
<propertyValuesHolder android:propertyName="x">
<keyframe
android:fraction="0"
android:value="800" />
<keyframe
android:fraction=".2"
android:interpolator="@android:anim/accelerate_interpolator"
android:value="1000" />
<keyframe
android:fraction="1"
android:interpolator="@android:anim/accelerate_interpolator"
android:value="400" />
</propertyValuesHolder> <propertyValuesHolder android:propertyName="y">
<keyframe />
<keyframe
android:fraction=".2"
android:interpolator="@android:anim/accelerate_interpolator"
android:value="300" />
<keyframe
android:interpolator="@android:anim/accelerate_interpolator"
android:value="1000" />
</propertyValuesHolder>
】
說白了,就是可以通過<objectAnimator>標籤下的<propertyValuesHolder>子標籤同時定義多個動畫作用於一個View,具體的應用和單個xml屬性動畫一樣。這裡就不在累述了。
5,View的animate方法
這個API也是伴隨屬性動畫產生而產生的,下面是其主要使用方法的關鍵程式碼:
imageView.animate().translationX(100).translationY(200)
.alpha(0.2f).rotation(90).setDuration(8000).withStartAction(
new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this,"動畫開始",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
).withEndAction(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this,"動畫結束",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}).start();
效果圖如下:
由結果可知:
- 這是一種動畫集合效果的簡易書寫方式
- 可以動畫集合結束和開始處做相應的邏輯操作
- 其實就是對動畫的API做了一些封裝
- 裡面的引數不是增量,是最終值,具體請看下面,我們拿translationX(float value)舉例,其原始碼為:
/**
* This method will cause the View's <code>translationX</code> property to be animated to the
* specified value. Animations already running on the property will be canceled.
*
* @param value The value to be animated to.
* @see View#setTranslationX(float)
* @return This object, allowing calls to methods in this class to be chained.
*/
public ViewPropertyAnimator translationX(float value) {
animateProperty(TRANSLATION_X, value);
return this;
}
關於引數的解釋:
@param value The value to be animated to. 所以這個是目標值,不是增量值。
總結:好的,到這裡,關於這一塊的內容就介紹完了,前前後後也寫了不少時間。整體的內容不難,多動手操作一下,會體會很多,這裡面我關於xml實現屬性動畫結束的比較少,但其實和介面實現一樣,就是屬性的組合而已。