C#系列 ----- 3 值引用和物件引用
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-11-01
值型別和引用型別(Value Types Versus Reference Types)
上一篇對於type的定義其實不準確,在此給出更準確的定義。
所有的C#型別包括:
- Value types
- Reference types
- Generic type parameters
- Pointer types
先看一下值型別和引用型別,其餘的之後再看
- 值型別: 內建的 all
numerictypes, thechartype, and thebooltype和自定義的struct和enum型別 - 引用型別:class, array, delegate, and interface types 和內建的string type
兩者的基本不同是在記憶體中的處理方式不同
-
Value types
值型別的變數或常量僅僅是一個值,比如內建整型int的變數僅僅是一個32位的資料public struct Point { public int X, Y; }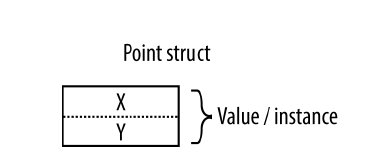
對於值型別而言,例項賦值直接深拷貝一份,即建立另一份記憶體
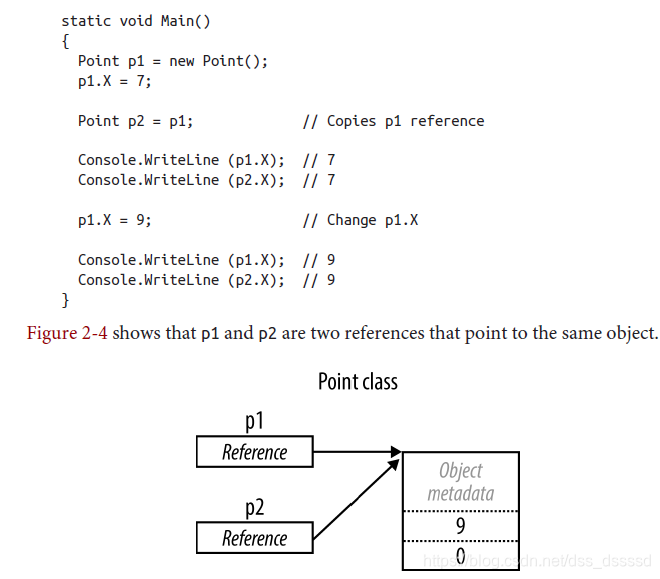
static void Main() { Point p1 = new Point(); p1.X = 7; Point p2 = p1; // Assignment causes copy Console.WriteLine (p1.X); // 7 Console.WriteLine (p2.X); // 7 p1.X = 9; // Change p1.X Console.WriteLine (p1.X); // 9 Console.WriteLine (p2.X); // 7 }
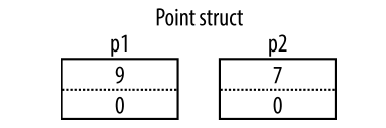
- 引用型別
引用型別包含兩部分: 物件和物件的引用。而引用型別的例項物件是包含值得物件的引用。簡單的就是一個指向記憶體的指標,指向的記憶體中包含值。和C++的指標一樣
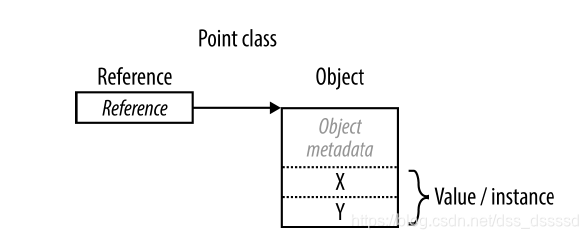
Null: 引用可以賦值為null, 表示沒有指向任何物件
class Point {...} ... Point p = null; Console.WriteLine (p == null); // True // The following line generates a runtime error // (a NullReferenceException is thrown): Console.WriteLine (p.X);
而值不可以賦值為null
struct Point {...}
...
Point p = null; // Compile-time error
int x = null; // Compile-time error
記憶體佔用(Storage overhead)
- 值型別例項精確地佔用了儲存欄位所需的記憶體
下面的Point佔用8個位元組
struct Point
{
int x; // 4 bytes
int y; // 4 bytes
}
而引用型別需要為物件和引用(指標)分配記憶體,需要的記憶體更大
-
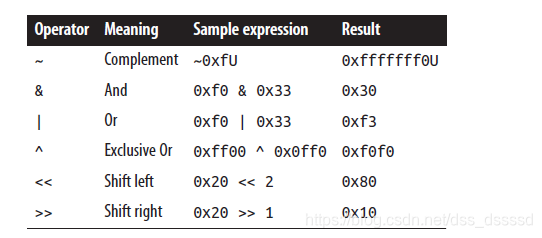
位操作符:
-
條件操作符
|| && != ==
res = q ?a : b => if q{ res= a} else{res=b}
