【Android】原始碼分析 - LRUCache快取實現原理
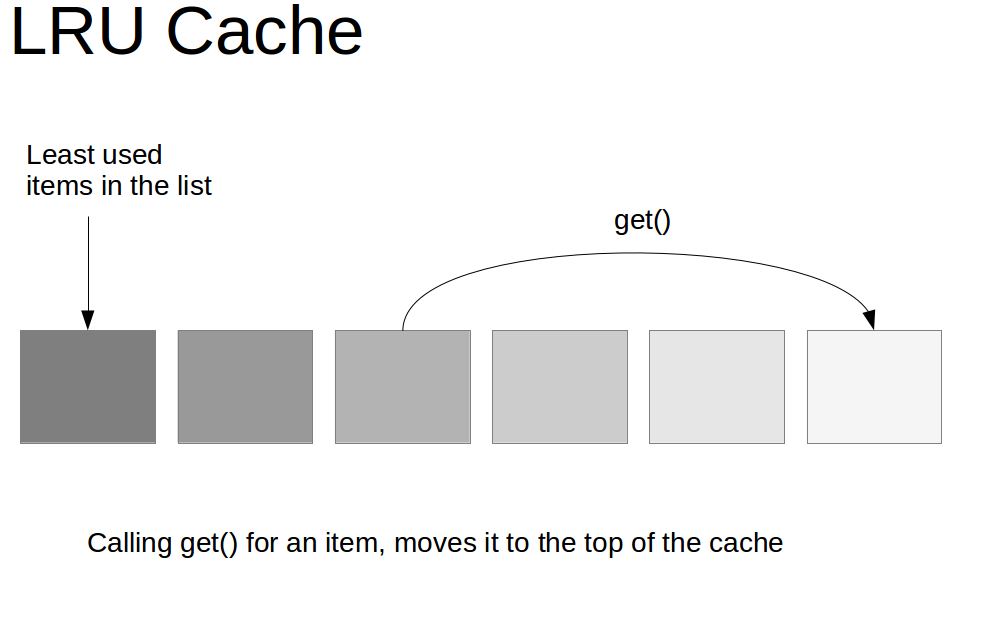
一、Android中的快取策略
一般來說,快取策略主要包含快取的新增、獲取和刪除這三類操作。如何新增和獲取快取這個比較好理解,那麼為什麼還要刪除快取呢?這是因為不管是記憶體快取還是硬碟快取,它們的快取大小都是有限的。當快取滿了之後,再想其新增快取,這個時候就需要刪除一些舊的快取並新增新的快取。
因此LRU(Least Recently Used)快取演算法便應運而生,LRU是近期最少使用的演算法,它的核心思想是當快取滿時,會優先淘汰那些近期最少使用的快取物件,有效的避免了OOM的出現。在Android中採用LRU演算法的常用快取有兩種:LruCache和DisLruCache,分別用於實現記憶體快取和硬碟快取,其核心思想都是LRU快取演算法。
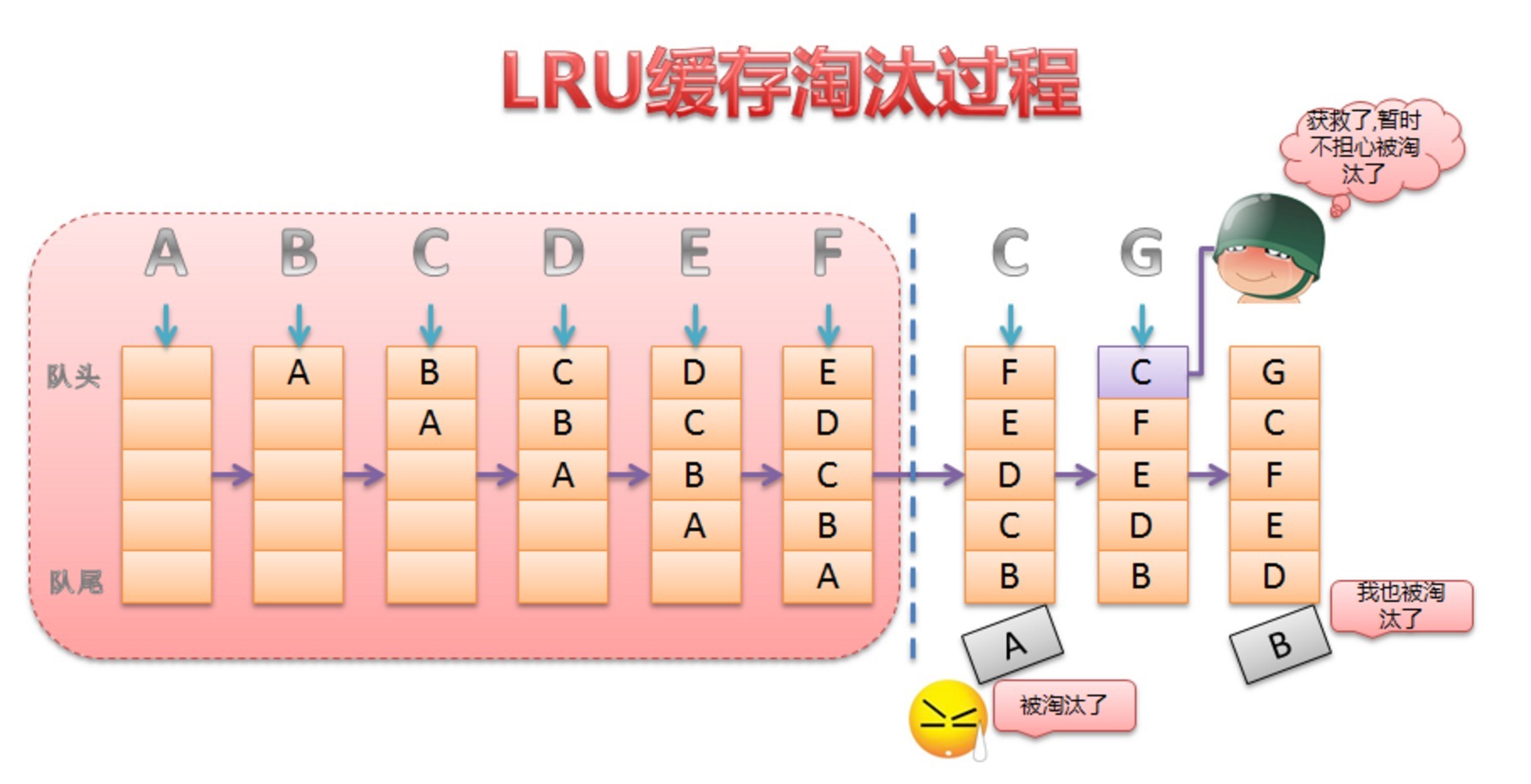
其實LRU快取的實現類似於一個特殊的棧,把訪問過的元素放置到棧頂(若棧中存在,則更新至棧頂;若棧中不存在則直接入棧),然後如果棧中元素數量超過限定值,則刪除棧底元素(即最近最少使用的元素)。詳細演算法實現如下圖:
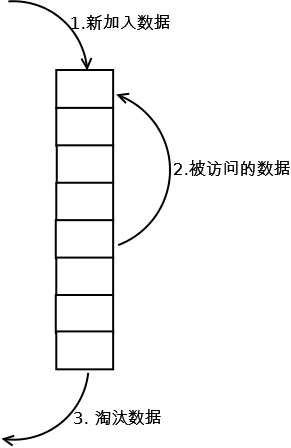
- 新資料壓入到棧頂;
- 每當快取命中(即快取資料被訪問),則將資料移到棧頂;
- 當棧滿的時候,將棧底的資料丟棄。
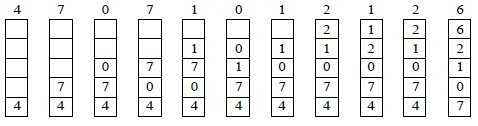
舉個例子演示一下:
二、LruCache的使用
LruCache是Android 3.1所提供的一個快取類,所以在Android中可以直接使用LruCache實現記憶體快取。而DisLruCache目前在Android 還不是Android SDK的一部分,但Android官方文件推薦使用該演算法來實現硬碟快取。
講到LruCache不得不提一下LinkedHashMap,因為LruCache中Lru演算法的實現就是通過LinkedHashMap來實現的。LinkedHashMap繼承於HashMap,它使用了一個雙向連結串列來儲存Map中的Entry順序關係,這種順序有兩種,一種是LRU順序,一種是插入順序,這可以由其建構函式public LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity,float loadFactor, boolean accessOrder)的最後一個引數accessOrder來指定。所以,對於get、put、remove等操作,LinkedHashMap
HashMap做的事情,還做些調整Entry順序連結串列的工作。LruCache中將LinkedHashMap的順序設定為LRU順序來實現LRU快取,每次呼叫get(也就是從記憶體快取中取圖片),則將該物件移到連結串列的尾端。呼叫put插入新的物件也是儲存在連結串列尾端,這樣當記憶體快取達到設定的最大值時,將連結串列頭部的物件(近期最少用到的)移除。關於LinkedHashMap詳解請前往:理解LinkedHashMap
LruCache使用示例
LruCache的使用非常簡單,我們就以圖片快取為例:
int maxMemory = (int) (Runtime.getRuntime().totalMemory()/1024);
int cacheSize = maxMemory/8;
mMemoryCache = new LruCache<String,Bitmap>(cacheSize){
@Override
protected int sizeOf(String key, Bitmap value) {
return value.getRowBytes()*value.getHeight()/1024;
}
};① 設定LruCache快取的大小,一般為當前程序可用容量的1/8。
② 重寫sizeOf方法,計算出要快取的每張圖片的大小。
注意:快取的總容量和每個快取物件的大小所用單位要一致。
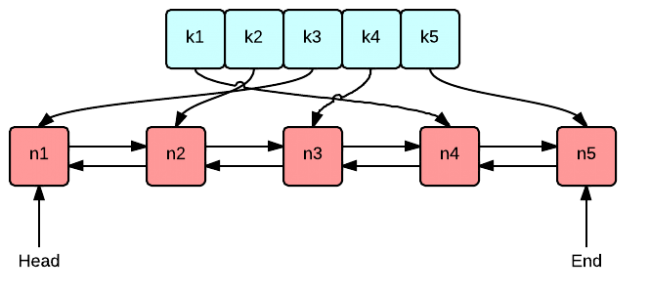
LruCache的實現原理
LruCache的核心思想很好理解,就是要維護一個快取物件列表,其中物件列表的排列方式是按照訪問順序實現的,即一直沒訪問的物件,將放在隊尾,即將被淘汰。而最近訪問的物件將放在隊頭,最後被淘汰。如下圖所示:
那麼這個佇列到底是由誰來維護的,前面已經介紹了是由LinkedHashMap來維護。
而LinkedHashMap是由陣列+雙向連結串列的資料結構來實現的。其中雙向連結串列的結構可以實現訪問順序和插入順序,使得LinkedHashMap中的
/**
* Constructs a new {@code LinkedHashMap} instance with the specified
* capacity, load factor and a flag specifying the ordering behavior.
*
* @param initialCapacity
* the initial capacity of this hash map.
* @param loadFactor
* the initial load factor.
* @param accessOrder
* {@code true} if the ordering should be done based on the last
* access (from least-recently accessed to most-recently
* accessed), and {@code false} if the ordering should be the
* order in which the entries were inserted.
*/
public LinkedHashMap(
int initialCapacity, float loadFactor, boolean accessOrder) {
super(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
init();
this.accessOrder = accessOrder;
}其中accessOrder設定為true則為訪問順序,為false,則為插入順序。
以具體例子解釋,當設定為true時:
public static final void main(String[] args) {
LinkedHashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new LinkedHashMap<>(0, 0.75f, true);
map.put(0, 0);
map.put(1, 1);
map.put(2, 2);
map.put(3, 3);
map.put(4, 4);
map.put(5, 5);
map.put(6, 6);
map.get(1); //訪問1
map.get(2); //訪問2
for (Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry : map.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey() + ":" + entry.getValue());
}
}輸出結果如下:
0:0
3:3
4:4
5:5
6:6
1:1
2:2
即最近訪問的物件會被放到隊尾,然後最後輸出,那麼這就正好滿足的LRU快取演算法的思想。可見LruCache巧妙實現,就是利用了LinkedHashMap的這種資料結構。
下面我們在LruCache原始碼中具體看看,怎麼應用LinkedHashMap來實現快取的新增,獲得和刪除的。
LruCache原始碼分析
我們先看看成員變數有哪些:
public class LruCache<K, V> {
private final LinkedHashMap<K, V> map;
/** Size of this cache in units. Not necessarily the number of elements. */
private int size; //當前cache的大小
private int maxSize; //cache最大大小
private int putCount; //put的次數
private int createCount; //create的次數
private int evictionCount; //驅逐剔除的次數
private int hitCount; //命中的次數
private int missCount; //未命中次數
//...省略...
}建構函式如下,可以看到LruCache正是用了LinkedHashMap的accessOrder=true構造引數實現LRU訪問順序:
public LruCache(int maxSize) {
if (maxSize <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("maxSize <= 0");
}
this.maxSize = maxSize;
//將LinkedHashMap的accessOrder設定為true來實現LRU順序
this.map = new LinkedHashMap<K, V>(0, 0.75f, true);
}put方法
public final V put(K key, V value) {
//不可為空,否則丟擲異常
if (key == null || value == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("key == null || value == null");
}
V previous; //舊值
synchronized (this) {
putCount++; //插入次數加1
size += safeSizeOf(key, value); //更新快取的大小
previous = map.put(key, value);
//如果已有快取物件,則快取大小的值需要剔除這個舊的大小
if (previous != null) {
size -= safeSizeOf(key, previous);
}
}
//entryRemoved()是個空方法,可以自行實現
if (previous != null) {
entryRemoved(false, key, previous, value);
}
//調整快取大小(關鍵方法)
trimToSize(maxSize);
return previous;
}可以看到put()方法並沒有什麼難點,重要的就是在新增過快取物件後,呼叫trimToSize()方法,來判斷快取是否已滿,如果滿了就要刪除近期最少使用的演算法。
trimToSize方法
public void trimToSize(int maxSize) {
while (true) {
K key;
V value;
synchronized (this) {
//如果map為空並且快取size不等於0或者快取size小於0,丟擲異常
if (size < 0 || (map.isEmpty() && size != 0)) {
throw new IllegalStateException(getClass().getName()
+ ".sizeOf() is reporting inconsistent results!");
}
//如果快取大小size小於最大快取,或者map為空,則不需要再刪除快取物件,跳出迴圈
if (size <= maxSize || map.isEmpty()) {
break;
}
//迭代器獲取第一個物件,即隊頭的元素,近期最少訪問的元素
Map.Entry<K, V> toEvict = map.entrySet().iterator().next();
key = toEvict.getKey();
value = toEvict.getValue();
//刪除該物件,並更新快取大小
map.remove(key);
size -= safeSizeOf(key, value);
evictionCount++;
}
entryRemoved(true, key, value, null);
}
}trimToSize()方法不斷地刪除LinkedHashMap中隊頭的元素,即近期最少訪問的,直到快取大小小於最大值。
當呼叫LruCache的get()方法獲取集合中的快取物件時,就代表訪問了一次該元素,將會更新佇列,保持整個佇列是按照訪問順序排序。這個更新過程就是在LinkedHashMap中的get()方法中完成的。
我們先看LruCache的get()方法。
get方法
//LruCache的get()方法
public final V get(K key) {
if (key == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("key == null");
}
V mapValue;
synchronized (this) {
//獲取對應的快取物件
//LinkedHashMap的get()方法會實現將訪問的元素更新到佇列尾部的功能
mapValue = map.get(key);
//mapValue不為空表示命中,hitCount+1並返回mapValue物件
if (mapValue != null) {
hitCount++;
return mapValue;
}
missCount++; //未命中
}
/*
* Attempt to create a value. This may take a long time, and the map
* may be different when create() returns. If a conflicting value was
* added to the map while create() was working, we leave that value in
* the map and release the created value.
* 如果未命中,則試圖建立一個物件,這裡create方法預設返回null,並沒有實現建立物件的方法。
* 如果需要事項建立物件的方法可以重寫create方法。因為圖片快取時記憶體快取沒有命中會去
* 檔案快取中去取或者從網路下載,所以並不需要建立,下面的就不用看了。
*/
V createdValue = create(key);
if (createdValue == null) {
return null;
}
//假如建立了新的物件,則繼續往下執行
synchronized (this) {
createCount++;
//將createdValue加入到map中,並且將原來鍵為key的物件儲存到mapValue
mapValue = map.put(key, createdValue);
if (mapValue != null) {
// There was a conflict so undo that last put
//如果mapValue不為空,則撤銷上一步的put操作。
map.put(key, mapValue);
} else {
//加入新建立的物件之後需要重新計算size大小
size += safeSizeOf(key, createdValue);
}
}
if (mapValue != null) {
entryRemoved(false, key, createdValue, mapValue);
return mapValue;
} else {
//每次新加入物件都需要呼叫trimToSize方法看是否需要回收
trimToSize(maxSize);
return createdValue;
}
}其中LinkedHashMap的get()方法如下:
//LinkedHashMap中的get方法
public V get(Object key) {
Node<K,V> e;
if ((e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null)
return null;
//實現排序的關鍵方法
if (accessOrder)
afterNodeAccess(e);
return e.value;
}呼叫的afterNodeAccess()方法將該元素移到隊尾,保證最後才刪除,如下:
void afterNodeAccess(Node<K,V> e) { // move node to last
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> last;
if (accessOrder && (last = tail) != e) {
LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> p =
(LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V>)e, b = p.before, a = p.after;
p.after = null;
if (b == null)
head = a;
else
b.after = a;
if (a != null)
a.before = b;
else
last = b;
if (last == null)
head = p;
else {
p.before = last;
last.after = p;
}
//當前節點p移動到尾部之後,尾部指標指向當前節點
tail = p;
++modCount;
}
}由此可見LruCache中維護了一個集合LinkedHashMap,該LinkedHashMap是以訪問順序排序的。當呼叫put()方法時,就會在結合中新增元素,並呼叫trimToSize()判斷快取是否已滿,如果滿了就用LinkedHashMap的迭代器刪除隊頭元素,即近期最少訪問的元素。當呼叫get()方法訪問快取物件時,就會呼叫LinkedHashMap的get()方法獲得對應集合元素,同時會更新該元素到隊尾。
以上便是LruCache實現的原理,理解了LinkedHashMap的資料結構就能理解整個原理。如果不懂,可以先看看LinkedHashMap的具體實現。
