Android實現BMP和PNG轉換為JPEG格式
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-11-03
專案需求,需要把BMP24位的圖片轉換成jpeg的格式,在網上查詢了一些不同格式圖片的基本知識,加以總結,實現了一個簡單的Demo程式,先貼程式碼,然後再進行理解
picSwitcher.java檔案:
package com.example.bmptojpeg;
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.File;
import android.graphics.Bitmap;
import 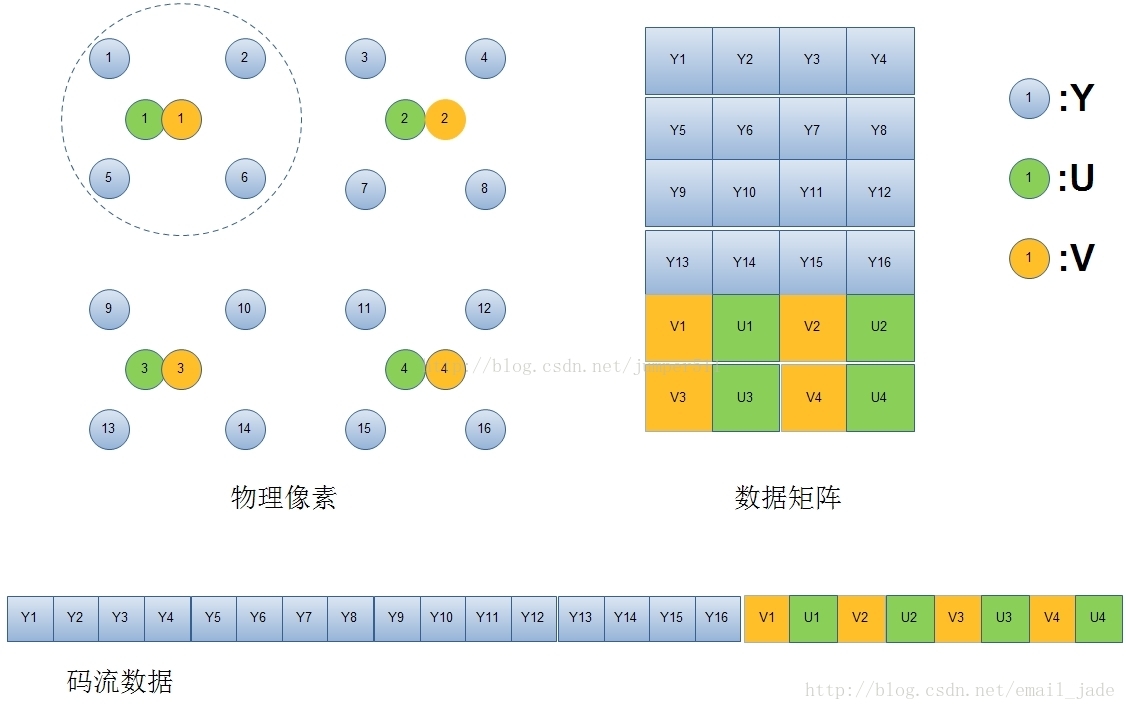
ImageFormat.NV21的YUV分量儲存格式如上圖,對應encodeYUV420SP的演算法
測試部分,比較簡單
MainActivity.java檔案:
package com.example.bmptojpeg;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private picSwitcher bs;
private String src = "/data/local/logo.bmp";
private String dst = "/data/local/boot0.jpg";
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
bs = new picSwitcher(src);
bs.init();
if(bs.mFileType == bs.BMP_TYPE){
bs.toJpeg(dst);
}else if(bs.mFileType == bs.PNG_TYPE){
bs.toJpeg(dst);
}else if(bs.mFileType == bs.JPEG_TYPE){
Log.i("picSwitcher", "type is jpeg, doNothing");
}
}
}
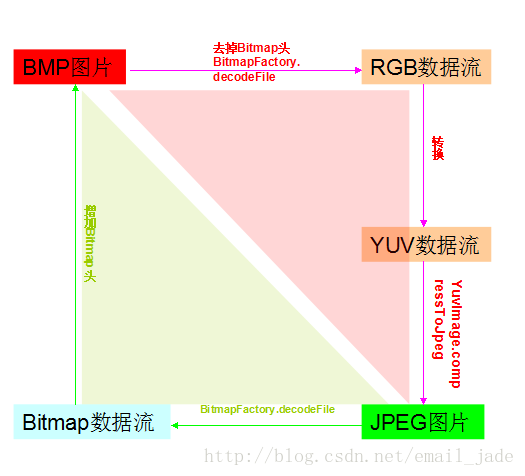
程式碼的大概流程如下圖,不過只做了從BMP轉換到JPEG格式的部分(紅色部分)
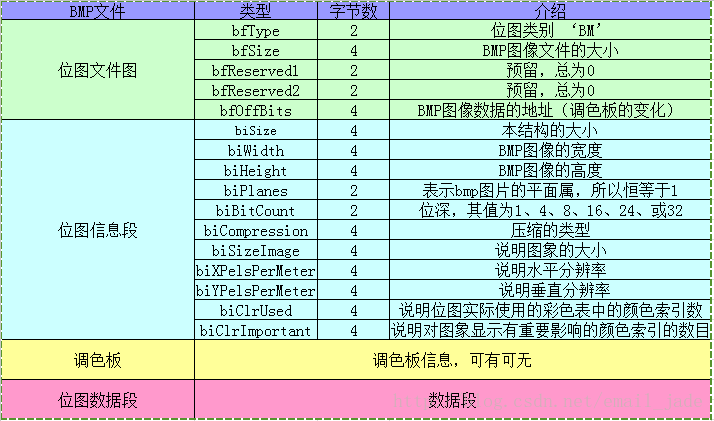
要理解這部分的流程,必須要知道bmp的檔案格式:
隨意找了一個720P(1920*1080)bmp的檔案開啟後如下
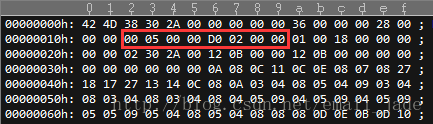
紅色部分代表的是圖片的寬和高
重要說一下程式碼裡面用到的部分:
0-1位:bmp格式的圖片為‘BM’,可作為改格式的判斷根據
18-21位表示圖片的寬width
22-25位表示圖片的高height
程式碼裡還涉及到png轉jpeg的部分,做簡單介紹,720P(1920*1080)png的檔案開啟後如下
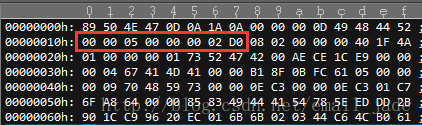
紅色部分代表的是圖片的寬和高
將PNG和BMP的圖片寬高資料比較會發現,資料儲存的模式不一樣,BMP為小端模式儲存,而PNG為大端模式儲存,所以在讀取寬高資料的時候要做相應的轉換
剩餘知識可以根據程式碼來理解,參考雷神部落格基礎篇
http://blog.csdn.net/leixiaohua1020/article/details/50534150
下面簡單寫下其他格式轉換成BMP的思路:
//通過BitmapFactory.decodeFile(path)得到Bitmap資料
Bitmap bitmap=BitmapFactory.decodeFile(path);
//然後根據以上的BMP頭訊息來填充
public void saveBmp(Bitmap bitmap ,String filename) {
if (bitmap == null)
return;
// 點陣圖大小
int nBmpWidth = bitmap.getWidth();
int nBmpHeight = bitmap.getHeight();
// 影象資料大小
int bufferSize = nBmpHeight * (nBmpWidth * 3 + nBmpWidth % 4);
try {
File file = new File(filename);
Log.w(TAG,"------File : " +filename );
if (!file.exists()) {
Log.w(TAG,"- not exist-----File : " +filename );
file.createNewFile();
}
else{
file.delete();
}
FileOutputStream fileos = new FileOutputStream(filename);
// bmp檔案頭
int bfType = 0x4d42;
long bfSize = 14 + 40 + bufferSize;
int bfReserved1 = 0;
int bfReserved2 = 0;
long bfOffBits = 14 + 40;
// 儲存bmp檔案頭
writeWord(fileos, bfType);
writeDword(fileos, bfSize);
writeWord(fileos, bfReserved1);
writeWord(fileos, bfReserved2);
writeDword(fileos, bfOffBits);
// bmp資訊頭
long biSize = 40L;
long biWidth = nBmpWidth;
long biHeight = nBmpHeight;
int biPlanes = 1;
int biBitCount = 24;
long biCompression = 0L;
long biSizeImage = 0L;
long biXpelsPerMeter = 0L;
long biYPelsPerMeter = 0L;
long biClrUsed = 0L;
long biClrImportant = 0L;
// 儲存bmp資訊頭
writeDword(fileos, biSize);
writeLong(fileos, biWidth);
writeLong(fileos, biHeight);
writeWord(fileos, biPlanes);
writeWord(fileos, biBitCount);
writeDword(fileos, biCompression);
writeDword(fileos, biSizeImage);
writeLong(fileos, biXpelsPerMeter);
writeLong(fileos, biYPelsPerMeter);
writeDword(fileos, biClrUsed);
writeDword(fileos, biClrImportant);
// 畫素掃描
byte bmpData[] = new byte[bufferSize];
int wWidth = (nBmpWidth * 3 + nBmpWidth % 4);
for (int nCol = 0, nRealCol = nBmpHeight - 1; nCol < nBmpHeight; ++nCol, --nRealCol)
for (int wRow = 0, wByteIdex = 0; wRow < nBmpWidth; wRow++, wByteIdex += 3) {
int clr = bitmap.getPixel(wRow, nCol);
bmpData[nRealCol * wWidth + wByteIdex] = (byte) Color.blue(clr);
bmpData[nRealCol * wWidth + wByteIdex + 1] = (byte) Color.green(clr);
bmpData[nRealCol * wWidth + wByteIdex + 2] = (byte) Color.red(clr);
}
fileos.write(bmpData);
fileos.flush();
fileos.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//其中writeDword等代表按小端序的模式寫入對應的資料位元組數,給一個簡單的例子
public static void writeLong(FileOutputStream stream, long value) throws IOException {
byte[] b = new byte[4];
b[0] = (byte) (value & 0xff);
b[1] = (byte) (value >> 8 & 0xff);
b[2] = (byte) (value >> 16 & 0xff);
b[3] = (byte) (value >> 24 & 0xff);
stream.write(b);
}以後有空再繼續研究,完善!