PAT-ADVANCED1013——Battle Over Cities
我的PAT-ADVANCED程式碼倉:https://github.com/617076674/PAT-ADVANCED
原題連結:https://pintia.cn/problem-sets/994805342720868352/problems/994805500414115840
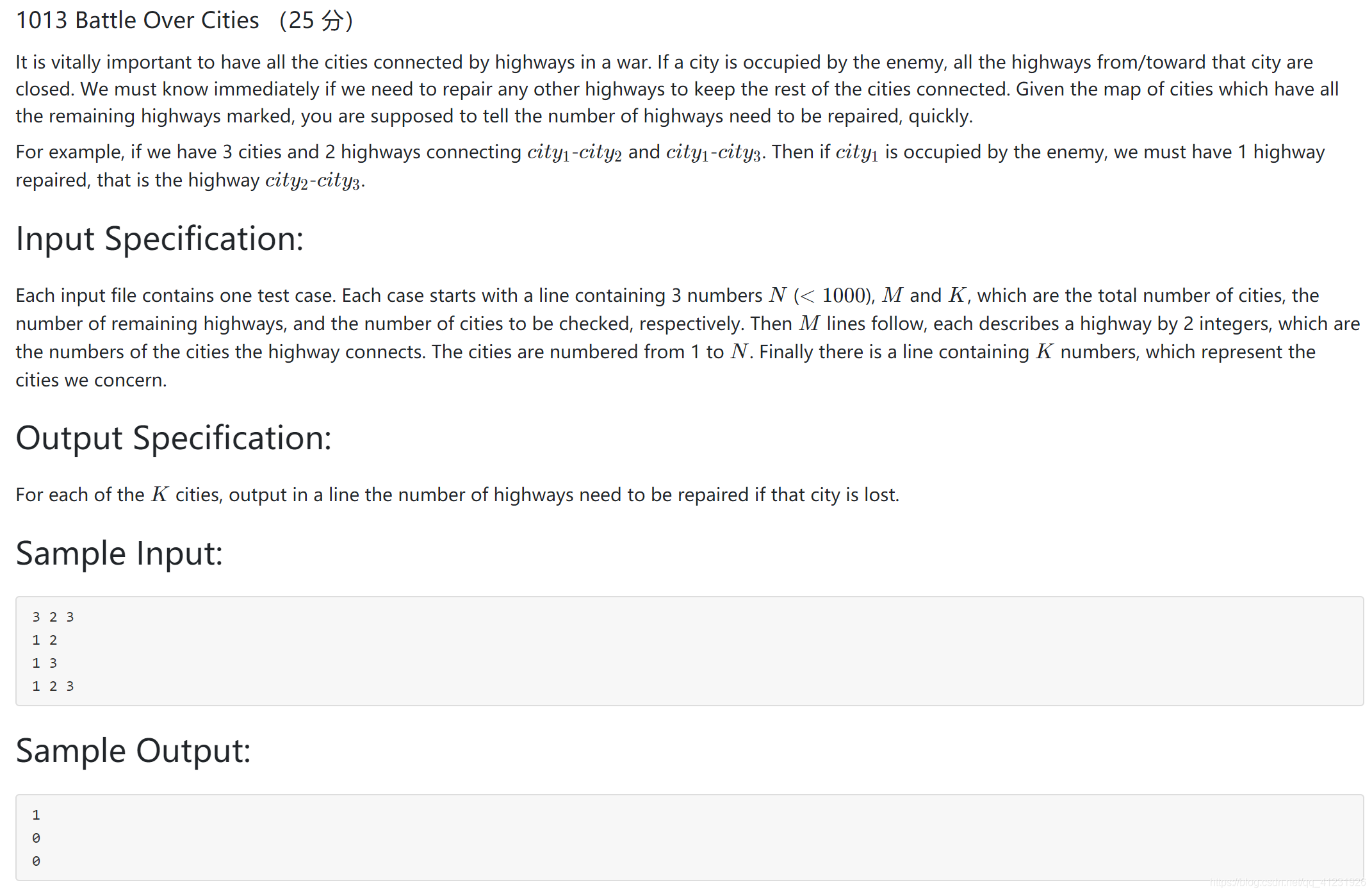
題目描述:
題目翻譯:
1013 城市之間的戰爭
在戰爭中,所有的城市都通過高速公路連線在一起,這一點是至關重要的。如果一個城市被敵人佔領了,那麼所有連線這個城市的高速公路都會被封閉。我們必須馬上知道為了使得餘下的城市保持連線狀態,我們是否需要修建其他的高速公路。給你一張城市地圖,上面標識出了所有餘下的高速公路,你需要快速說出需要修建的高速公路的數量。
舉個例子,如果我們有3座城市,2條高速公路分別連線city1-city2、city1-city3。如果city1被敵人佔領了,我們就需要修建一條高速公路,那就是city2-city3。
輸入格式:
每個輸入檔案包含一個測試用例。對每個測試用例,第一行包含3個數字:N(<= 1000)表示城市總數量,M表示高速公路數量,K表示需要檢查的城市數量。接下來的M行,每行用2個整數描述一條高速公路,這2個整數分別代表這條高速公路所連線的兩個城市的編號。城市編號從1到N。最後一行有K個數字,代表了我們關注的城市。
輸出格式:
對K個城市中的每一個城市,分別在1行中輸出如果該城市被敵人佔領所需要修建的高速公路的數量。
輸入樣例:
3 2 3
1 2
1 3
1 2 3輸出樣例:
1
0
0知識點:圖的深度優先遍歷、並查集
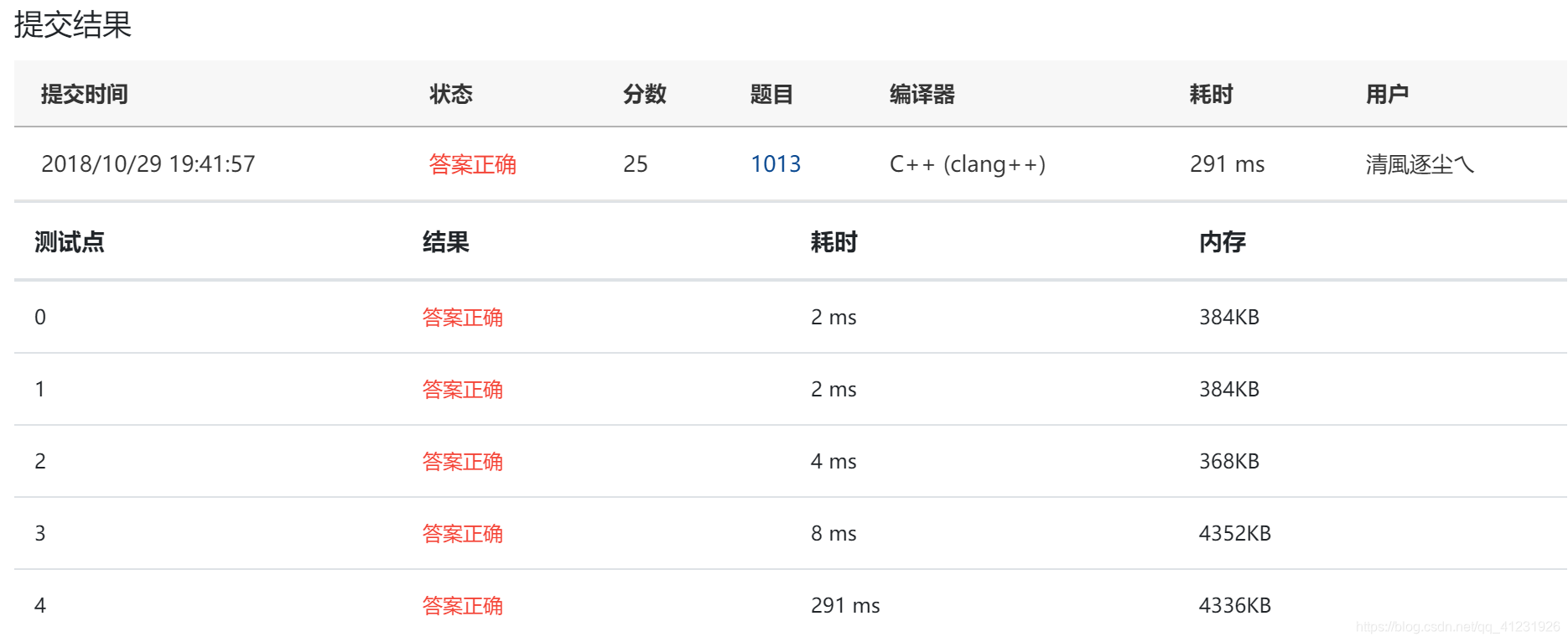
思路一:圖的深度優先遍歷(鄰接矩陣實現)
本題的實質是求除去某個點之外,圖中有幾個連通塊。用圖的深度優先遍歷演算法即可。
時間複雜度是O(K * N)。空間複雜度是O(N ^ 2)。
注意點:
城市編號是1 ~ N,而不是0 ~ N - 1。
C++程式碼:
#include<iostream> #include<vector> using namespace std; int n; //城市數量 int m; //高速公路數量 int k; //需要檢查的城市數量 int graph[1001][1001] = {0}; //無向圖 bool visited[1001]; void dfs(int nowVisit, int city); int main(){ cin >> n >> m >> k; int city1, city2; for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){ cin >> city1 >> city2; graph[city1 - 1][city2 - 1] = 1; graph[city2 - 1][city1 - 1] = 1; } int city; for(int i = 0; i < k; i++){ cin >> city; int count = 0; for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){ visited[j] = false; } for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){ if(j == city - 1){ continue; } if(!visited[j]){ dfs(j, city); count++; } } cout << count - 1 << endl; } } void dfs(int nowVisit, int city){ visited[nowVisit] = true; for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){ if(i != city - 1 && !visited[i] && graph[i][nowVisit] != 0){ dfs(i, city); } } }
C++解題報告:
思路二:並查集(鄰接表實現)
時間複雜度是O(kN)。空間複雜度是O(N + M)。
注意為並查集新增路徑壓縮操作。
C++程式碼:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int n; //城市數量
int m; //高速公路數量
int k; //需要檢查的城市數量
vector<int> graph[1001]; //無向圖
int father[1001]; //並查集陣列
bool visited[1001]; //標記陣列
int findFather(int x);
bool isConnected(int x, int y);
void unionTwo(int x, int y);
void init();
int main(){
cin >> n >> m >> k;
int city1, city2;
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){
cin >> city1 >> city2;
graph[city1 - 1].push_back(city2 - 1);
graph[city2 - 1].push_back(city1 - 1);
}
int city;
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++){
cin >> city;
init();
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){
for(int l = 0; l < graph[j].size(); l++){
int u = j, v = graph[j][l];
if(u == city - 1 || v == city - 1){
continue;
}
unionTwo(u, v);
}
}
int count = 0;
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){
if(j == city - 1){
continue;
}
int jFather = findFather(j);
if(!visited[jFather]){
count++;
visited[jFather] = true;
}
}
cout << count - 1 << endl;
}
return 0;
}
int findFather(int x){
int a = x;
while(x != father[x]){
x = father[x];
}
while(a != father[a]){ //路徑壓縮
int z = a;
a = father[a];
father[z] = x;
}
return x;
}
bool isConnected(int x, int y){
int xFather = findFather(x);
int yFather = findFather(y);
if(xFather != yFather){
return false;
}
return true;
}
void unionTwo(int x, int y){
if(!isConnected(x, y)){
father[father[x]] = father[y];
}
}
void init(){
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
father[i] = i;
visited[i] = false;
}
}C++解題報告:

思路三:圖的廣度優先遍歷(鄰接矩陣實現)(測試點4會超時)
本題的實質是求除去某個點之外,圖中有幾個連通塊。用圖的廣度優先遍歷演算法也可以實現。
時間複雜度是O(K * N)。空間複雜度是O(N ^ 2)。
C++程式碼:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
int n; //城市數量
int m; //高速公路數量
int k; //需要檢查的城市數量
int graph[1001][1001] = {0}; //無向圖
bool inq[1001];
void bfs(int nowVisit, int city);
int main() {
cin >> n >> m >> k;
int city1, city2;
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
cin >> city1 >> city2;
graph[city1 - 1][city2 - 1] = 1;
graph[city2 - 1][city1 - 1] = 1;
}
int city;
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
cin >> city;
int count = 0;
fill(inq, inq + 1001, false);
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if(j == city - 1) {
continue;
}
if(!inq[j]) {
bfs(j, city);
count++;
}
}
cout << count - 1 << endl;
}
}
void bfs(int nowVisit, int city) {
queue<int> q;
q.push(nowVisit);
while(!q.empty()) {
int now = q.front();
inq[now] = true;
q.pop();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if(i != city - 1 && !inq[i] && graph[i][now] != 0) {
q.push(i);
}
}
}
}C++解題報告:

