hdu 1325Is It A Tree?(並查集判斷有向樹)
Problem Description
A tree is a well-known data structure that is either empty (null, void, nothing) or is a set of one or more nodes connected by directed edges between nodes satisfying the following properties.
There is exactly one node, called the root, to which no directed edges point.
Every node except the root has exactly one edge pointing to it.
There is a unique sequence of directed edges from the root to each node.
For example, consider the illustrations below, in which nodes are represented by circles and edges are represented by lines with arrowheads. The first two of these are trees, but the last is not.
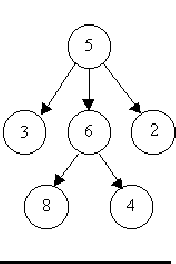
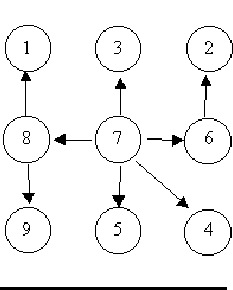
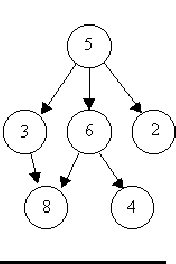
In this problem you will be given several descriptions of collections of nodes connected by directed edges. For each of these you are to determine if the collection satisfies the definition of a tree or not.
Input
The input will consist of a sequence of descriptions (test cases) followed by a pair of negative integers. Each test case will consist of a sequence of edge descriptions followed by a pair of zeroes Each edge description will consist of a pair of integers; the first integer identifies the node from which the edge begins, and the second integer identifies the node to which the edge is directed. Node numbers will always be greater than zero.
Output
For each test case display the line ``Case k is a tree." or the line ``Case k is not a tree.", where k corresponds to the test case number (they are sequentially numbered starting with 1).
Sample Input
6 8 5 3 5 2 6 4 5 6 0 0 8 1 7 3 6 2 8 9 7 5 7 4 7 8 7 6 0 0 3 8 6 8 6 4 5 3 5 6 5 2 0 0 -1 -1
Sample Output
Case 1 is a tree. Case 2 is a tree. Case 3 is not a tree.
Source
North Central North America 1997
Recommend
Ignatius.L | Wehave carefully selected several similar problems for you: 1856 1233 1102 1875 1863
和hdu1272相似,我照著改了一個小時wa了無數遍才過,注意這裡是有向圖,而且不是兩個-1,是兩個負數
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define maxn 105
int father[maxn];
int vis[maxn];
void init()
{
for(int i=0;i<=maxn;i++)
{
father[i]=i;
vis[i]=0;
}
}
int find(int x)
{
if(x!=father[x])
father[x]=find(father[x]);
return father[x];
}
void unionn(int x,int y,int &flag)
{
int fx=find(x);
int fy=find(y);
if(fx!=fy&&fy==y)
father[fy]=fx;
else flag=0;
}
int main()
{
int x,y,a,b;
int w=0;
while(~scanf("%d%d",&x,&y))
{
if(x<0&&y<0)
break;
w++;
if(x==0&&y==0)
{printf("Case %d is a tree.\n",w);
continue;}
init();
int flag=1;
while(x!=0&&y!=0)
{
vis[x]=1;
vis[y]=1;
unionn(x,y,flag);
scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
}
int ans=0;
for(int i=1;i<maxn;i++)
{
if(vis[i]&&father[i]==i)
ans++;
if(ans>1)
{
flag=0;
break;
}
}
if(flag)
printf("Case %d is a tree.\n",w);
else
printf("Case %d is not a tree.\n",w);
}
return 0;
}
