Mybatis事務管理
一、Mybatis事務概述
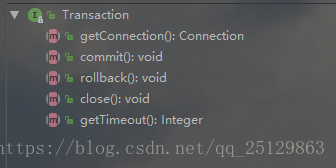
對於資料庫事務而言,一般包括以下幾個操作:建立、提交、回滾、關閉。MyBatis把這些抽象為Transaction介面: 介面定義如下:
介面定義了Connection連線、提交、回滾、關閉等功能。
Mybatis事務管理分為兩種方式:
1、使用JDBC的事務管理機制:利用java.sql.Connection物件完成對事務的提交、回滾、關閉。
2、使用MANAGED的事務管理機制:這種方式Mybatis自身不會去實現事務管理,而是交給容器(Tomcat、JBOSS)去管理。
二、Mybatis事務使用
1、 事務配置:
我們在用Mybatis時,一般會用如下配置檔案:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd"> <configuration> <environments default="development"> <environment id="development"> <transactionManager type="JDBC"/> <dataSource type="POOLED"> <property name="driver" value="${driver}"/> <property name="url" value="${url}"/> <property name="username" value="${username}"/> <property name="password" value="${password}"/> </dataSource> </environment> </environments> <mappers> <mapper resource="org/mybatis/example/BlogMapper.xml"/> </mappers> </configuration>
其子節點<transactionManager> 的type 會決定我們用什麼型別的事務管理機制。
2、事務工廠的建立:
Mybatis的事務是交給TransactionFactory來建立,如果我們將<transactionManager>的type 配置為"JDBC",那麼,在Mybatis初始化解析<environment>節點時,XMLConfigBuilder會根據type="JDBC"建立一個JdbcTransactionFactory工廠,其原始碼如下:
private TransactionFactory transactionManagerElement(XNode context) throws Exception {
if (context != null) {
String type = context.getStringAttribute("type");
Properties props = context.getChildrenAsProperties();
TransactionFactory factory = (TransactionFactory) resolveClass(type).newInstance();
factory.setProperties(props);
return factory;
}
throw new BuilderException("Environment declaration requires a TransactionFactory.");
}如果type = "JDBC",則Mybatis會建立一個JdbcTransactionFactory ;如果type="MANAGED",則Mybatis會建立一個MangedTransactionFactory。
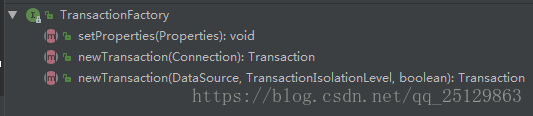
TransactionFactory介面:
建立Transaction有兩個方法:一是通過Connection物件建立,另一個是通過資料來源DataSource來建立。
看下JdbcTransactionFactory 建立過程,如下:
public class JdbcTransactionFactory implements TransactionFactory {
public void setProperties(Properties props) {
}
//根據給定的資料庫連線Connection建立Transaction
public Transaction newTransaction(Connection conn) {
return new JdbcTransaction(conn);
}
// 根據DataSource、隔離級別和是否自動提交建立Transacion
public Transaction newTransaction(DataSource ds, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
return new JdbcTransaction(ds, level, autoCommit);
}
}
3、事物管理的實現
我們以 JdbcTransaction為例看下事務怎麼實現的,如下:
public class JdbcTransaction implements Transaction {
private static final Log log = LogFactory.getLog(JdbcTransaction.class);
//資料庫連線
protected Connection connection;
//資料來源
protected DataSource dataSource;
//隔離級別
protected TransactionIsolationLevel level;
//是否為自動提交
protected boolean autoCommmit;
public JdbcTransaction(DataSource ds, TransactionIsolationLevel desiredLevel, boolean desiredAutoCommit) {
dataSource = ds;
level = desiredLevel;
autoCommmit = desiredAutoCommit;
}
public JdbcTransaction(Connection connection) {
this.connection = connection;
}
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
if (connection == null) {
openConnection();
}
return connection;
}
// 使用connection的commit()
public void commit() throws SQLException {
if (connection != null && !connection.getAutoCommit()) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Committing JDBC Connection [" + connection + "]");
}
connection.commit();
}
}
//使用connection的rollback()
public void rollback() throws SQLException {
if (connection != null && !connection.getAutoCommit()) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Rolling back JDBC Connection [" + connection + "]");
}
connection.rollback();
}
}
//使用connection的close()
public void close() throws SQLException {
if (connection != null) {
resetAutoCommit();
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Closing JDBC Connection [" + connection + "]");
}
connection.close();
}
}
protected void setDesiredAutoCommit(boolean desiredAutoCommit) {
try {
//事務提交狀態不一致時修改
if (connection.getAutoCommit() != desiredAutoCommit) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Setting autocommit to " + desiredAutoCommit + " on JDBC Connection [" + connection + "]");
}
connection.setAutoCommit(desiredAutoCommit);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new TransactionException("Error configuring AutoCommit. "
+ "Your driver may not support getAutoCommit() or setAutoCommit(). "
+ "Requested setting: " + desiredAutoCommit + ". Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
protected void resetAutoCommit() {
//select操作沒有commit和rollback事務,一些資料庫在select操作是會開啟事務,一個變通方法是在關閉連線之前將autocommit設定為true。
try {
if (!connection.getAutoCommit()) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Resetting autocommit to true on JDBC Connection [" + connection + "]");
}
connection.setAutoCommit(true);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
log.debug("Error resetting autocommit to true "
+ "before closing the connection. Cause: " + e);
}
}
protected void openConnection() throws SQLException {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Opening JDBC Connection");
}
connection = dataSource.getConnection();
if (level != null) {
connection.setTransactionIsolation(level.getLevel());
}
setDesiredAutoCommit(autoCommmit);
}
}