CodeForces - 932D. Tree(書上倍增+LCA)
題目連結:http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/932/D
You are given a node of the tree with index 1 and with weight 0. Let cnt be the number of nodes in the tree at any instant (initially, cnt is set to 1). Support Q queries of following two types:
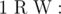 Add a new node (index cnt+ 1) with weight W and add edge between node R and this node.
Add a new node (index cnt+ 1) with weight W and add edge between node R and this node.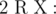 Output the maximum length of sequence of nodes which
Output the maximum length of sequence of nodes which
- starts with R.
- Every node in the sequence is an ancestor of its predecessor.
- Sum of weight of nodes in sequence does not exceed X.
- For some nodes i, j that are consecutive in the sequence if i is an ancestor of j then w[i] ≥ w[j] and there should not exist a node k on simple path from i to j such that w[k] ≥ w[j]
The tree is rooted at node 1 at any instant.
Note that the queries are given in a modified way.
Input
First line containing the number of queries Q (1 ≤ Q ≤ 400000).
Let last be the answer for previous query of type 2 (initially last equals 0).
Each of the next Q lines contains a query of following form:
- 1 p q (1 ≤ p, q ≤ 1018): This is query of first type where
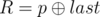 and
and 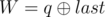 . It is guaranteed that 1 ≤ R ≤ cnt and 0 ≤ W ≤ 109.
. It is guaranteed that 1 ≤ R ≤ cnt and 0 ≤ W ≤ 109. - 2 p q (1 ≤ p, q ≤ 1018): This is query of second type where
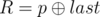 and
and 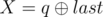 . It is guaranteed that 1 ≤ R ≤ cntand 0 ≤ X ≤ 1015.
. It is guaranteed that 1 ≤ R ≤ cntand 0 ≤ X ≤ 1015.
 denotes bitwise XOR of a and b.
denotes bitwise XOR of a and b.
It is guaranteed that at least one query of type 2 exists.
Output
Output the answer to each query of second type in separate line.
Examples
input
Copy
6 1 1 1 2 2 0 2 2 1 1 3 0 2 2 0 2 2 2
output
Copy
0 1 1 2
input
Copy
6 1 1 0 2 2 0 2 0 3 1 0 2 2 1 3 2 1 6
output
Copy
2 2 3 2
input
Copy
7 1 1 2 1 2 3 2 3 3 1 0 0 1 5 1 2 5 0 2 4 0
output
Copy
1 1 2
input
Copy
7 1 1 3 1 2 3 2 3 4 1 2 0 1 5 3 2 5 5 2 7 22
output
Copy
1 2 3
Note
In the first example,
last = 0
- Query 1: 1 1 1, Node 2 with weight 1 is added to node 1.
- Query 2: 2 2 0, No sequence of nodes starting at 2 has weight less than or equal to 0. last = 0
- Query 3: 2 2 1, Answer is 1 as sequence will be {2}. last = 1
- Query 4: 1 2 1, Node 3 with weight 1 is added to node 2.
- Query 5: 2 3 1, Answer is 1 as sequence will be {3}. Node 2 cannot be added as sum of weights cannot be greater than 1. last = 1
- Query 6: 2 3 3, Answer is 2 as sequence will be {3, 2}. last = 2
題目大意:
題目好繞啊!我斷斷續續讀了一天半,後來問dalao,才知道題目什麼意思,題讀懂了就是板子了,下面是題目大意:
給出一個樹,根節點是1,權值為0,然後又兩個操作:
1操作,在p節點下加一個權值為q的節點(注意異或last)
2操作,輸入p,q(對last異或)
從p節點開始(包括p節點),向上找祖先,符合要求的祖先:(權值>=子節點),並且符合要求的節點加起來不能超過輸入的那個q;
真是坑啊!一還是沒有注意到祖先是可以跳的(吐血!)
簡單的lca,還不用dfs建樹,就是要稍微改一下,還是比較簡單的(看我的註釋就知道改的多麼心力交瘁了。。。)
ac:
//#pragma comment(linker, "/STACK:1024000000,1024000000")
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
//#include<map>
//#include<set>
#include<deque>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#include<bitset>
#include<string>
#include<fstream>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
//#define max(a,b) (a)>(b)?(a):(b)
//#define min(a,b) (a)<(b)?(a):(b)
#define clean(a,b) memset(a,b,sizeof(a))// 水印
//std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
const int MAXN=1e6+10;
const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
const ll mod=1e9+7;
//struct node{
// ll v,nxt,w;
// node(ll _v=0,ll _w=0,ll nxt=0):
// v(_v),w(_w),nxt(_nxt){}
//}edge[MAXN<<1];
ll head[MAXN<<1],ecnt;
ll fa[MAXN][30],v[MAXN],sum[MAXN][30];
int n,m;
void intt()
{
clean(head,-1);
clean(fa,0);
clean(v,0);
clean(sum,0);
ecnt=1;
}
void add(ll u,ll w)
{
//cout<<"u下面放w:"<<u<<" "<<w<<endl;
ll temp=++ecnt;
v[temp]=w;
if(v[u]>=w)
fa[temp][0]=u;
else
{
for(int i=29;i>=0;--i)
{
if(v[fa[u][i]]<v[temp]&&fa[u][i])
u=fa[u][i];
}
fa[temp][0]=fa[u][0];
}
//找到祖先
if(fa[temp][0])//存在祖先
sum[temp][0]=v[fa[temp][0]];//第一個祖先的權值即為向上求的sum
else
sum[temp][0]=INF;
//cout<<temp<<" :"<<fa[temp][0]<<endl;
ll up=0,pre=fa[temp][0];
while(fa[pre][up])//重新整理祖先 && 記錄該點~祖先的和
{
fa[temp][up+1]=fa[pre][up];
sum[temp][up+1]=sum[temp][up]+sum[fa[temp][up]][up];
//cout<<temp<<": "<<(1<<(up+1))<<" :"<<fa[pre][up]<<endl;
pre=fa[pre][up++];
}
// for(int i=0;i<30;++i)
// {
// cout<<fa[temp][i]<<" "<<sum[temp][i]<<endl;
// }
// cout<<endl;
}
ll lca(ll a,ll w)
{
// for(int i=0;i<30;++i)
// cout<<fa[a][i]<<" "<<sum[a][i]<<endl;
// cout<<endl;
if(v[a]>w)//本身>w
return 0;
w=w-v[a];
//cout<<w<<": "<<endl;
ll ans=1;
for(int i=29;i>=0;--i)
{
//cout<<i<<endl;
//cout<<i<<": "<<w<<" "<<sum[a][i]<<" "<<fa[a][i]<<endl;
if(w-sum[a][i]>=0&&fa[a][i])//祖先可以被重新整理到 && 祖先存在
{
w=w-sum[a][i];//
ans=ans+(1<<i);
//cout<<w<<" :"<<ans<<" "<<fa[a][i]<<endl;
a=fa[a][i];
}
}
return ans;
}
int main()
{
std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
intt();
ll last=0;
cin>>n;
while(n--)
{
ll oper,p,q;
cin>>oper>>p>>q;
p=p^last,q=q^last;
if(oper==1)//插入q到p下面
add(p,q);
else//查詢從p開始所有<=q的節點
{
last=lca(p,q);
cout<<last<<endl;
}
}
}
