【凸包+旋轉卡殼思想】 BZOJ 1069
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-11-10
【題目大意】在某塊平面土地上有N個點,你可以選擇其中的任意四個點,將這片土地圍起來,當然,你希望這四個點圍成的多邊形面積最大。
【資料範圍】4≤n≤2000, |x|,|y|<=100000
【思路】毫無疑問,這四個點肯定在凸包上。然後可以列舉對角線,然後再列舉對角線兩邊的點。當對角線定下來了以後,對於一側的三角形,可以發現它的面積是單峰的——三角形頂點沿一個方向移動的時候,面積先增後減。那麼當三角形面積開始減小的時候就可以停止枚舉了。這時候,我們就得到了此對角線下的最優解。
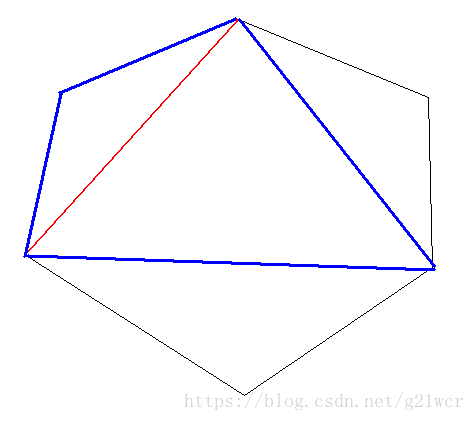
然後移動這個對角線的一個頂點。如下:
我們發現這時可以利用前一個的最優解!因為前面保證了是單增的。
然後就可以從前一個的最優解開始列舉,過程如下:
思想和旋轉卡殼類似。
#include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <vector> #include <cstring> #include <cmath> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; const int maxn=10000; struct point{ double x,y; point(double _x=0,double _y=0){x=_x,y=_y;} friend inline point operator +(const point &a,const point &b){ return point(a.x+b.x,a.y+b.y); } friend inline point operator -(const point &a,const point &b){ return point(a.x-b.x,a.y-b.y); } friend inline double operator *(const point &a,const point &b){ return (a.x*b.y-a.y*b.x); } }p[maxn],st[maxn]; double ang[maxn],ans=0,parta=0,partb=0; int id=1,top=0,n; inline double dist(point a,point b){ return sqrt((a.x-b.x)*(a.x-b.x)+(a.y-b.y)*(a.y-b.y)); } inline bool cmp(const point &a,const point &b){ double K=(a-p[1])*(b-p[1]); return (K==0)?(dist(a,p[1])<dist(b,p[1])):(K>0); } inline int add(int a){return ((a+1)>top)? a+1-top : a+1;} inline void Graham(){ swap(p[id],p[1]); sort(p+2,p+n+1,cmp); st[++top]=p[1]; for(int i=2;i<=n;++i){ while((top>=3)&&((p[i]-st[top-1])*(st[top]-st[top-1])>=0)) top--; st[++top]=p[i]; } st[top+1]=st[1]; } //i和j是對角線頂點,k和l是兩邊的頂點。 inline void rotating_calipers(){ int i,j,k,l; for(i=1;i<=top;++i){ k=i,l=add(i); for(j=i+1;j<=top;++j) { while((st[add(k)]-st[i])*(st[j]-st[i])>(st[k]-st[i])*(st[j]-st[i])) k=add(k); while((st[j]-st[i])*(st[add(l)]-st[i])>(st[j]-st[i])*(st[l]-st[i])) l=add(l); ans=max(ans,(st[j]-st[i])*(st[l]-st[i])+(st[k]-st[i])*(st[j]-st[i])); } } } int main(){ scanf("%d",&n); for(int i=1;i<=n;++i){ scanf("%lf%lf",&p[i].x,&p[i].y); if(p[i].y>p[id].y||((p[i].y==p[id].y)&&(p[i].x<p[id].x))) id=i; } Graham(),rotating_calipers(); printf("%.3f\n",ans/2); }


