node——4-node 中的 js
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-11-10
- 支援 EcmaScript
- 區別:沒有 DOM、BOM
- 核心模組
- 第三方模組
- 使用者自定義模組
核心模組
Node 為 JavaScript 提供了很多伺服器級別的 API,這些 API 絕大多數都被包裝到了一個具名的核心模組中了
例如:檔案操作的 fs 核心模組,http 服務構建的 http 模組,path 路徑操作模組,os 作業系統資訊模組。。。
模組載入:var fs = require('fs');
// 用來獲取機器資訊的
var os = require('os');
// 用來獲取當前機器的 cpu 資訊 使用者自定義模組
注意:require 相對路徑必須加 ./
推薦:可以省略字尾名
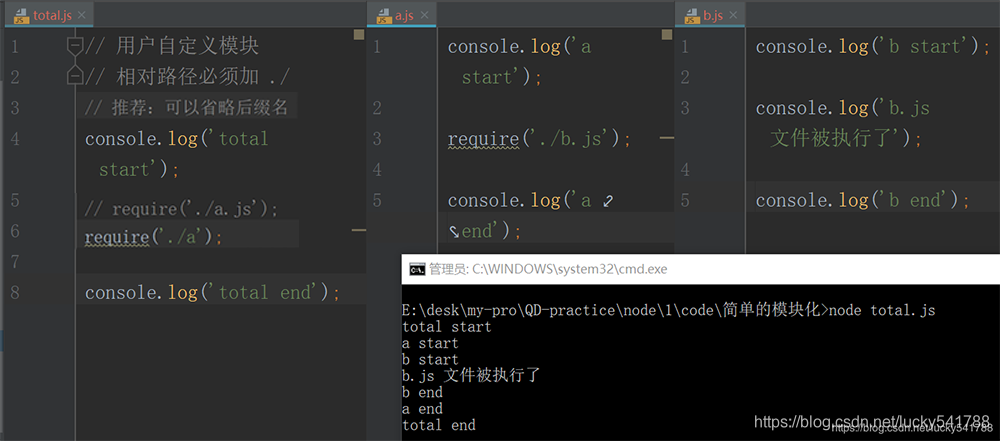
在 Node 中,沒有全域性作用域,只有模組作用域
- 外部訪問不到內部
- 內部也訪問不到外部
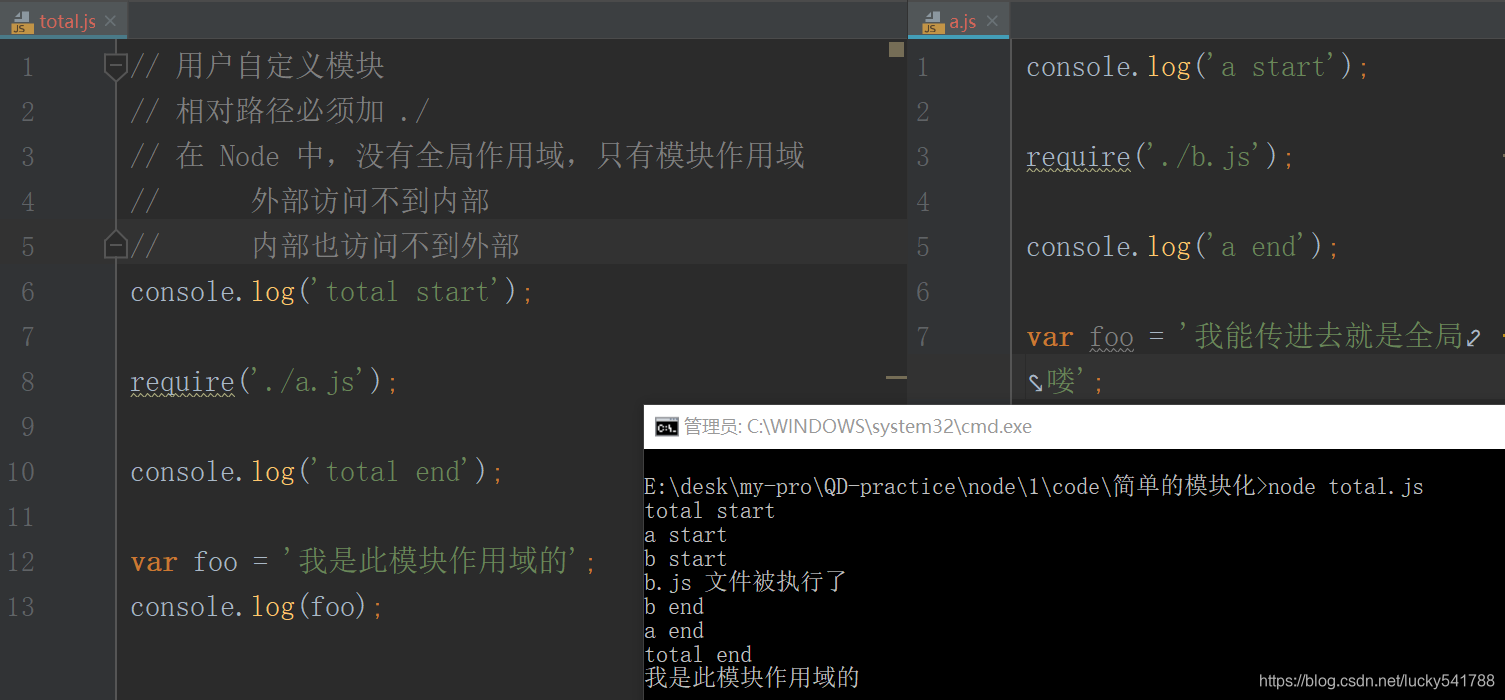
模組之間傳值
require 方法有兩個作用
- 載入檔案模組並執行裡面的程式碼
- 拿到被載入檔案模組匯出的介面物件
- 在每個檔案模組中都提供了一個物件:exports ,exports 預設是一個空物件,把所有需要被外部訪問的成員掛載到這個 exports 物件中
將 2.js 檔案內容傳給 1.js
1.js
var res = require('./2');
console.log(res.foo);// hello
console.log(res.add(20, 10)); 2.js
var foo = 'hello';
// console.log(exports);// {}
exports.foo = foo;
exports.add = function (x, y) {
return x + y;
};
