Android平臺 串列埠232通訊
開發串列埠程式首先要求你的裝置需要支援串列埠通訊,可以在裝置上裝一個App端的串列埠工具來檢測一下http://dl.pconline.com.cn/download/1214519.html,或者在電腦端下載一個友善串列埠助手檢測一下,一般在Android工控主機板上面都會帶有串列埠。
首先我們是用到了谷歌開源的API serialPort
先貼出來下載地址 https://github.com/cepr/android-serialport-api
第一步 配置環境
1、開發工具Android studio,2.2-3.1.2都可以
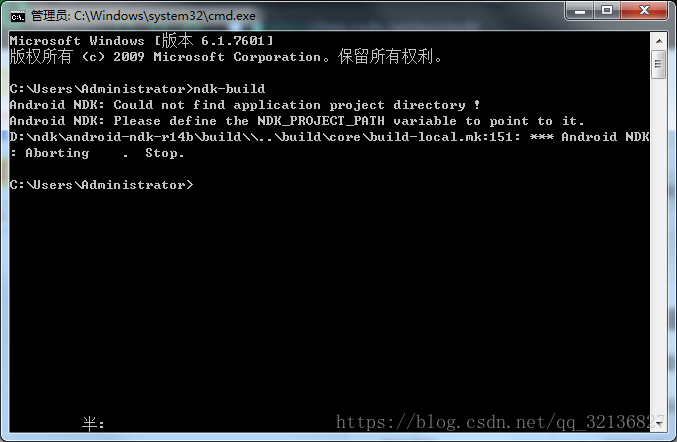
2、配置NDK(
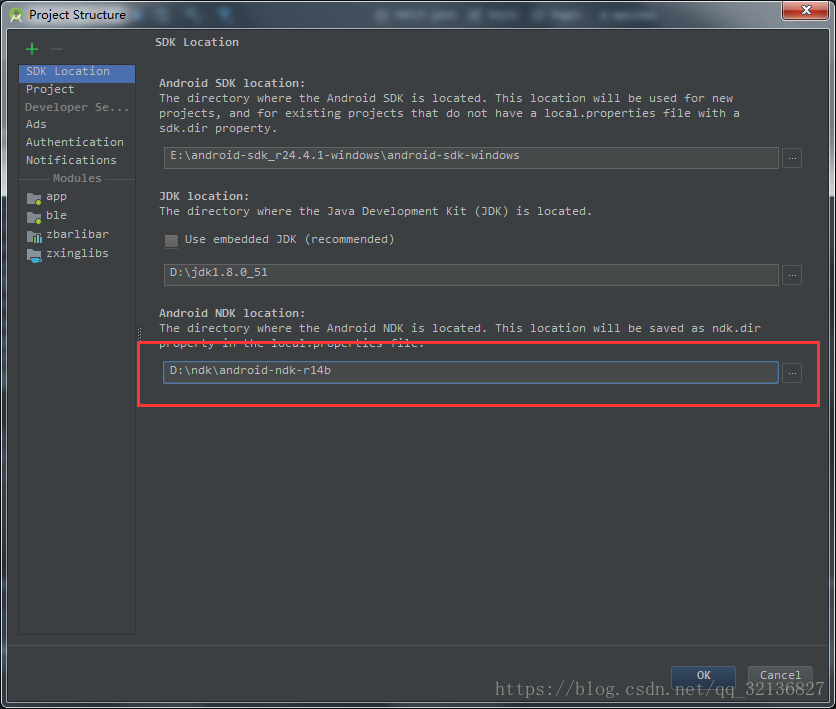
3、Android studio配置ndk
二、用開源庫程式碼複製到自己專案裡
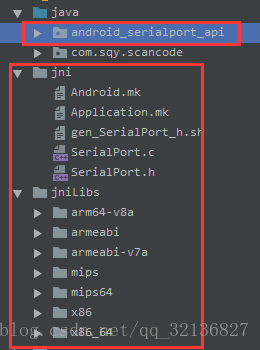
1、如下圖所示
裡面的操作類我做了重構,可能會跟開源裡面的不一樣,不過都是為了達到自己的需求嘛
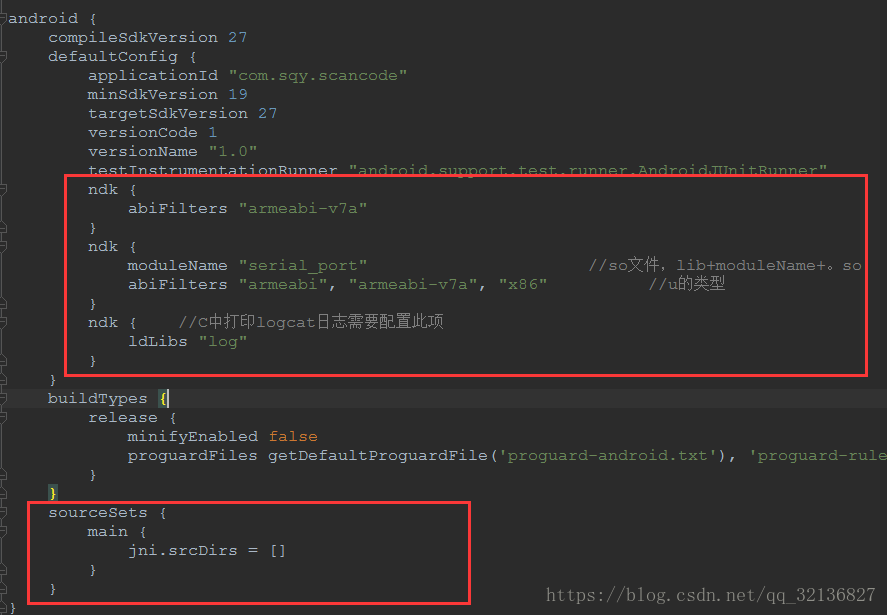
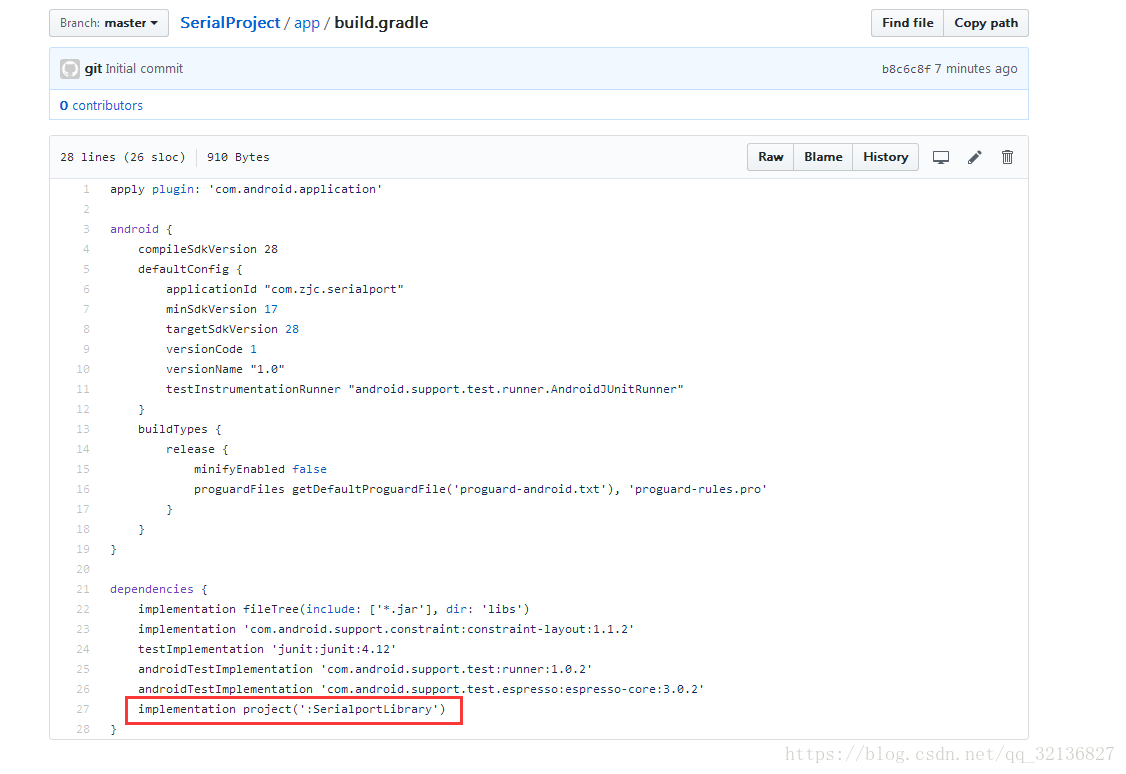
2、配置build-gridle
配置資訊直接粘上去就可以了
在project目錄下的gradle.properties檔案內加上
Android.useDeprecatedNdk=true這句話 ,為了相容新老版本ndk3、類的講解
public class SerialPortFinder { public class Driver { public Driver(String name, String root) { mDriverName = name; mDeviceRoot = root; } private String mDriverName; private String mDeviceRoot; Vector<File> mDevices = null; public Vector<File> getDevices() { if (mDevices == null) { mDevices = new Vector<File>(); File dev = new File("/dev"); File[] files = dev.listFiles(); int i; for (i = 0; i < files.length; i++) { if (files[i].getAbsolutePath().startsWith(mDeviceRoot)) { Log.d(TAG, "Found new device: " + files[i]); mDevices.add(files[i]); } } } return mDevices; } public String getName() { return mDriverName; } } private static final String TAG = "SerialPort"; private Vector<Driver> mDrivers = null; Vector<Driver> getDrivers() throws IOException { if (mDrivers == null) { mDrivers = new Vector<Driver>(); LineNumberReader r = new LineNumberReader(new FileReader("/proc/tty/drivers")); String l; while ((l = r.readLine()) != null) { // Issue 3: // Since driver name may contain spaces, we do not extract driver name with split() String drivername = l.substring(0, 0x15).trim(); String[] w = l.split(" +"); if ((w.length >= 5) && (w[w.length - 1].equals("serial"))) { Log.d(TAG, "Found new driver " + drivername + " on " + w[w.length - 4]); mDrivers.add(new Driver(drivername, w[w.length - 4])); } } r.close(); } return mDrivers; } public String[] getAllDevices() { Vector<String> devices = new Vector<String>(); // Parse each driver Iterator<Driver> itdriv; try { itdriv = getDrivers().iterator(); while (itdriv.hasNext()) { Driver driver = itdriv.next(); Iterator<File> itdev = driver.getDevices().iterator(); while (itdev.hasNext()) { String device = itdev.next().getName(); String value = String.format("%s (%s)", device, driver.getName()); devices.add(value); } } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return devices.toArray(new String[devices.size()]); } //獲取裝置上所有的串列埠節點 public String[] getAllDevicesPath() { Vector<String> devices = new Vector<String>(); // Parse each driver Iterator<Driver> itdriv; try { itdriv = getDrivers().iterator(); while (itdriv.hasNext()) { Driver driver = itdriv.next(); Iterator<File> itdev = driver.getDevices().iterator(); while (itdev.hasNext()) { String device = itdev.next().getAbsolutePath(); devices.add(device); } } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return devices.toArray(new String[devices.size()]); } }
這個類一般不用,不佔主要作用,根據需求新增
public class SerialPort {
private static final String TAG = "SerialPort";
private FileDescriptor mFd;
private FileInputStream mFileInputStream;
private FileOutputStream mFileOutputStream;
public SerialPort(File device, int baudrate, int flags) throws SecurityException, IOException {
//檢查訪問許可權,如果沒有讀寫許可權,進行檔案操作,修改檔案訪問許可權
if (!device.canRead() || !device.canWrite()) {
try {
//通過掛載到linux的方式,修改檔案的操作許可權
Process su = Runtime.getRuntime().exec("/system/bin/su");
String cmd = "chmod 777 " + device.getAbsolutePath() + "\n" + "exit\n";
su.getOutputStream().write(cmd.getBytes());
if ((su.waitFor() != 0) || !device.canRead() || !device.canWrite()) {
throw new SecurityException();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw new SecurityException();
}
}
mFd = open(device.getAbsolutePath(), baudrate, flags);
if (mFd == null) {
Log.e(TAG, "native open returns null");
throw new IOException();
}
mFileInputStream = new FileInputStream(mFd);
mFileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(mFd);
}
// Getters and setters
public InputStream getInputStream() {
return mFileInputStream;
}
public OutputStream getOutputStream() {
return mFileOutputStream;
}
// JNI(呼叫java本地介面,實現串列埠的開啟和關閉)
/**
* 串列埠有五個重要的引數:串列埠裝置名,波特率,檢驗位,資料位,停止位
* 其中檢驗位一般預設位NONE,資料位一般預設為8,停止位預設為1
*/
/**
* @param path 串列埠裝置的絕對路徑
* @param baudrate 波特率
* @param flags 校驗位
*/
private native static FileDescriptor open(String path, int baudrate, int flags);
public native void close();
static {//載入jni下的C檔案庫
System.loadLibrary("serial_port");
}
}這個SerialPort類是開源的,沒有經過修改,Android可以,裡面的直接呼叫,native方法直接和C通訊,我們做Android的不需要管
jni目錄下放著c原始碼和h標頭檔案,
jniLibs下面放的就是so庫。
注意:因為用的谷歌原生so庫,所以SerialPort類的包名一定要是android_serialport_api,如果想修改這個包名,就需要重新生成對應的so庫
public class SerialPortUtil {
public static String TAG = "SerialPortUtil";
/**
* 標記當前串列埠狀態(true:開啟,false:關閉)
**/
public static boolean isFlagSerial = false;
public static SerialPort serialPort = null;
public static InputStream inputStream = null;
public static OutputStream outputStream = null;
public static Thread receiveThread = null;
public static String strData = "";
public static Handler mHandler;
/**
* 開啟串列埠
*/
public static boolean open() {
boolean isopen = false;
if(isFlagSerial){
LogUtils.e(TAG,"串列埠已經開啟,開啟失敗");
return false;
}
try {
serialPort = new SerialPort(new File("/dev/ttyS3"), 115200, 0);
inputStream = serialPort.getInputStream();
outputStream = serialPort.getOutputStream();
receive();
isopen = true;
isFlagSerial = true;
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
isopen = false;
}
return isopen;
}
/**
* 關閉串列埠
*/
public static boolean close() {
if(isFlagSerial){
LogUtils.e(TAG,"串列埠關閉失敗");
return false;
}
boolean isClose = false;
LogUtils.e(TAG, "關閉串列埠");
try {
if (inputStream != null) {
inputStream.close();
}
if (outputStream != null) {
outputStream.close();
}
isClose = true;
isFlagSerial = false;//關閉串列埠時,連線狀態標記為false
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
isClose = false;
}
return isClose;
}
/**
* 傳送串列埠指令
*/
public static void sendString(String data, Handler handler) {
mHandler = handler;
if (!isFlagSerial) {
LogUtils.e(TAG, "串列埠未開啟,傳送失敗" + data);
return;
}
try {
outputStream.write(ByteUtil.hex2byte(data));
outputStream.flush();
LogUtils.e(TAG, "sendSerialData:" + data);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
LogUtils.e(TAG, "傳送指令出現異常");
}
}
/**
* 接收串列埠資料的方法
*/
public static void receive() {
if (receiveThread != null && !isFlagSerial) {
return;
}
receiveThread = new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
while (isFlagSerial) {
try {
byte[] readData = new byte[32];
if (inputStream == null) {
return;
}
int size = inputStream.read(readData);
if (size > 0 && isFlagSerial) {
strData = ByteUtil.byteToStr(readData, size);
LogUtils.e(TAG, "readSerialData:" + strData);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
};
receiveThread.start();
}
}這個類就比較重要了,開啟串列埠、關閉串列埠、讀寫操作,都在這個類裡面寫了詳細的註釋,另外下面在貼一個工具類出來
package com.sqy.scancode.util;
import android.graphics.Bitmap;
import android.graphics.BitmapFactory;
import android.util.Base64;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import Decoder.BASE64Decoder;
import Decoder.BASE64Encoder;
/**
* Created by Administrator on 2018/6/15.
*/
public class ByteUtil {
/**
* 字串轉化成為16進位制字串
*
* @param s
* @return
*/
public static String strTo16(String s) {
String str = "";
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
int ch = (int) s.charAt(i);
String s4 = Integer.toHexString(ch);
str = str + s4;
}
return str;
}
/**
* 16進位制轉換成為string型別字串
*
* @param s
* @return
*/
public static String hexStringToString(String s) {
if (s == null || s.equals("")) {
return null;
}
s = s.replace(" ", "");
byte[] baKeyword = new byte[s.length() / 2];
for (int i = 0; i < baKeyword.length; i++) {
try {
baKeyword[i] = (byte) (0xff & Integer.parseInt(s.substring(i * 2, i * 2 + 2), 16));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
try {
s = new String(baKeyword, "UTF-8");
new String();
} catch (Exception e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
return s;
}
/**
* 向串列埠傳送資料轉為位元組陣列
*/
public static byte[] hex2byte(String hex) {
String digital = "0123456789ABCDEF";
String hex1 = hex.replace(" ", "");
char[] hex2char = hex1.toCharArray();
byte[] bytes = new byte[hex1.length() / 2];
byte temp;
for (int p = 0; p < bytes.length; p++) {
temp = (byte) (digital.indexOf(hex2char[2 * p]) * 16);
temp += digital.indexOf(hex2char[2 * p + 1]);
bytes[p] = (byte) (temp & 0xff);
}
return bytes;
}
/**
* 接收到的位元組陣列轉換16進位制字串
*/
public static String bytes2HexString(byte[] b, int size) {
String ret = "";
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
String hex = Integer.toHexString(b[i] & 0xFF);
if (hex.length() == 1) {
hex = '0' + hex;
}
ret += hex.toUpperCase();
}
return ret;
}
public static String bytesToHexString(byte[] src) {
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder("");
if (src == null || src.length <= 0) {
return null;
}
for (int i = 0; i < src.length; i++) {
int v = src[i] & 0xFF;
String hv = Integer.toHexString(v);
if (hv.length() < 2) {
stringBuilder.append(0);
}
stringBuilder.append(hv);
}
return stringBuilder.toString();
}
/**
* 接收到的位元組陣列轉換16進位制字串
*/
public static String byteToStr(byte[] b, int size) {
String ret = "";
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
String hex = Integer.toHexString(b[i] & 0xFF);
if (hex.length() == 1) {
hex = '0' + hex;
}
ret += hex.toUpperCase();
}
return ret;
}
/**
* BASE64碼解密成圖片
*/
public static Bitmap Base64ToImage(String imgStr) { // 對位元組陣列字串進行Base64解碼並生成圖片
BASE64Decoder decoder = new BASE64Decoder();
Bitmap bitmap = null;
try {
// Base64解碼
byte[] b = decoder.decodeBuffer(imgStr);
for (int i = 0; i < b.length; ++i) {
if (b[i] < 0) {// 調整異常資料
b[i] += 256;
}
}
bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeByteArray(b,0,b.length);
return bitmap;
} catch (Exception e) {
LogUtils.e("TAG","解析異常");
return bitmap;
}
}
/**
* 將圖片轉換為base64加密資料
*/
public static String ImageToBase64(String imgFile) {
InputStream in = null;
byte[] data = null;
try {
in = new FileInputStream(imgFile);
data = new byte[in.available()];
in.read(data);
in.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
LogUtils.e("TAG","加密異常");
e.printStackTrace();
}
BASE64Encoder encoder = new BASE64Encoder();
return encoder.encode(data);
}
/**
* 計算CRC16校驗碼
* 逐個求和
*
* @param bytes 位元組陣列
* @return {@link String} 校驗碼
* @since 1.0
*/
public static String getCRC_16(byte[] bytes) {
int CRC = 0x0000ffff;
int POLYNOMIAL = 0x0000a001;
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < bytes.length; i++) {
CRC ^= ((int) bytes[i] & 0x000000ff);
for (j = 0; j < 8; j++) {
if ((CRC & 0x00000001) != 0) {
CRC >>= 1;
CRC ^= POLYNOMIAL;
} else {
CRC >>= 1;
}
}
}
if (Integer.toHexString(CRC).toUpperCase().length() == 2) {
return byteToStr(bytes, bytes.length) + "00" + Integer.toHexString(CRC).toUpperCase();
} else if (Integer.toHexString(CRC).toUpperCase().length() == 3) {
return byteToStr(bytes, bytes.length) + "0" + Integer.toHexString(CRC).toUpperCase();
}
return byteToStr(bytes, bytes.length) + Integer.toHexString(CRC).toUpperCase();
}
/**
* 指令校驗和,並取出後兩位位元組
* */
public static String getSum16(byte[] msg, int length) {
long mSum = 0;
byte[] mByte = new byte[length];
/** 逐Byte新增位數和 */
for (byte byteMsg : msg) {
long mNum = ((long) byteMsg >= 0) ? (long) byteMsg : ((long) byteMsg + 256);
mSum += mNum;
} /** end of for (byte byteMsg : msg) */
/** 位數和轉化為Byte陣列 */
for (int liv_Count = 0; liv_Count < length; liv_Count++) {
mByte[length - liv_Count - 1] = (byte) (mSum >> (liv_Count * 8) & 0xff);
} /** end of for (int liv_Count = 0; liv_Count < length; liv_Count++) */
return byteToStr(msg, length) + byteToStr(mByte, mByte.length).substring(byteToStr(mByte, mByte.length).length() - 4, byteToStr(mByte, mByte.length).length());
}
}4、demo下載地址 : https://github.com/z-jc/ScanCode 裡面可能還會有一些別的功能,需要的話自行下載
5、另外再提供一個自己封裝好的module,https://github.com/z-jc/SerialProject-master,app匯入module
然後在activity內直接這樣呼叫
省心又省勁是不是
以上全為原創,如有講解不到之處,還請廣大朋友指點一下