C#:泛型
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-11-11
按照我的理解,泛型指的是“加強的型別”。舉例來說,我們使用傳統的基礎資料型別,int,float,double這樣的變數,需要先宣告再賦值然後才能引用,但是如果聲明瞭沒賦值就開始引用呢?那麼就會報錯。但是有時候,對於一些程式中的某些變數而言,空(null)是被允許而且在有些情況下是有意義的,那這時候我們就要使用泛型。
對於基礎資料型別的泛型來說,區別僅僅在於它可以為空,接下來用一個例子進行說明,該例子是在控制檯中由使用者輸入兩個向量,然後計算出兩個向量的和向量。在輸入的時候,可能會出現向量的某個值為空的情況。
(一):建立新的控制檯程式,新建新類Vector,將該類設定為public級別,在預處理部分寫上using static System.Math;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using static System.Math;
namespace Ch12Ex01
{
public class Vector
{
}
}
向量我們一般使用一個距離r和一個角度theta來表示,因此我們需要兩個欄位分別表示,因為我們這裡可能會出現null的情況,因此使用泛型來表示這兩個欄位,
public double? R = null; public double? Theta = null;
這裡的Theta是用角度來表示,但是System.Math裡提供的函式都是使用的弧度制,因此我們設定一個泛型屬性作為弧度。
public double? ThetaRadians
{
get { return (Theta * PI / 180.0); }
}在輸入向量的過程中可能會出現r為負數的情況,為了避免這種情況,修改建構函式
public Vector(double? r,double? theta) { if(r<0) { r = -r; theta += 180; } theta = theta % 360; R = r; Theta = theta; }
重新定義"+"的運算,
public static Vector operator +(Vector op1,Vector op2)
{
try
{
double newY = op1.R.Value * Sin(op1.ThetaRadians.Value)
+ op2.R.Value * Sin(op2.ThetaRadians.Value);
double newX = op1.R.Value * Cos(op1.ThetaRadians.Value)
+ op2.R.Value * Cos(op2.ThetaRadians.Value);
double newR = Sqrt(newX * newX + newY * newY);
double newTheta = Atan2(newY, newX) * 180 / PI;
return new Vector(newR, newTheta);
}
catch
{
return new Vector(null, null);
}
}接下來在Program類中,編寫獲取輸入值的方法
static double? GetNullableDouble()
{
double? result;
string userInput = ReadLine();
try
{ result = double.Parse(userInput); }
catch
{ result = null; }
return result;
}編寫獲取向量的方法
static Vector GetVector(string name)
{
WriteLine($"Input {name} magnitude:");
double? r = GetNullableDouble();
WriteLine($"Input {name} angle (in degrees):");
double? theta = GetNullableDouble();
return new Vector(r, theta);
}最後在主函式寫上
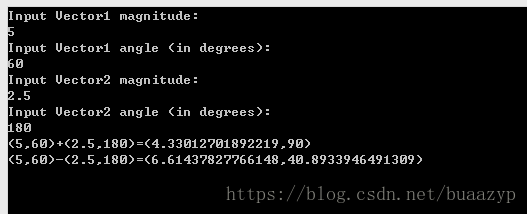
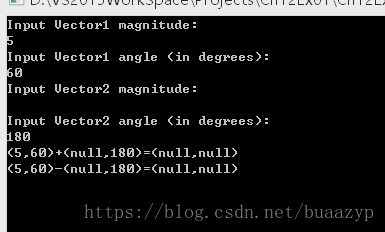
Vector v1 = GetVector("Vector1");
Vector v2 = GetVector("Vector2");
WriteLine($"{v1}+{v2}={v1 + v2}");
WriteLine($"{v1}-{v2}={v1 - v2}");
ReadKey();(二):程式執行結果
1:正常輸入
2:輸入時有一個值為空
(三):總結
從這個案例來看似乎泛型也不是很難?也就是原來的基礎資料結構加上了個空值判斷。
(四):原始碼
1:Program類
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using static System.Console;
namespace Ch12Ex01
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Vector v1 = GetVector("Vector1");
Vector v2 = GetVector("Vector2");
WriteLine($"{v1}+{v2}={v1 + v2}");
WriteLine($"{v1}-{v2}={v1 - v2}");
ReadKey();
}
static Vector GetVector(string name)
{
WriteLine($"Input {name} magnitude:");
double? r = GetNullableDouble();
WriteLine($"Input {name} angle (in degrees):");
double? theta = GetNullableDouble();
return new Vector(r, theta);
}
static double? GetNullableDouble()
{
double? result;
string userInput = ReadLine();
try
{ result = double.Parse(userInput); }
catch
{ result = null; }
return result;
}
}
}
2:Vector類
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using static System.Math;
namespace Ch12Ex01
{
public class Vector
{
public double? R = null;
public double? Theta = null;
public double? ThetaRadians
{
get { return (Theta * PI / 180.0); }
}
public Vector(double? r,double? theta)
{
if(r<0)
{
r = -r;
theta += 180;
}
theta = theta % 360;
R = r;
Theta = theta;
}
public static Vector operator +(Vector op1,Vector op2)
{
try
{
double newY = op1.R.Value * Sin(op1.ThetaRadians.Value)
+ op2.R.Value * Sin(op2.ThetaRadians.Value);
double newX = op1.R.Value * Cos(op1.ThetaRadians.Value)
+ op2.R.Value * Cos(op2.ThetaRadians.Value);
double newR = Sqrt(newX * newX + newY * newY);
double newTheta = Atan2(newY, newX) * 180 / PI;
return new Vector(newR, newTheta);
}
catch
{
return new Vector(null, null);
}
}
///////////////////////////////////////////
public static Vector operator -(Vector op1)=>new Vector(-op1.R,op1.Theta);
public static Vector operator -(Vector op1,Vector op2)=>op1+(-op2);
public override string ToString()
{
string rString = R.HasValue ? R.ToString() : "null";
string thetaString = Theta.HasValue ? Theta.ToString() : "null";
return string.Format($"({rString},{thetaString})");
}
}
}