執行緒同步鎖和非同步鎖的幾種方式
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-11-11
同步鎖:當在一個java虛擬機器多個執行緒操作一個變數的時候就會出現執行緒安全問題,這個時候就會用到同步鎖。
同步鎖的解決方式:
先看下一個執行緒異常的售票
public class ThreadSafe { public static void main(String[] args) { MyThread t1 = new MyThread("視窗一"); MyThread t2 = new MyThread("視窗一"); t1.start(); t2.start(); try { t1.join(); t2.join(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } static class MyThread extends Thread{ private static int count = 10; public MyThread(String name) { super(name); } @Override public void run() { while(count > 0) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"售出:"+(count--) +" 票"); try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }
synchronized 解決的三種方式:1)使用synchronized 靜態程式碼塊 2)synchronized 同步方法 3)synchronized 同步類
public class ThreadSafe { public static Object obj = new Object(); public static void main(String[] args) { MyThread t1 = new MyThread("視窗一"); MyThread t2 = new MyThread("視窗一"); t1.start(); t2.start(); try { t1.join(); t2.join(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } static class MyThread extends Thread{ private static int count = 10; public MyThread(String name) { super(name); } @Override public void run() { while(count > 0) { //靜態程式碼塊鎖,定義同一個物件 synchronized (obj) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"售出:"+(count--) +" 票"); } try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }
//使用synchronized 定義的方法鎖 public class ThreadSafe1 { public static Object obj = new Object(); public static void main(String[] args) { //這個地方必須是對同一個物件進行操作 MyThread myThread = new MyThread(); Thread t1 = new Thread(myThread, "視窗一"); Thread t2 = new Thread(myThread, "視窗二"); t1.start(); t2.start(); try { t1.join(); t2.join(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } static class MyThread implements Runnable{ private static int count = 10; //方法鎖 public synchronized void increse() { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"售出:"+(count--) +" 票"); } @Override public void run() { while(count > 0) { increse(); try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }
//使用類鎖
public class ThreadSafe2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread t1 = new MyThread("視窗一");
MyThread t2 = new MyThread("視窗一");
t1.start();
t2.start();
try {
t1.join();
t2.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
static class MyThread extends Thread{
private static int count = 10;
public MyThread(String name) {
super(name);
}
public static synchronized void increase() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"售出:"+(count--) +" 票");
}
@Override
public void run() {
while(count > 0) {
//靜態程式碼塊鎖,定義同一個物件
increase();
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}2.使用lock的解決方式
//使用類鎖
public class ThreadSafe3 {
public static Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread t1 = new MyThread("視窗一");
MyThread t2 = new MyThread("視窗二");
t1.start();
t2.start();
try {
t1.join();
t2.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
static class MyThread extends Thread{
private static int count = 10;
public MyThread(String name) {
super(name);
}
public static void increase() {
lock.lock();
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"售出:"+(count--) +" 票");
}catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
@Override
public void run() {
while(count > 0) {
//靜態程式碼塊鎖,定義同一個物件
increase();
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}非同步鎖:就是多個java 虛擬機器或者說是伺服器,操作同一個變數是,會出現執行緒安全問題,使用需要使用非同步鎖來處理。
1)資料庫 樂觀鎖 悲觀鎖 唯一標示 不推薦使用,容易出現鎖表,出現死鎖。
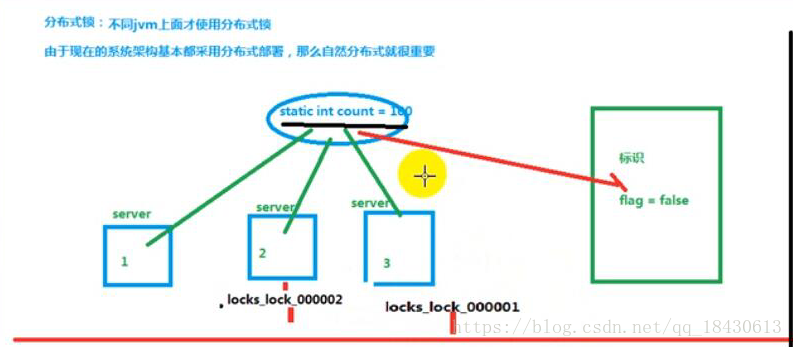
2)Redis 分散式鎖 ,就是設定一個flag標識,當一個服務拿到鎖以後立即把對應的標識設定為false 用完後釋放鎖,並把標識修改為true 詳見如下:
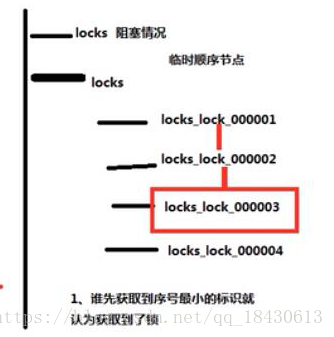
3)使用dubbo zookeeper (共享鎖,排它鎖),這裡就根據自己的情況,共享鎖還是會出現阻塞的情況,排它鎖就是會生成很多臨時的節點,誰先獲取最小的序號標識誰就先獲取到鎖。