Java IO流學習總結一:輸入輸出流
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-11-12
Java流類圖結構:
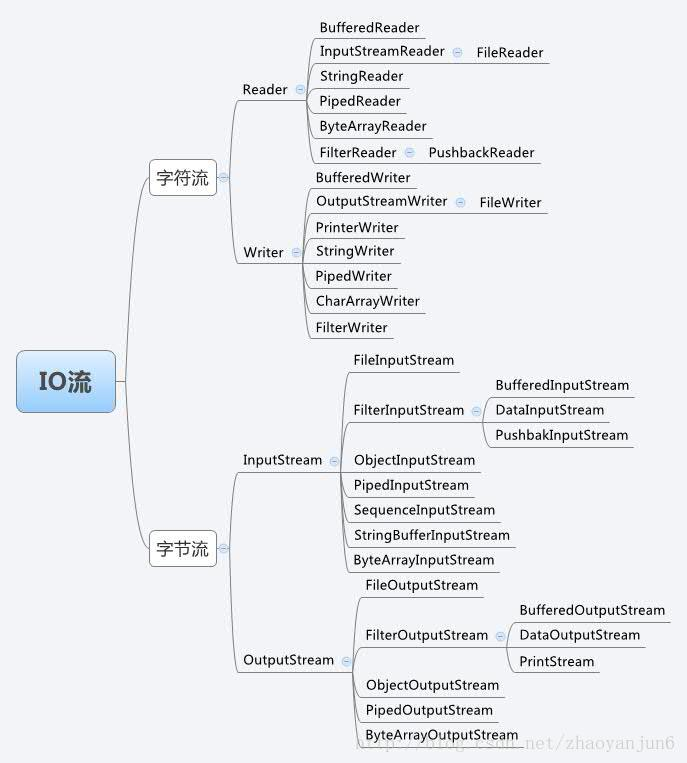
流的概念和作用
流是一組有順序的,有起點和終點的位元組集合,是對資料傳輸的總稱或抽象。即資料在兩裝置間的傳輸稱為流,流的本質是資料傳輸,根據資料傳輸特性將流抽象為各種類,方便更直觀的進行資料操作。
IO流的分類
- 根據處理資料型別的不同分為:字元流和位元組流
- 根據資料流向不同分為:輸入流和輸出流
字元流和位元組流
字元流的由來: 因為資料編碼的不同,而有了對字元進行高效操作的流物件。本質其實就是基於位元組流讀取時,去查了指定的碼錶。 位元組流和字元流的區別:
- 讀寫單位不同:位元組流以位元組(8bit)為單位,字元流以字元為單位,根據碼錶對映字元,一次可能讀多個位元組。
-
處理物件不同:位元組流能處理所有型別的資料(如圖片、avi等),而字元流只能處理字元型別的資料。
- 位元組流:一次讀入或讀出是8位二進位制。
-
字元流:一次讀入或讀出是16位二進位制。
裝置上的資料無論是圖片或者視訊,文字,它們都以二進位制儲存的。二進位制的最終都是以一個8位為資料單元進行體現,所以計算機中的最小資料單元就是位元組。意味著,位元組流可以處理裝置上的所有資料,所以位元組流一樣可以處理字元資料。
結論:只要是處理純文字資料,就優先考慮使用字元流。 除此之外都使用位元組流。
輸入流和輸出流
輸入流只能進行讀操作,輸出流只能進行寫操作,程式中需要根據待傳輸資料的不同特性而使用不同的流。
輸入位元組流 InputStream
InputStream是所有的輸入位元組流的父類,它是一個抽象類。ByteArrayInputStream、StringBufferInputStream、FileInputStream是三種基本的介質流,它們分別從Byte 陣列、StringBuffer、和本地檔案中讀取資料。PipedInputStream是從與其它執行緒共用的管道中讀取資料,與Piped 相關的知識後續單獨介紹。ObjectInputStream和所有FilterInputStream的子類都是裝飾流(裝飾器模式的主角)。
輸出位元組流 OutputStream
OutputStream是所有的輸出位元組流的父類,它是一個抽象類。ByteArrayOutputStream、FileOutputStream是兩種基本的介質流,它們分別向Byte 陣列、和本地檔案中寫入資料。PipedOutputStream是向與其它執行緒共用的管道中寫入資料。ObjectOutputStream和所有FilterOutputStream的子類都是裝飾流。
總結:
- 輸入流:InputStream或者Reader:從檔案中讀到程式中;
- 輸出流:OutputStream或者Writer:從程式中輸出到檔案中;
節點流
節點流:直接與資料來源相連,讀入或讀出。
直接使用節點流,讀寫不方便,為了更快的讀寫檔案,才有了處理流。
常用的節點流
- 父 類 :
InputStream、OutputStream、Reader、Writer - 文 件 :
FileInputStream、FileOutputStrean、FileReader、FileWriter檔案進行處理的節點流 - 數 組 :
ByteArrayInputStream、ByteArrayOutputStream、CharArrayReader、CharArrayWriter對陣列進行處理的節點流(對應的不再是檔案,而是記憶體中的一個數組) - 字串 :
StringReader、StringWriter對字串進行處理的節點流 - 管 道 :
PipedInputStream、PipedOutputStream、PipedReader、PipedWriter對管道進行處理的節點流
處理流
處理流和節點流一塊使用,在節點流的基礎上,再套接一層,套接在節點流上的就是處理流。如BufferedReader.處理流的構造方法總是要帶一個其他的流物件做引數。一個流物件經過其他流的多次包裝,稱為流的連結。
常用的處理流
- 緩衝流:
BufferedInputStrean、BufferedOutputStream、BufferedReader、BufferedWriter增加緩衝功能,避免頻繁讀寫硬碟。 - 轉換流:
InputStreamReader、OutputStreamReader實現位元組流和字元流之間的轉換。 - 資料流:
DataInputStream、DataOutputStream等-提供將基礎資料型別寫入到檔案中,或者讀取出來。
轉換流
InputStreamReader 、OutputStreamWriter 要InputStream或OutputStream作為引數,實現從位元組流到字元流的轉換。
建構函式
InputStreamReader(InputStream); //通過建構函式初始化,使用的是本系統預設的編碼表GBK。
InputStreamWriter(InputStream,String charSet); //通過該建構函式初始化,可以指定編碼表。
OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream); //通過該建構函式初始化,使用的是本系統預設的編碼表GBK。 OutputStreamwriter(OutputStream,String charSet); //通過該建構函式初始化,可以指定編碼表。 實戰演練
- FileInputStream類的使用:讀取檔案內容
package com.app; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.IOException; public class A1 { public static void main(String[] args) { A1 a1 = new A1(); //電腦d盤中的abc.txt 文件 String filePath = "D:/abc.txt" ; String reslut = a1.readFile( filePath ) ; System.out.println( reslut ); } /** * 讀取指定檔案的內容 * @param filePath : 檔案的路徑 * @return 返回的結果 */ public String readFile( String filePath ){ FileInputStream fis=null; String result = "" ; try { // 根據path路徑例項化一個輸入流的物件 fis = new FileInputStream( filePath ); //2. 返回這個輸入流中可以被讀的剩下的bytes位元組的估計值; int size = fis.available() ; //3. 根據輸入流中的位元組數建立byte陣列; byte[] array = new byte[size]; //4.把資料讀取到陣列中; fis.read( array ) ; //5.根據獲取到的Byte陣列新建一個字串,然後輸出; result = new String(array); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ if ( fis != null) { try { fis.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } return result ; } }
- FileOutputStream 類的使用:將內容寫入檔案
package com.app; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; public class A2 { public static void main(String[] args) { A2 a2 = new A2(); //電腦d盤中的abc.txt 文件 String filePath = "D:/abc.txt" ; //要寫入的內容 String content = "今天是2017/1/9,天氣很好" ; a2.writeFile( filePath , content ) ; } /** * 根據檔案路徑建立輸出流 * @param filePath : 檔案的路徑 * @param content : 需要寫入的內容 */ public void writeFile( String filePath , String content ){ FileOutputStream fos = null ; try { //1、根據檔案路徑建立輸出流 fos = new FileOutputStream( filePath ); //2、把string轉換為byte陣列; byte[] array = content.getBytes() ; //3、把byte陣列輸出; fos.write( array ); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ if ( fos != null) { try { fos.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }
注意:
- 在實際的專案中,所有的IO操作都應該放到子執行緒中操作,避免堵住主執行緒。
FileInputStream在讀取檔案內容的時候,我們傳入檔案的路徑("D:/abc.txt"), 如果這個路徑下的檔案不存在,那麼在執行readFile()方法時會報FileNotFoundException異常。FileOutputStream在寫入檔案的時候,我們傳入檔案的路徑("D:/abc.txt"), 如果這個路徑下的檔案不存在,那麼在執行writeFile()方法時, 會預設給我們建立一個新的檔案。還有重要的一點,不會報異常。
效果圖:
- 綜合練習,實現複製檔案,從D盤複製到E盤
package com.app; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; public class A3 { public static void main(String[] args) { A3 a2 = new A3(); //電腦d盤中的cat.png 圖片的路徑 String filePath1 = "D:/cat.png" ; //電腦e盤中的cat.png 圖片的路徑 String filePath2 = "E:/cat.png" ; //複製檔案 a2.copyFile( filePath1 , filePath2 ); } /** * 檔案複製 * @param filePath_old : 需要複製檔案的路徑 * @param filePath_new : 複製檔案存放的路徑 */ public void copyFile( String filePath_old , String filePath_new){ FileInputStream fis=null ; FileOutputStream fout = null ; try { // 根據path路徑例項化一個輸入流的物件 fis = new FileInputStream( filePath_old ); //2. 返回這個輸入流中可以被讀的剩下的bytes位元組的估計值; int size = fis.available() ; //3. 根據輸入流中的位元組數建立byte陣列; byte[] array = new byte[size]; //4.把資料讀取到陣列中; fis.read( array ) ; //5、根據檔案路徑建立輸出流 fout = new FileOutputStream( filePath_new ) ; //5、把byte陣列輸出; fout.write( array ); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ if ( fis != null) { try { fis.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } if ( fout != null ) { try { fout.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }
轉載 https://www.cnblogs.com/zhaoyanjun/p/6292384.html



