HDFS基於檔案的資料結構
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-11-14
存在原因
Hadoop處理少量大檔案時效率較高,但處理大量小檔案是效率較低,因此設計了以下兩種檔案模式容器用於將大量小檔案組織起來統一儲存。
SequenceFile檔案
檔案的基本格式。
- 檔案的基本格式是一種鍵值對檔案記錄。
- 檔案的鍵、值對所代表的類必須支援序列化及反序列化
- Hadoop預定義了一些class,他們已經直接或間接實現了Writable介面(序列化介面)。例如:
Text等同於Java中的StringIntWritable等同於Java中的IntBooleanWritable等同於Java中的Boolean
檔案儲存結構
在儲存結構上,SequenceFile主要由一個Header後跟多條Record組成,如圖所示:
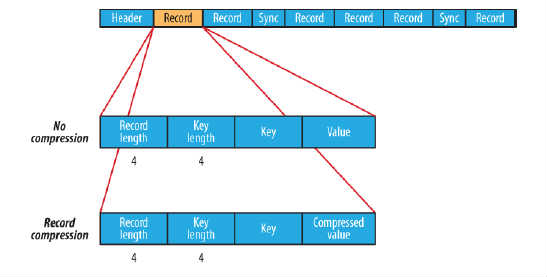
- Header主要包含了Key classname,Value classname,儲存壓縮演算法,使用者自定義元資料等資訊,此外,還包含了一些同步標識,用於快速定位到記錄的邊界。
- 每條Record以鍵值對的方式進行儲存,用來表示它的字元陣列可依次解析成:記錄的長度、Key的長度、Key值和Value值,並且Value值的結構取決於該記錄是否被壓縮。
- 同步標記位於順序檔案記錄與記錄之間,用於在讀取檔案時能夠從任意位置開始識別記錄邊界。
- 該檔案有兩種壓縮方式:record compression和block
- record compression通過圖中很明顯可以看出,檔案壓縮是僅壓縮值,未壓縮鍵,壓縮單條資料。
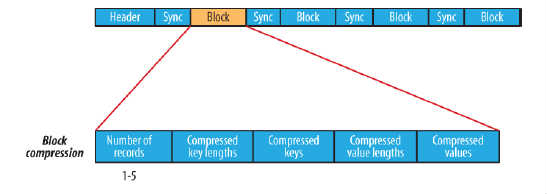
- block compression指塊壓縮,是將一連串的record組織到一起,統一壓縮成一個block,block資訊主要儲存了:塊所包含的記錄數、所包含的Key的長度、所包含的Key值的集合、所包含的Value長度,所包含的Value值的集合.如圖所示:···
檔案寫入
createWriter()靜態方法建立SequenceFile物件,並返回SequenceFile.Writer例項- 通過
SequenceFile.Writer例項的append()在檔案末尾追加鍵值對。 - 通過呼叫
close()方法關閉檔案,其實現了java.io.Closeable介面。
package chapter5;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IOUtils;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.SequenceFile;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.SequenceFile.Writer;
public class SequenceFileWrite {
private static final String[] data = {
"Hello, this is Hadoop",
"End, this is sequenceFile write demon"
};
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String output = args[0];
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
FileSystem fs = FileSystem.get(conf);
Path path = new Path(output);
if (fs.exists(path)) {
fs.delete(path, true);
}
IntWritable key = new IntWritable();
Text value = new Text();
Writer write = null;
try {
// Hadoop權威指南第4版程式碼,該方法已過時
// writer = SequenceFile.createWriter(fs, conf, path, key.getClass(), value.getClass());
// 新API寫法,使用註釋掉的語法時報錯,原因未知
// Writer.Option fileOption = Writer.file(path);
// Writer.Option keyOption = Writer.keyClass(key.getClass());
// Writer.Option valueOption = Writer.keyClass(value.getClass());
// write = SequenceFile.createWriter(conf, fileOption, keyOption, valueOption);
write = SequenceFile.createWriter(conf,Writer.file(path), Writer.keyClass(IntWritable.class), Writer.valueClass(Text.class));
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
key.set(100-i);
value.set(data[i%data.length]);
System.out.printf("[%s]\t%s\t%s\n", write.getLength(), key, value);
write.append(key, value);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
IOUtils.closeStream(write);
}
}
}
// STDOUT
[128] 100 Hello, this is Hadoop
[168] 99 End, this is sequenceFile write demon
[224] 98 Hello, this is Hadoop
[264] 97 End, this is sequenceFile write demon
[320] 96 Hello, this is Hadoop
[360] 95 End, this is sequenceFile write demon
[416] 94 Hello, this is Hadoop
[456] 93 End, this is sequenceFile write demon
[512] 92 Hello, this is Hadoop
[552] 91 End, this is sequenceFile write demon
[608] 90 Hello, this is Hadoop
[648] 89 End, this is sequenceFile write demon
[704] 88 Hello, this is Hadoop
[744] 87 End, this is sequenceFile write demon
[800] 86 Hello, this is Hadoop
---
[4680] 6 Hello, this is Hadoop
[4720] 5 End, this is sequenceFile write demon
[4776] 4 Hello, this is Hadoop
[4816] 3 End, this is sequenceFile write demon
[4872] 2 Hello, this is Hadoop
[4912] 1 End, this is sequenceFile write demon
檔案讀入
package chapter5;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IOUtils;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.SequenceFile;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Writable;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.ReflectionUtils;
import java.io.IOException;
public class SequenceFileReader {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String uri = args[0];
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
FileSystem fs = FileSystem.get(conf);
SequenceFile.Reader reader = null;
Path path = new Path(uri);
try {
// 舊版API寫法
// reader = new SequenceFile.Reader(fs, path, conf);
// 新版API寫法
reader = new SequenceFile.Reader(conf, SequenceFile.Reader.file(path));
Writable key = (Writable) ReflectionUtils.newInstance(reader.getKeyClass(), conf);
Writable value = (Writable) ReflectionUtils.newInstance(reader.getValueClass(), conf);
long position = reader.getPosition();
while (reader.next(key, value)) {
// 標記出同步點位置
String syncSecc = reader.syncSeen() ? "*" : "-";
System.out.printf("[%s%s]\t%s\t%s\n", position, syncSecc, key, value);
position = reader.getPosition();
}
} finally {
IOUtils.closeStream(reader);
}
}
}
// STDOUT
[[email protected] artifacts]$ hadoop chapter5.SequenceFileReader /zpy/bigdata/chapter5/number.seq
18/11/02 11:09:32 INFO zlib.ZlibFactory: Successfully loaded & initialized native-zlib library
18/11/02 11:09:32 INFO compress.CodecPool: Got brand-new decompressor [.deflate]
[128-] 100 Hello, this is Hadoop
[168-] 99 End, this is sequenceFile write demon
[224-] 98 Hello, this is Hadoop
[264-] 97 End, this is sequenceFile write demon
[320-] 96 Hello, this is Hadoop
[360-] 95 End, this is sequenceFile write demon
[416-] 94 Hello, this is Hadoop
---
[4028-] 19 End, this is sequenceFile write demon
[4084*] 18 Hello, this is Hadoop
[4144-] 17 End, this is sequenceFile write demon
[4200-] 16 Hello, this is Hadoop
[4240-] 15 End, this is sequenceFile write demon
[4296-] 14 Hello, this is Hadoop
[4336-] 13 End, this is sequenceFile write demon
[4392-] 12 Hello, this is Hadoop
[4432-] 11 End, this is sequenceFile write demon
[4488-] 10 Hello, this is Hadoop
[4528-] 9 End, this is sequenceFile write demon
[4584-] 8 Hello, this is Hadoop
[4624-] 7 End, this is sequenceFile write demon
[4680-] 6 Hello, this is Hadoop
[4720-] 5 End, this is sequenceFile write demon
[4776-] 4 Hello, this is Hadoop
[4816-] 3 End, this is sequenceFile write demon
[4872-] 2 Hello, this is Hadoop
[4912-] 1 End, this is sequenceFile write demon
命令列檢視檔案
格式:hadoop fs -text (File PATH)
eg: hadoop fs -text /zpy/bigdata/chapter5/number.seq
同步點操作
Reader物件
- 呼叫
Reader的seek(long position),將指標指向檔案中指定位置。該方法給定的位置不是同步點時,呼叫next()方法會報錯。 - 呼叫
Reader的sync(long position),將指標指向檔案中指定位置。該方法會將位置指向檔案當前位置的下一個同步點,若無下一個同步點,則指向檔案尾。
Writer物件
呼叫Writer的sync(),將在檔案當前位置插入一個同步點,請區別於hsync,後者用於檔案底層IO
更詳細連結
https://blog.csdn.net/qianshangding0708/article/details/47666735
