E. Mahmoud and a xor trip 按位處理 異或 dp
Description
Mahmoud and Ehab live in a country with n cities numbered from 1 to n and connected by n - 1 undirected roads. It's guaranteed that you can reach any city from any other using these roads. Each city has a number ai attached to it.
We define the distance from city x

 is bitwise xor operation.
is bitwise xor operation.
Mahmoud and Ehab want to choose two cities and make a journey from one to another. The index of the start city is always less than or equal to the index of the finish city (they may start and finish in the same city and in this case the distance equals the number attached to that city). They can't determine the two cities so they try every city as a start and every city with greater index as a finish. They want to know the total distance between all pairs of cities.
Input
The first line contains integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 105) — the number of cities in Mahmoud and Ehab's country.
Then the second line contains n integers a1, a2, ..., an (0 ≤ ai ≤ 106) which represent the numbers attached to the cities. Integer ai is attached to the city i.
Each of the next n - 1 lines contains two integers u and v (1 ≤ u, v ≤ n, u ≠ v), denoting that there is an undirected road between cities u and v. It's guaranteed that you can reach any city from any other using these roads.
Output
Output one number denoting the total distance between all pairs of cities.
Examples
input
3 1 2 3 1 2 2 3
output
10
input
5 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 2 3 3 4 3 5
output
52
input
5 10 9 8 7 6 1 2 2 3 3 4 3 5
output
131
In the first sample the available paths are:
- city 1 to itself with a distance of 1,
- city 2 to itself with a distance of 2,
- city 3 to itself with a distance of 3,
- city 1 to city 2 with a distance of
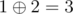 ,
, - city 1 to city 3 with a distance of
 ,
, - city 2 to city 3 with a distance of
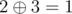 .
.
The total distance between all pairs of cities equals 1 + 2 + 3 + 3 + 0 + 1 = 10.
解:按位統計+樹形DP
題目要求在一棵帶權樹上的兩兩路徑上點權異或和的總和。
對於這種位運算的題目,我們的想法必然是按位考慮的,因為位與位之間彼此獨立,可以單獨考慮。
那麼拆成每一位之後,題目變成了統計0和1兩種情況的組合的數目,最後乘2的冪次即可。f[x][0、1]表示x這一位為0、1時的數量,考慮我們可以每次把之前做完的子樹與其父親節點合併,然後再與當前節點組合計算貢獻。
值得一提的是,有必要注意一下向上轉移的細節。如果x的這一位是0,顯然沒有影響;但是如果這一位是1,就會導致往上異或之後改變一下,需要注意。
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
#include<cstring>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int n;
int a[100005];
vector<int>e[100006];
long long powd[28];
long long ct[100005][28][2];
long long ans;
void dfs1(int u,int fa,int cur)
{
cur=cur^a[u];
int tp=cur;
for(int i=0;i<=25;i++)
{
int f=tp%2;
ct[u][i][f]++;
tp/=2;
}
int len=e[u].size();
for(int i=0;i<len;i++)
{
int v=e[u][i];
if(v!=fa)
{
dfs1(v,u,cur);
}
}
}
void dfs2(int u,int fa)
{
int len=e[u].size();
int tb[28];
//cout<<"u:"<<u<<endl;
int tp=a[u];
for(int i=0;i<=25;i++)
{
tb[i]=tp%2;
tp/=2;
//cout<<tb[i]<<" ";
}
//cout<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++)
{
int v=e[u][i];
if(v!=fa)
{
dfs2(v,u);
for(int j=0;j<=25;j++)
{
if(tb[j]==0)
{
ans+=(powd[j]*(ct[u][j][0]*ct[v][j][1]+ct[u][j][1]*ct[v][j][0]));
}
else
{
ans+=(powd[j]*(ct[u][j][0]*ct[v][j][0]+ct[u][j][1]*ct[v][j][1]));
}
ct[u][j][0]+=ct[v][j][0];
ct[u][j][1]+=ct[v][j][1];
}
}
}
//cout<<u<<":"<<ans<<endl;
}
int main()
{
powd[0]=1;
for(int i=1;i<=25;i++)
powd[i]=2*powd[i-1];
while(~scanf("%d",&n))
{
ans=0;
for(int i=0;i<=100000;i++)
{
e[i].clear();
for(int j=0;j<=25;j++)
{
ct[i][j][0]=ct[i][j][1]=0;
}
}
long long sum=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
sum+=a[i];
}
for(int i=1;i<n;i++)
{
int u,v;
scanf("%d%d",&u,&v);
e[u].push_back(v);
e[v].push_back(u);
}
dfs1(1,-1,0);
dfs2(1,-1);
//cout<<ans<<":"<<sum<<endl;
printf("%lld\n",ans+sum);
}
}
