IO流(File類,IO流的分類,位元組流和字元流,轉換流,緩衝流,物件序列化)
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-11-16
1.File類 File類可以在程式中 操作檔案和目錄。File類是通過建立File類物件,在呼叫File類的物件來進行相關操作的。 示例: --------------------- 本文來自 dajiahuooo 的CSDN 部落格 ,全文地址請點選:https://blog.csdn.net/dajiahuooo/article/details/47014705?utm_source=copy
public class Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { File f = new File("f:/我的歌聲裡.txt"); //訪問檔名相關 String name = f.getName(); System.out.println("檔名:" + name); String absolutePath = f.getAbsolutePath(); System.out.println("絕對路徑:" + absolutePath); String parent = f.getParent(); System.out.println("父目錄:" + parent); //檢測相關 System.out.println("是否存在:" + f.exists()); System.out.println("是否可讀" + f.canRead()); System.out.println("是否可寫:" + f.canWrite()); //獲取檔案資訊 System.out.println("檔案的大小: " + f.length()); //以當前路徑建立File物件 File file = new File("."); String[] list = file.list(); //遍歷目錄下的檔案 System.out.println(); System.out.println("當前目錄下有檔案:"); for(String name1:list){ System.out.println(name1); } } }
執行結果:
2.IO流的分類 按照方向:輸入流和輸出流 按照流的大小:位元組流和字元流 按照流的角色:節點流和處理流 流的類關係圖如下:
3.位元組流和字元流 位元組流:FileInputStream 和 FileOutputStream 示例:
public class Demo02 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { /* * 需求把檔案“我的歌聲裡.txt” 複製並改檔名為 “我的歌聲裡.java” * */ //建立輸入流 InputStream is = new FileInputStream(new File("f:/我的歌聲裡.txt")); //建立輸出流 OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream(new File("f:/我的歌聲裡.java")); //建立接收位元組陣列 byte[] bytes = new byte[1024]; int len = 0; //迴圈輸入輸出 while((len = is.read(bytes)) != -1 ){ os.write(bytes, 0, len); } //關閉資源 os.close(); is.close(); } }
字元流:FileReader和FileWriter
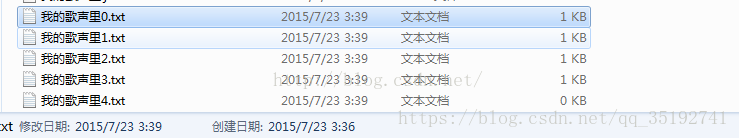
示例:切割檔案
public class Demo03 { public static void main(String[] args) { FileReader r = null; FileWriter w = null; try { int count = 0;//定義一個標記 int flag = 0;//檔名標記 r = new FileReader("f:/我的歌聲裡.txt"); w = new FileWriter("f:/我的歌聲裡" + flag +".txt"); char[] chars = new char[10]; int len = 0; while((len = r.read(chars)) != -1){ System.out.println(new String(chars, 0, len)); w.write(chars, 0, len); w.flush(); count++; //定義切割的條件 if(count >10 ){ flag++; w = new FileWriter("f:/我的歌聲裡" + flag +".txt"); count = 0; } } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ try { w.close(); r.close(); } catch (IOException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
4.轉換流 轉換流:把位元組流轉換為字元流,一次來實現效能優化 InputStreamReader 和 OutputStreamWriter
示例:
public class Demo04 {
/**
* @param args
* @throws IOException
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//鍵盤輸入到檔案
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(System.in);
char[] chars = new char[1024];
int len = 0;
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("f:/我的檔案.txt"));
int count = 0;
while((len = isr.read(chars)) != -1){
osw.write(chars, 0, len);
osw.flush();
count++;
if(count == 10){
break;
}
}
isr.close();
osw.close();
}
}
執行結果:
5.緩衝流 把流讀到緩衝區,然後再一次讀到記憶體中來,以此來提高效能
BuffererInputStream 和BufferedOutputStream
BufferedReader 和 BufferedWriter
示例:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//讀取並複製儲存圖片
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("f:/qq.jpg")));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("f:/qqq.png")));
String line = null;
while((line = br.readLine()) != null){
bw.write(line);
bw.flush();
}
bw.close();
br.close();
}
執行結果:
6.物件序列化 物件流:ObjectInStream和 ObjectOutputStream Serialiazable關鍵字:標記介面可序列化 transient關鍵字:標記瞬態例項變數
示例:
public class Demo06 {
/**
* @param args
* @throws IOException
* @throws FileNotFoundException
* @throws ClassNotFoundException
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException, IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
Student s1 = new Student("小紅", 19);
Student s2 = new Student("小白", 18);
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("f:/序列化.txt"));
oos.writeObject(s1);
oos.writeObject(s2);
s2.setName("小白白");
oos.writeObject(s2);//更改變數的屬性,即使重新序列化也不會改變原屬性值
oos.close();
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("f:/序列化.txt"));
Student rs1 = (Student) ois.readObject();
Student rs2 = (Student) ois.readObject();
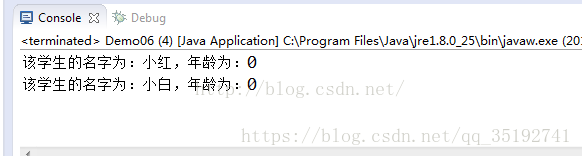
System.out.println(rs1);
System.out.println(rs2);
}
}
class Student implements Serializable{
private String name;//學生姓名
private transient int age;//年齡設定為瞬時變數,將不被序列化
public Student(String name, int age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "該學生的名字為:" + name + ",年齡為:" + age;
}
}
執行結果: