java中動態代理原始碼詳解
在研究程式碼之前,我們先看看一個例項,然後我們根據例項來進行原始碼研究。
例項程式碼如下:
package com.jd.dynamicproxy.dynamicproxy; import java.io.Serializable; import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.lang.reflect.Proxy; /** * Created by IntelliJ IDEA. * User: MessengerOfSpring * Date: 2017/12/3 * Time: 21:39 */ public class App { private interface Account { public Account deposit (double value); public double getBalance (); } private class ExampleInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler { private double balance; @Override public Object invoke (Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { // simplified method checks, would need to check the parameter count and types too if ("deposit".equals(method.getName())) { Double value = (Double) args[0]; System.out.println("deposit: " + value); balance += value; return proxy; // here we use the proxy to return 'this' } if ("getBalance".equals(method.getName())) { return balance; } return null; } } public static void main(String[] args) { new App(); } public App() { //設定儲存屬性,用來將代理類位元組碼檔案儲存下來 System.getProperties().put("sun.misc.ProxyGenerator.saveGeneratedFiles", "true"); Account account = (Account) Proxy.newProxyInstance( getClass().getClassLoader(), new Class[] {Account.class,Serializable.class}, new ExampleInvocationHandler()); // method chaining for the win! account.deposit(5000).deposit(4000).deposit(-2500); System.out.println("Balance: " + account.getBalance()); } }
我們從Proxy中的public static Object newProxyInstance(ClassLoader loader,Class<?>[] interfaces,InvocationHandler h)函式開始講起,這個函式的程式碼如下:
@CallerSensitive public static Object newProxyInstance(ClassLoader loader, Class<?>[] interfaces, InvocationHandler h) throws IllegalArgumentException { //判斷h是否為null,如果為null的話就跑出NullPointerException異常 Objects.requireNonNull(h); //將interfaces介面陣列拷貝到intfs中 final Class<?>[] intfs = interfaces.clone(); //進行許可權檢查,關於這個可以查相關資料,這裡不展開講 final SecurityManager sm = System.getSecurityManager(); if (sm != null) { checkProxyAccess(Reflection.getCallerClass(), loader, intfs); } /* * 該方法先從快取獲取代理類, 如果沒有再去生成一個代理類 */ Class<?> cl = getProxyClass0(loader, intfs); /* * Invoke its constructor with the designated invocation handler. */ try { if (sm != null) { checkNewProxyPermission(Reflection.getCallerClass(), cl); } // final Constructor<?> cons = cl.getConstructor(constructorParams); final InvocationHandler ih = h; if (!Modifier.isPublic(cl.getModifiers())) { AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Void>() { public Void run() { cons.setAccessible(true); return null; } }); } return cons.newInstance(new Object[]{h}); } catch (IllegalAccessException|InstantiationException e) { throw new InternalError(e.toString(), e); } catch (InvocationTargetException e) { Throwable t = e.getCause(); if (t instanceof RuntimeException) { throw (RuntimeException) t; } else { throw new InternalError(t.toString(), t); } } catch (NoSuchMethodException e) { throw new InternalError(e.toString(), e); } }
我們開始解析getProxyClass0函式,這個函式用來建立一個代理類物件,程式碼如下:
/** * Generate a proxy class. Must call the checkProxyAccess method * to perform permission checks before calling this. */ private static Class<?> getProxyClass0(ClassLoader loader, Class<?>... interfaces) { if (interfaces.length > 65535) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("interface limit exceeded"); } // If the proxy class defined by the given loader implementing // the given interfaces exists, this will simply return the cached copy; // otherwise, it will create the proxy class via the ProxyClassFactory //如果快取中存在代理類物件,那麼就直接返回,否則就會呼叫ProxyClassFactory這個工廠去生成一個代理類。 return proxyClassCache.get(loader, interfaces); }
我們現在進入proxyClassCache.get函式中(proxyClassCache類物件的建立程式碼如下:
private static final WeakCache<ClassLoader, Class<?>[], Class<?>> proxyClassCache = new WeakCache<>(new KeyFactory(), new ProxyClassFactory());)KeyFactory實現BiFunction<ClassLoader, Class<?>[], Object>,ProxyClassFactory實現BiFunction<ClassLoader, Class<?>[], Class<?>>。
其中KeyFactory的程式碼如下:
/**
* A function that maps an array of interfaces to an optimal key where
* Class objects representing interfaces are weakly referenced.
*/
private static final class KeyFactory
implements BiFunction<ClassLoader, Class<?>[], Object>
{
@Override
public Object apply(ClassLoader classLoader, Class<?>[] interfaces) {
switch (interfaces.length) {
case 1: return new Key1(interfaces[0]); // the most frequent
case 2: return new Key2(interfaces[0], interfaces[1]);
case 0: return key0;
default: return new KeyX(interfaces);
}
}
}ProxyClassFactory類程式碼如下:
/**
* A factory function that generates, defines and returns the proxy class given
* the ClassLoader and array of interfaces.
*/
private static final class ProxyClassFactory
implements BiFunction<ClassLoader, Class<?>[], Class<?>>
{
// prefix for all proxy class names
private static final String proxyClassNamePrefix = "$Proxy";
// next number to use for generation of unique proxy class names
private static final AtomicLong nextUniqueNumber = new AtomicLong();
@Override
public Class<?> apply(ClassLoader loader, Class<?>[] interfaces) {
Map<Class<?>, Boolean> interfaceSet = new IdentityHashMap<>(interfaces.length);
for (Class<?> intf : interfaces) {
/*
* Verify that the class loader resolves the name of this
* interface to the same Class object.
*/
Class<?> interfaceClass = null;
try {
interfaceClass = Class.forName(intf.getName(), false, loader);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
}
if (interfaceClass != intf) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
intf + " is not visible from class loader");
}
/*
* Verify that the Class object actually represents an
* interface.
*/
if (!interfaceClass.isInterface()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
interfaceClass.getName() + " is not an interface");
}
/*
* Verify that this interface is not a duplicate.
*/
if (interfaceSet.put(interfaceClass, Boolean.TRUE) != null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"repeated interface: " + interfaceClass.getName());
}
}
String proxyPkg = null; // package to define proxy class in
int accessFlags = Modifier.PUBLIC | Modifier.FINAL;
/*
* Record the package of a non-public proxy interface so that the
* proxy class will be defined in the same package. Verify that
* all non-public proxy interfaces are in the same package.
*/
for (Class<?> intf : interfaces) {
int flags = intf.getModifiers();
if (!Modifier.isPublic(flags)) {
accessFlags = Modifier.FINAL;
String name = intf.getName();
int n = name.lastIndexOf('.');
String pkg = ((n == -1) ? "" : name.substring(0, n + 1));
if (proxyPkg == null) {
proxyPkg = pkg;
} else if (!pkg.equals(proxyPkg)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"non-public interfaces from different packages");
}
}
}
if (proxyPkg == null) {
// if no non-public proxy interfaces, use com.sun.proxy package
proxyPkg = ReflectUtil.PROXY_PACKAGE + ".";
}
/*
* Choose a name for the proxy class to generate.
*/
long num = nextUniqueNumber.getAndIncrement();
String proxyName = proxyPkg + proxyClassNamePrefix + num;
/*
* Generate the specified proxy class.
*/
byte[] proxyClassFile = ProxyGenerator.generateProxyClass(
proxyName, interfaces, accessFlags);
try {
return defineClass0(loader, proxyName,
proxyClassFile, 0, proxyClassFile.length);
} catch (ClassFormatError e) {
/*
* A ClassFormatError here means that (barring bugs in the
* proxy class generation code) there was some other
* invalid aspect of the arguments supplied to the proxy
* class creation (such as virtual machine limitations
* exceeded).
*/
throw new IllegalArgumentException(e.toString());
}
}
}上面兩個類我們後面再講,在進入到proxyClassCache.get(loader, interfaces)的get函式前,我們先看看它的建構函式和成員變數,它們所在的類為WeakCache,程式碼如下:
//Reference引用佇列
private final ReferenceQueue<K> refQueue = new ReferenceQueue<>();
// the key type is Object for supporting null key
//快取的底層實現, key為一級快取, value為二級快取。 為了支援null, map的key型別設定為Object
private final ConcurrentMap<Object, ConcurrentMap<Object, Supplier<V>>> map = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
//reverseMap記錄了所有代理類生成器是否可用, 這是為了實現快取的過期機制
private final ConcurrentMap<Supplier<V>, Boolean> reverseMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
//生成二級快取key的工廠, 這裡傳入的是KeyFactory
private final BiFunction<K, P, ?> subKeyFactory;
//生成二級快取value的工廠, 這裡傳入的是ProxyClassFactory
private final BiFunction<K, P, V> valueFactory;
/**
* Construct an instance of {@code WeakCache}
*
* @param subKeyFactory a function mapping a pair of
* {@code (key, parameter) -> sub-key}
* @param valueFactory a function mapping a pair of
* {@code (key, parameter) -> value}
* @throws NullPointerException if {@code subKeyFactory} or
* {@code valueFactory} is null.
*/
//構造器, 傳入生成二級快取key的工廠和生成二級快取value的工廠
public WeakCache(BiFunction<K, P, ?> subKeyFactory,
BiFunction<K, P, V> valueFactory) {
this.subKeyFactory = Objects.requireNonNull(subKeyFactory);
this.valueFactory = Objects.requireNonNull(valueFactory);
}proxyClassCache.get(loader, interfaces)中get程式碼如下:
/**
* Look-up the value through the cache. This always evaluates the
* {@code subKeyFactory} function and optionally evaluates
* {@code valueFactory} function if there is no entry in the cache for given
* pair of (key, subKey) or the entry has already been cleared.
*
* @param key possibly null key
* @param parameter parameter used together with key to create sub-key and
* value (should not be null)
* @return the cached value (never null)
* @throws NullPointerException if {@code parameter} passed in or
* {@code sub-key} calculated by
* {@code subKeyFactory} or {@code value}
* calculated by {@code valueFactory} is null.
*/
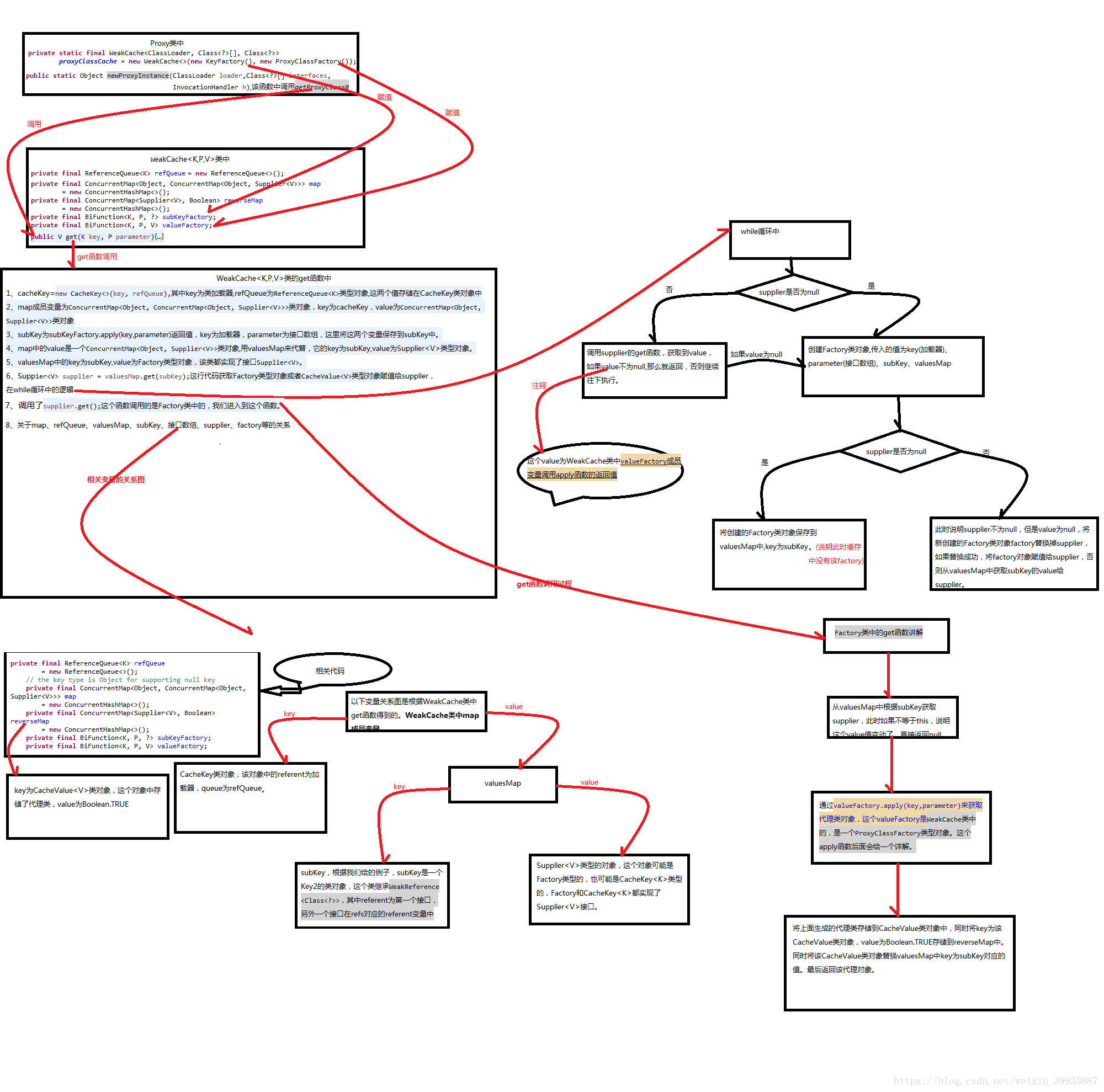
public V get(K key, P parameter) {
Objects.requireNonNull(parameter);
//清除過期的快取
expungeStaleEntries();
//將ClassLoader包裝成CacheKey, 作為一級快取的key,其中cacheKey中的referent成員變數值為key,queue成員變數為refQueue
Object cacheKey = CacheKey.valueOf(key, refQueue);
// lazily install the 2nd level valuesMap for the particular cacheKey
//獲取得到二級快取
ConcurrentMap<Object, Supplier<V>> valuesMap = map.get(cacheKey);
//如果根據ClassLoader沒有獲取到對應的值
if (valuesMap == null) {
//以CAS方式放入, 如果不存在則放入,否則返回原先的值
ConcurrentMap<Object, Supplier<V>> oldValuesMap = map.putIfAbsent(cacheKey, valuesMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>());
//如果oldValuesMap有值, 說明放入失敗,即cacheKey存在(至於為什麼可以去看看putIfAbsent這個方法),否則cacheKey不存在
if (oldValuesMap != null) {
valuesMap = oldValuesMap;
}
}
// create subKey and retrieve the possible Supplier<V> stored by that
// subKey from valuesMap
//根據代理類實現的介面陣列來生成二級快取key, 分為key0, key1, key2, keyx,這裡apply呼叫的是KeyFactory類中的,返回Key2型別對 //象,其中parameter中兩個介面,其中第一個儲存到Key2中的referent成員變數,第二個在此基礎上建立一個新的WeakReference類對 //象中,這個類物件中的referent成員變數為第二個介面。
Object subKey = Objects.requireNonNull(subKeyFactory.apply(key, parameter));
//這裡通過subKey獲取到二級快取的值
Supplier<V> supplier = valuesMap.get(subKey);
Factory factory = null;
while (true) {
//如果通過subKey取出來的值不為空
if (supplier != null) {
// supplier might be a Factory or a CacheValue<V> instance
//在這裡supplier可能是一個Factory也可能會是一個CacheValue,在這裡不作判斷, 而是在Supplier實現類的get方法裡面進行驗證
V value = supplier.get();
if (value != null) {
return value;
}
}
// else no supplier in cache
// or a supplier that returned null (could be a cleared CacheValue
// or a Factory that wasn't successful in installing the CacheValue)
// lazily construct a Factory
if (factory == null) {
//新建一個Factory例項作為subKey對應的值
factory = new Factory(key, parameter, subKey, valuesMap);
}
if (supplier == null) {
//到這裡表明subKey沒有對應的值, 就將factory作為subKey的值放入
supplier = valuesMap.putIfAbsent(subKey, factory);
if (supplier == null) {
// successfully installed Factory
supplier = factory;
}
// else retry with winning supplier
} else {
//期間可能其他執行緒修改了值, 那麼就將原先的值替換
if (valuesMap.replace(subKey, supplier, factory)) {
// successfully replaced
// cleared CacheEntry / unsuccessful Factory
// with our Factory
supplier = factory;
} else {
// retry with current supplier
supplier = valuesMap.get(subKey);
}
}
}
}進入Factory類,程式碼如下:
/**
* A factory {@link Supplier} that implements the lazy synchronized
* construction of the value and installment of it into the cache.
*/
private final class Factory implements Supplier<V> {
//一級快取key, 根據ClassLoader生成
private final K key;
//代理類實現的介面陣列
private final P parameter;
//二級快取key, 根據介面陣列生成
private final Object subKey;
//二級快取
private final ConcurrentMap<Object, Supplier<V>> valuesMap;
Factory(K key, P parameter, Object subKey,
ConcurrentMap<Object, Supplier<V>> valuesMap) {
this.key = key;
this.parameter = parameter;
this.subKey = subKey;
this.valuesMap = valuesMap;
}
@Override
public synchronized V get() { // serialize access
//這裡再一次去二級快取裡面獲取Supplier, 用來驗證是否是Factory本身
Supplier<V> supplier = valuesMap.get(subKey);
if (supplier != this) {
// something changed while we were waiting:
// might be that we were replaced by a CacheValue
// or were removed because of failure ->
// return null to signal WeakCache.get() to retry
// the loop
//在這裡驗證supplier是否是Factory例項本身, 如果不則返回null讓呼叫者繼續輪詢重試
//期間supplier可能替換成了CacheValue, 或者由於生成代理類失敗被從二級快取中移除了
return null;
}
// else still us (supplier == this)
// create new value
V value = null;
try {
//委託valueFactory去生成代理類, 這裡會通過傳入的ProxyClassFactory去生成代理類
value = Objects.requireNonNull(valueFactory.apply(key, parameter));
} finally {
if (value == null) { // remove us on failure
//如果生成代理類失敗, 就將這個二級快取刪除
valuesMap.remove(subKey, this);
}
}
// the only path to reach here is with non-null value
//只有value的值不為空才能到達這裡
assert value != null;
// wrap value with CacheValue (WeakReference)
//使用弱引用包裝生成的代理類
CacheValue<V> cacheValue = new CacheValue<>(value);
// put into reverseMap
//對cacheValue進行標記
reverseMap.put(cacheValue, Boolean.TRUE);
// try replacing us with CacheValue (this should always succeed)
//將包裝後的cacheValue放入二級快取中, 這個操作必須成功, 否則就報錯
if (!valuesMap.replace(subKey, this, cacheValue)) {
throw new AssertionError("Should not reach here");
}
// successfully replaced us with new CacheValue -> return the value
// wrapped by it
return value;
}
}流程如下:
接下來我們進入ProxyClassFactory類中的apply函式中,相關程式碼如下:
/**
* A factory function that generates, defines and returns the proxy class given
* the ClassLoader and array of interfaces.
*/
private static final class ProxyClassFactory
implements BiFunction<ClassLoader, Class<?>[], Class<?>>
{
// prefix for all proxy class names
//代理類名稱字首
private static final String proxyClassNamePrefix = "$Proxy";
// next number to use for generation of unique proxy class names
//採用一個原子類物件,用來生成一個計數,這個計數用來拼成代理類物件名稱
private static final AtomicLong nextUniqueNumber = new AtomicLong();
@Override
//loader為載入器類物件,interfaces為介面陣列
public Class<?> apply(ClassLoader loader, Class<?>[] interfaces) {
Map<Class<?>, Boolean> interfaceSet = new IdentityHashMap<>(interfaces.length);
//遍歷介面陣列
for (Class<?> intf : interfaces) {
/*
* Verify that the class loader resolves the name of this
* interface to the same Class object.
*/
Class<?> interfaceClass = null;
try {
//通過loader載入器獲取到介面對應的Class類物件
interfaceClass = Class.forName(intf.getName(), false, loader);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
}
if (interfaceClass != intf) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
intf + " is not visible from class loader");
}
/*
* Verify that the Class object actually represents an
* interface.
*/
if (!interfaceClass.isInterface()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
interfaceClass.getName() + " is not an interface");
}
/*
* Verify that this interface is not a duplicate.
*/
//將該介面的Class類物件儲存到map容器interfaceSet中
if (interfaceSet.put(interfaceClass, Boolean.TRUE) != null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"repeated interface: " + interfaceClass.getName());
}
}
//整個迴圈下來,將所有的介面的Class類物件都儲存在了interfaceSet中
String proxyPkg = null; // package to define proxy class in
int accessFlags = Modifier.PUBLIC | Modifier.FINAL;
/*
* Record the package of a non-public proxy interface so that the
* proxy class will be defined in the same package. Verify that
* all non-public proxy interfaces are in the same package.
*/
//繼續對介面進行迴圈
for (Class<?> intf : interfaces) {
int flags = intf.getModifiers();
//如果該介面不為public
if (!Modifier.isPublic(flags)) {
accessFlags = Modifier.FINAL;
//返回介面名稱(例如String.class.getName()獲得java.lang.String)
String name = intf.getName();
int n = name.lastIndexOf('.');
//獲取該介面對應的包名稱
String pkg = ((n == -1) ? "" : name.substring(0, n + 1));
if (proxyPkg == null) {
proxyPkg = pkg;
} else if (!pkg.equals(proxyPkg)) {
//走到這裡說明有些介面不在同一個包中,也就是這些介面要麼都是public,要麼都不為public且要在同一個包中。
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"non-public interfaces from different packages");
}
}
}
//如果proxyPkg為null,那麼就採用預設的包名稱
if (proxyPkg == null) {
// if no non-public proxy interfaces, use com.sun.proxy package
//此時proxyPkg為com.sun.proxy.
proxyPkg = ReflectUtil.PROXY_PACKAGE + ".";
}
/*
* Choose a name for the proxy class to generate.
*/
//獲取一個唯一計數值
long num = nextUniqueNumber.getAndIncrement();
//拼成代理類名稱,如果num為0且在預設包的情況下那麼proxyName為com.sun.proxy.$Proxy0
String proxyName = proxyPkg + proxyClassNamePrefix + num;
/*
* Generate the specified proxy class.
*/
//開始針對該代理類名稱獲取相應的class位元組碼內容
byte[] proxyClassFile = ProxyGenerator.generateProxyClass(
proxyName, interfaces, accessFlags);
try {
//根據該位元組碼內容生成一個對應的Class類物件。
return defineClass0(loader, proxyName,
proxyClassFile, 0, proxyClassFile.length);
} catch (ClassFormatError e) {
/*
* A ClassFormatError here means that (barring bugs in the
* proxy class generation code) there was some other
* invalid aspect of the arguments supplied to the proxy
* class creation (such as virtual machine limitations
* exceeded).
*/
throw new IllegalArgumentException(e.toString());
}
}
}接下來我們進入到ProxyGenerator.generateProxyClass(proxyName, interfaces, accessFlags)函式中,程式碼如下:
public static byte[] generateProxyClass(String s, Class aclass[], int i)
{
ProxyGenerator proxygenerator = new ProxyGenerator(s, aclass, i);
//生成Class位元組碼內容
byte abyte0[] = proxygenerator.generateClassFile();
//判斷是否要將該位元組碼內容儲存到檔案中,
//我們在例項程式碼中新增System.getProperties().put("sun.misc.ProxyGenerator.saveGeneratedFiles", "true");就可以將位元組碼保 //存到相應的檔案中
if(saveGeneratedFiles)
AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction(s, abyte0) {
public Void run()
{
try
{
int j = name.lastIndexOf('.');
Path path;
if(j > 0)
{
Path path1 = Paths.get(name.substring(0, j).replace('.', File.separatorChar), new String[0]);
Files.createDirectories(path1, new FileAttribute[0]);
path = path1.resolve((new StringBuilder()).append(name.substring(j + 1, name.length())).append(".class").toString());
} else
{
path = Paths.get((new StringBuilder()).append(name).append(".class").toString(), new String[0]);
}
Files.write(path, classFile, new OpenOption[0]);
return null;
}
catch(IOException ioexception)
{
throw new InternalError((new StringBuilder()).append("I/O exception saving generated file: ").append(ioexception).toString());
}
}
public volatile Object run()
{
return run();
}
final String val$name;
final byte val$classFile[];
{
name = s;
classFile = abyte0;
super();
}
}
);
//如果不用儲存,那麼就直接返回位元組碼內容
return abyte0;
}接下來我們開始分析defineClass0(loader, proxyName,proxyClassFile, 0, proxyClassFile.length);函式,這是一個native方法,負責位元組碼載入的實現,並返回對應的Class物件。根據上面的例子,我們得到的代理類位元組碼檔案結構如下:
經過反編譯後,程式碼如下:
package com.jd.dynamicproxy.dynamicproxy;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.lang.reflect.UndeclaredThrowableException;
final class $Proxy0 extends Proxy
implements App.Account, Serializable
{
private static Method m1;
private static Method m4;
private static Method m2;
private static Method m3;
private static Method m0;
public $Proxy0(InvocationHandler paramInvocationHandler)
throws
{
super(paramInvocationHandler);
}
public final boolean equals(Object paramObject)
throws
{
try
{
return ((Boolean)this.h.invoke(this, m1, new Object[] { paramObject })).booleanValue();
}
catch (RuntimeException localRuntimeException)
{
throw localRuntimeException;
}
catch (Throwable localThrowable)
{
}
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(localThrowable);
}
public final double getBalance()
throws
{
try
{
return ((Double)this.h.invoke(this, m4, null)).doubleValue();
}
catch (RuntimeException localRuntimeException)
{
throw localRuntimeException;
}
catch (Throwable localThrowable)
{
}
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(localThrowable);
}
public final String toString()
throws
{
try
{
return (String)this.h.invoke(this, m2, null);
}
catch (RuntimeException localRuntimeException)
{
throw localRuntimeException;
}
catch (Throwable localThrowable)
{
}
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(localThrowable);
}
public final App.Account deposit(double paramDouble)
throws
{
try
{
return (Serializable)this.h.invoke(this, m3, new Object[] { Double.valueOf(paramDouble) });
}
catch (RuntimeException localRuntimeException)
{
throw localRuntimeException;
}
catch (Throwable localThrowable)
{
}
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(localThrowable);
}
public final int hashCode()
throws
{
try
{
return ((Integer)this.h.invoke(this, m0, null)).intValue();
}
catch (RuntimeException localRuntimeException)
{
throw localRuntimeException;
}
catch (Throwable localThrowable)
{
}
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(localThrowable);
}
static
{
try
{
m1 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object").getMethod("equals", new Class[] { Class.forName("java.lang.Object") });
m4 = Class.forName("com.jd.dynamicproxy.dynamicproxy.App$Account").getMethod("getBalance", new Class[0]);
m2 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object").getMethod("toString", new Class[0]);
m3 = Class.forName("com.jd.dynamicproxy.dynamicproxy.App$Account").getMethod("deposit", new Class[] { Double.TYPE });
m0 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object").getMethod("hashCode", new Class[0]);
return;
}
catch (NoSuchMethodException localNoSuchMethodException)
{
throw new NoSuchMethodError(localNoSuchMethodException.getMessage());
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException localClassNotFoundException)
{
}
throw new NoClassDefFoundError(localClassNotFoundException.getMessage());
}
}從中可以看到,該代理類繼承了Proxy類且實現了相關的介面,你呼叫介面方法都會去呼叫InvocationHandler實現類中的invoke函式,Proxy中有m0、m1、m2、m3、m4五個Method類物件,其中包括了實現介面的。在呼叫invoke函式的時候會將相應的Method類物件作為引數傳入,從而實現代理的功能。