Apollo學習(二): Java客戶端使用
說明
本文主要是以springboot專案為基礎,學習從Apollo配置中心獲取值得使用方法。
正文
通過上篇《Apollo學習(一):在本地Windows系統下搭建Apollo配置中心》的學習,已經在本地快速搭建了一個Apollo配置中心,本篇通過構建springboot專案來學習配置中心的使用。本文主要依據官方文件來進行學習。
1.構建springboot專案
先通過start.spring.io構建springboot專案,選擇新增web依賴,eureka client依賴,再新增Apollo客戶端的依賴。
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.ctrip.framework.apollo</groupId> <artifactId>apollo-client</artifactId> <version>1.0.0</version> </dependency>
通過之前的學習,我們已經知道Apollo的configServer已經集成了eureka,它本身就是一個註冊中心,通過將springboot專案註冊到configserver用於服務發現。
Apollo客戶端依賴於AppId,Apollo Meta Server等環境資訊來工作。
AppId
首先AppId是應用的身份資訊,必須是唯一的且型別為String,在配置中心新建專案時建立的AppId必須與要使用該配置的專案的AppId一致。
這裡有三種方式設定AppId,優先順序從高到低:
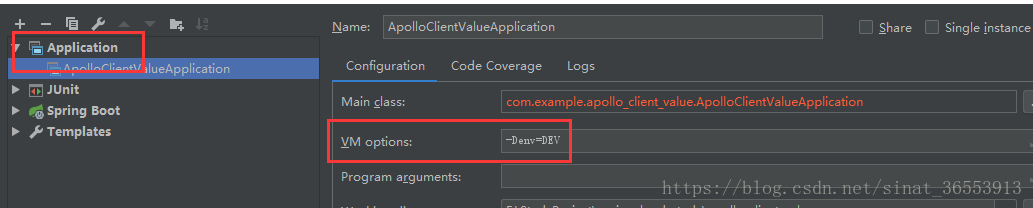
- 通過System Property, 在 IDEA中建立專案的Application,在VM options中指定AppId :
-Dapp.id=YOUR-APP-ID - 通過在application.properties檔案中指定,
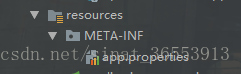
app.id=YOUR-APP-ID - 通過在resources檔案下建立META-INF檔案,在該目錄下建立app.properties檔案,在該檔案指定AppId:
app.id=YOUR-APP-ID
Apollo Meta Server
Apollo支援應用在不同的環境有不同的配置,所以需要在執行時提供給Apollo客戶端當前環境的Apollo Meta Server資訊。預設情況下meta server和config server時部署在一個jvm程序中,所以meta地址就是config server的地址。
接下來,介紹幾種常用的配置meta server的方式,詳見官方文件。
優先順序從高到低分別為:
- 通過Java System Property 在java的啟動指令碼中,在VM options中指定
-Dapollo.meta=http://config-service-url - 通過Spring Boot的配置檔案
在application.properties或bootstrap.properties檔案中指定apollo.meta=http://config-service-url - 通過在作業系統中的server.properties配置檔案
Windows中,檔案位置為C:\opt\settings\server.properties,在其中配置apollo.meta=http://config-service-url - 通過在app.properties配置檔案中指定
apollo.meta=http://config-service-url
Environment
指定程式的執行環境,這裡配置為DEV 也就是開發環境。介紹常用的幾種配置方式:
- 通過Java System Property 在java的啟動指令碼,在VM options中指定
-Denv=DEV - 通過系統的配置檔案 在C:\opt\settings\server.properties中配置
env=DEV
在啟動類添加註解
在啟動類上新增@EnableDiscoveryClient和@EnableApolloConfig註解
@EnableDiscoveryClient
@EnableApolloConfig
@SpringBootApplication
public class ApolloClientValueApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ApolloClientValueApplication.class, args);
}
}
構建專案的基礎配置介紹完畢,接下來學習客戶端的用法
2.客戶端的使用
Apollo支援API方式和Spring方式。
API方式靈活,功能完備,配置值實時更新(熱釋出),支援所有java環境。
Spring有多種方式,如Placeholder、Spring Boot的@ConfigurationProperties方式、和API結合的方式。
API
API是最簡單,高效使用Apollo配置的方式,不依賴Spring礦建即可使用。
以下程式碼在springboot中演示如何使用Config得到配置,其他的詳細的使用方法詳見官方文件
@Component
public class GetValueByAPI {
@PostConstruct
public void getValue(){
Config config = ConfigService.getAppConfig();
String key = "changeKey";
String defaultValue = "apollo_client";
zhujie String value = config.getProperty(key,defaultValue);
System.out.println(String.format("value is %s",value));
}
}
Spring
配置這裡只介紹基於java的配置和在Spring Boot初始bootstrap階段注入配置
基於java配置
基於java配置有兩個重要的註解,@EnableApolloConfig和@Configuration,這兩個註解必須同時使用,否則不會生效。
以下程式碼是注入預設namespace到spring中
@Configuration
@EnableApolloConfig(order = 1)
public class JavaConfig {
@Bean
public ConfigJavaBean configJavaBean(){
ConfigJavaBean configJavaBean = new ConfigJavaBean();
return configJavaBean;
}
}
namespace就相當於在專案中區分不同的配置檔案,如redis.properties,mongo.properties.預設的namespace就如application.properties,namespace有私有和公有,公有的namespace所有的專案都可以讀的,私有的只有本專案可以使用,並且如果公有的namespace和私有的namespace中有相同的key,私用的會覆蓋公有中的值。
通過@EnableApolloConfig來載入不同的namesapce
@Configuration
@EnableApolloConfig(value = {"javaconfig"},order = 2)
public class JavaConfigDiffNS {
@Bean
public ConfigJavaBean2 configJavaBean2(){
return new ConfigJavaBean2();
}
}
同時可以通過Order來指定配置順序,值越低優先順序越高。
這裡要注意當有不同namespace,且其中有相同的key, 私有的namespace中的值會覆蓋公有的,order順序在此時不起作用,也就是低優先順序的不會覆蓋高優先順序。但當不同的namespace都是私有的,這時order值決定使用的值,低優先順序namespace中會覆蓋掉高優先順序中相同key的值
在Spring Boot初始bootstrap階段注入配置
什麼時候需要在初始bootstrap階段注入配置?
當springboot啟動時需要提早準備好其他bean的初始化條件,如使用@ConditionalOnProperty或某些starter啟動階段需要讀取配置。
通常使用以下方式來進行配置:
在bootstrap.properties中注入預設namespace ,通過apollo.bootstrap.enabled = true,其他的namespace可以通過apollo.bootstrap.namespaces = application,othernamespace
如何配置介紹完後,接下來介紹怎麼使用配置,怎麼從Apollo配置中心讀取配置資訊。上面介紹了API的方式,直接使用Config物件的方法,在spring中Apollo也提供了多種方式。
Placeholder方式
該方式的使用基本格式為@Value("${key:defaultValue}"),建議在實際使用時儘量給出預設值,以免由於key沒有定義導致執行時錯誤。 從v0.10.0開始的版本支援placeholder在執行時自動更新
public class ConfigJavaBean {
@Value("${oneKey:defaultValue}")
private String oneKey;
@Value("${twoKey:22}")
private String twoKey;
public String getOneKey() {
return oneKey;
}
public void setOneKey(String oneKey) {
this.oneKey = oneKey;
}
public String getTwoKey() {
return twoKey;
}
public void setTwoKey(String twoKey) {
this.twoKey = twoKey;
}
}
@ConfigurationOnProperties方式
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "redis")
public class RedisConInfo {
private String host;
private String port;
public String getHost() {
return host;
}
public void setHost(String host) {
this.host = host;
}
public String getPort() {
return port;
}
public void setPort(String port) {
this.port = port;
}
}
進行配置
@Configuration
@EnableApolloConfig(value = {"redis"},order = 3)
public class RedisConfig {
@Bean
@RefreshScope
public RedisConInfo redisConInfo(){
return new RedisConInfo();
}
}
使用這種方式若需要在Apollo配置變化時自動更新,需要配合Spring Cloud的RefreshScope使用
@Component
public class RedisConfigRefresh {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(RedisConfigRefresh.class);
@Autowired
private RedisConInfo redisConInfo;
@Autowired
private RefreshScope refreshScope;
@ApolloConfigChangeListener({"redis"})
public void onChange(ConfigChangeEvent changeEvent){
boolean ischanged = false;
for(String changeKey : changeEvent.changedKeys()){
if(changeKey.startsWith("redis")){
ischanged = true;
break;
}
}
if(!ischanged){
return;
}
logger.info("before refresh {}",redisConInfo.getHost() + " : " + redisConInfo.getPort());
refreshScope.refresh("redisConInfo");
// refreshScope.refreshAll(); //refresh all
logger.info("after refresh {}",redisConInfo.getHost() + " : " + redisConInfo.getPort());
}
}
注意 必須在配置資訊的bean上新增 @RefreshScope註解
Annotation
主要是@ApolloConfig 用來自動注入Config物件和@ApolloConfigChangeListener來自動注入ConfigChangeListener
@Configuration
@EnableApolloConfig({"mongo"})
public class MongoConfigAnno {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MongoConfigAnno.class);
@ApolloConfig("mongo") //inject config for namespace mongo
private Config config;
@Value("${mongo.host:localhost}")
private String host;
@Value("${mongo.port:1234}")
private String port;
public String getHost() {
return host;
}
public String getPort() {
return port;
}
@ApolloConfigChangeListener("mongo")
private void someOnChange(ConfigChangeEvent changeEvent){
logger.info("before update {} ",this.toString());
if(changeEvent.isChanged("mongo.host")){
this.host = config.getProperty("mongo.host","defaultValue");
}
if(changeEvent.isChanged("mongo.port")){
this.port = config.getProperty("mongo.port","1234");
}
logger.info("after update {} ",this.toString());
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return String.format("mongo configuration--- host: %s port: %s",this.host,this.port);
}
}
原始碼地址:https://github.com/Edenwds/springcloud_study/tree/master/apollo_client_value