選擇搜尋(selective search)python實現
選擇搜尋selsctive search
前言
最近在學習區域卷積神經網路(RCNN)時,候選框產生使用了選擇搜尋(selective search),為了更透徹地理解RCNN的工作原理,所以決定基於python程式碼,實現選擇搜尋(selective search)。
簡介
關於選擇搜尋(selective search)的基本原理和初步認知,可以參考以下部落格:
在這裡主要結合自己的理解作簡要總結和梳理:
- 使用 Efficient Graph-Based Image Segmentation的方法獲取原始分割區域R={r1,r2,…,rn},具體可見我的另一篇部落格:
https://blog.csdn.net/u014796085/article/details/83449972 - 初始化相似度集合S=∅
- 計算兩兩相鄰區域之間的相似度,將其新增到相似度集合S中
- 從相似度集合S中找出,相似度最大的兩個區域 ri 和rj,將其合併成為一個區域 rt,從相似度集合中除去原先與ri和rj相鄰區域之間計算的相似度,計算rt與其相鄰區域(原先與ri或rj相鄰的區域)的相似度,將其結果新增的到相似度集合S中。同時將新區域 rt 新增區域集合R中。
- 重複步驟5,直到S=∅,即最後一個新區域rt為整幅影象。
- 獲取R中每個區域的Bounding Boxes,去除畫素數量小於2000,以及寬高比大於1.2的,剩餘的框就是物體位置的可能結果L
程式碼實現與解讀
影象初步分割
def _generate_segments(img_path, neighbor, sigma, scale, min_size): # open the Image im_mask = graphbased_segmentation(img_path, neighbor, sigma, scale, min_size) im_orig = skimage.io.imread(img_path) # merge mask channel to the image as a 4th channel im_orig = numpy.append( im_orig, numpy.zeros(im_orig.shape[:2])[:, :, numpy.newaxis], axis=2) im_orig[:, :, 3] = im_mask return im_orig
對原影象作影象分割,把分割的每個畫素所屬區域的編號作為影象的第4通道。
區域相似度的定義
def _calc_colour_hist(img):
"""
calculate colour histogram for each region
the size of output histogram will be BINS * COLOUR_CHANNELS(3)
number of bins is 25 as same as [uijlings_ijcv2013_draft.pdf]
extract HSV
"""
BINS = 25
hist = numpy.array([])
for colour_channel in (0, 1, 2):
# extracting one colour channel
c = img[:, colour_channel]
# calculate histogram for each colour and join to the result
hist = numpy.concatenate(
[hist] + [numpy.histogram(c, BINS, (0.0, 255.0))[0]])
# L1 normalize
hist = hist / len(img)
return hist
def _calc_texture_gradient(img):
"""
calculate texture gradient for entire image
The original SelectiveSearch algorithm proposed Gaussian derivative
for 8 orientations, but we use LBP instead.
output will be [height(*)][width(*)]
"""
ret = numpy.zeros((img.shape[0], img.shape[1], img.shape[2]))
for colour_channel in (0, 1, 2):
ret[:, :, colour_channel] = skimage.feature.local_binary_pattern(
img[:, :, colour_channel], 8, 1.0)
return ret
def _calc_texture_hist(img):
"""
calculate texture histogram for each region
calculate the histogram of gradient for each colours
the size of output histogram will be
BINS * ORIENTATIONS * COLOUR_CHANNELS(3)
"""
BINS = 10
hist = numpy.array([])
for colour_channel in (0, 1, 2):
# mask by the colour channel
fd = img[:, colour_channel]
# calculate histogram for each orientation and concatenate them all
# and join to the result
hist = numpy.concatenate(
[hist] + [numpy.histogram(fd, BINS, (0.0, 1.0))[0]])
# L1 Normalize
hist = hist / len(img)
return hist
_calc_colour_hist(img),計算影象的顏色直方圖,用於計算兩個區域的顏色相似度。
_calc_texture_gradient(img),計算影象的紋理梯度,用於計算其紋理直方圖。
_calc_texture_hist(img),計算紋理直方圖,用來計算兩個區域的紋理相似度。
def _sim_colour(r1, r2):
"""
calculate the sum of histogram intersection of colour
"""
# return sum([min(a, b) for a, b in zip(r1["hist_c"], r2["hist_c"])])
return sum([1 if a==b else 1-float(abs(a - b))/max(a, b) for a, b in zip(r1["hist_c"], r2["hist_c"])])/len(r1)
def _sim_texture(r1, r2):
"""
calculate the sum of histogram intersection of texture
"""
# return sum([min(a, b) for a, b in zip(r1["hist_t"], r2["hist_t"])])
return sum([1 if a==b else 1-float(abs(a - b))/max(a, b) for a, b in zip(r1["hist_t"], r2["hist_t"])])/len(r1)
def _sim_size(r1, r2, imsize):
"""
calculate the size similarity over the image
"""
return 1.0 - (r1["size"] + r2["size"]) / imsize
def _sim_fill(r1, r2, imsize):
"""
calculate the fill similarity over the image
"""
bbsize = (
(max(r1["max_x"], r2["max_x"]) - min(r1["min_x"], r2["min_x"]))
* (max(r1["max_y"], r2["max_y"]) - min(r1["min_y"], r2["min_y"]))
)
return 1.0 - (bbsize - r1["size"] - r2["size"]) / imsize
def _calc_sim(r1, r2, imsize):
return (_sim_colour(r1, r2) + _sim_texture(r1, r2)
+ _sim_size(r1, r2, imsize) + _sim_fill(r1, r2, imsize))
計算區域r1,r2的顏色相似度、紋理相似度、大小相似度、吻合相似度,將幾種相似度結合到一起,得到r1、r2綜合相似度。具體可以參見簡介中第一篇部落格。
建立區域詞典R
def _extract_regions(img):
# 建立字典
R = {}
# get hsv image
hsv = skimage.color.rgb2hsv(img[:, :, :3])
# pass 1: count pixel positions
# 遍歷img中所有的元素,y為索引,i為一個(r,g,b,l)
for y, i in enumerate(img):
for x, (r, g, b, l) in enumerate(i):
# initialize a new region
if l not in R:
R[l] = {
"min_x": 0xffff, "min_y": 0xffff,
"max_x": 0, "max_y": 0, "labels": [l]}
# bounding box
if R[l]["min_x"] > x:
R[l]["min_x"] = x
if R[l]["min_y"] > y:
R[l]["min_y"] = y
if R[l]["max_x"] < x:
R[l]["max_x"] = x
if R[l]["max_y"] < y:
R[l]["max_y"] = y
# pass 2: calculate texture gradient
tex_grad = _calc_texture_gradient(img)
# pass 3: calculate colour histogram of each region
for k, v in list(R.items()):
# colour histogram
masked_pixels = hsv[:, :, :][img[:, :, 3] == k]
R[k]["size"] = len(masked_pixels / 4)
R[k]["hist_c"] = _calc_colour_hist(masked_pixels)
# texture histogram
R[k]["hist_t"] = _calc_texture_hist(tex_grad[:, :][img[:, :, 3] == k])
return R
建立區域字典R,n為區域數。
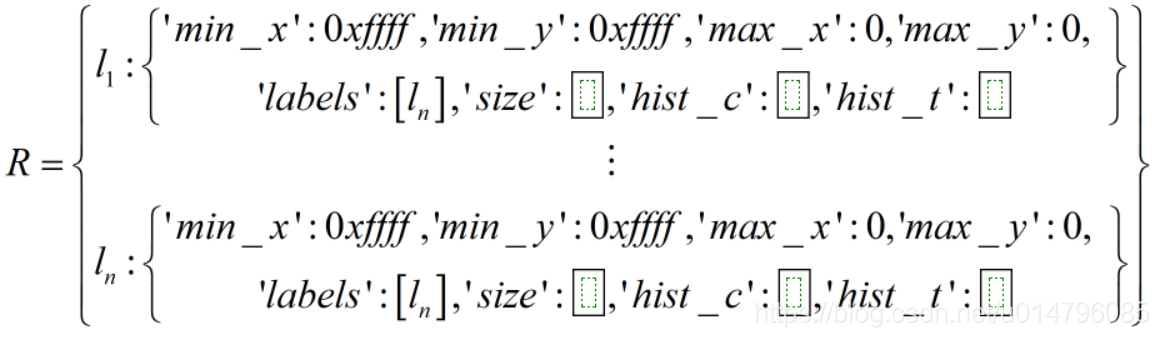
建立鄰接列表neighbours
def _extract_neighbours(regions):
def intersect(a, b):
if (a["min_x"] < b["min_x"] < a["max_x"]
and a["min_y"] < b["min_y"] < a["max_y"]) or (
a["min_x"] < b["max_x"] < a["max_x"]
and a["min_y"] < b["max_y"] < a["max_y"]) or (
a["min_x"] < b["min_x"] < a["max_x"]
and a["min_y"] < b["max_y"] < a["max_y"]) or (
a["min_x"] < b["max_x"] < a["max_x"]
and a["min_y"] < b["min_y"] < a["max_y"]):
return True
return False
R = list(regions.items())
neighbours = []
for cur, a in enumerate(R[:-1]):
for b in R[cur + 1:]:
if intersect(a[1], b[1]):
neighbours.append((a, b))
return neighbours
(1) 定義兩區域相交:區域b的最小外接矩形中任意一個頂點,在區域a的最小外接矩形內部,就認為區域a和b相交。a,b相交即認為a、b相鄰。
(2) 不重複遍歷R中所有的一對區域,如果相交,就加入到相鄰列表neighbours中。
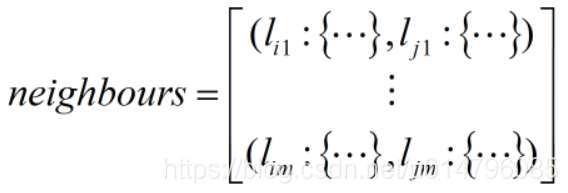
為區域的編號,{…}為描述該區域的詞典。
定義區域合併
def _merge_regions(r1, r2):
new_size = r1["size"] + r2["size"]
rt = {
"min_x": min(r1["min_x"], r2["min_x"]),
"min_y": min(r1["min_y"], r2["min_y"]),
"max_x": max(r1["max_x"], r2["max_x"]),
"max_y": max(r1["max_y"], r2["max_y"]),
"size": new_size,
"hist_c": (
r1["hist_c"] * r1["size"] + r2["hist_c"] * r2["size"]) / new_size,
"hist_t": (
r1["hist_t"] * r1["size"] + r2["hist_t"] * r2["size"]) / new_size,
"labels": r1["labels"] + r2["labels"]
}
return rt
合併區域r1、r2,生成新的區域rt,注意此時區域詞典R中r1、r2對應的詞典不刪除、不改變,只增加新區域rt對應的詞典。
選擇搜尋
def selective_search(
img_path, neighbor, sigma, scale, min_size):
# load image and get smallest regions
# region label is stored in the 4th value of each pixel [r,g,b,(region)]
img = _generate_segments(img_path, neighbor, sigma, scale, min_size)
if img is None:
return None, {}
imsize = img.shape[0] * img.shape[1]
R = _extract_regions(img)
# print(R[0])
# extract neighbouring information
neighbours = _extract_neighbours(R)
# print(neighbours[0])
# calculate initial similarities
# 建立字典
S = {}
for (ai, ar), (bi, br) in neighbours:
# print(ai)
# print(bi)
S[(ai, bi)] = _calc_sim(ar, br, imsize)
# hierarchal search
while S != {}:
# get highest similarity
i, j = sorted(S.items(), key=lambda i: i[1])[-1][0]
# merge corresponding regions
t = max(R.keys()) + 1.0
R[t] = _merge_regions(R[i], R[j])
# mark similarities for regions to be removed
key_to_delete = []
for k, v in list(S.items()):
if (i in k) or (j in k):
# 去除這兩個區域與相鄰區域的相似度
key_to_delete.append(k)
# remove old similarities of related regions
for k in key_to_delete:
del S[k]
# calculate similarity set with the new region
# 計算合併後區域與相鄰區域的相似度
for k in [a for a in key_to_delete if a != (i, j)]:
n = k[1] if k[0] in (i, j) else k[0]
S[(t, n)] = _calc_sim(R[t], R[n], imsize)
regions = []
for k, r in list(R.items()):
regions.append({
'rect': (
r['min_x'], r['min_y'],
r['max_x'] - r['min_x'], r['max_y'] - r['min_y']),
'size': r['size'],
'labels': r['labels']
})
return img, regions
(1) 圖片分割,生成原始的區域詞典R。
(2) 建立相似度詞典S,對所有相鄰區域,計算他們的相似度:
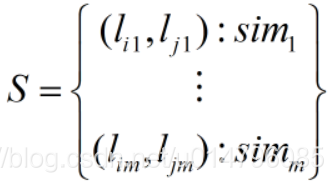
sim為兩個相鄰區域的綜合相似度。
(3) 得到相似度最高的兩個相鄰區域;合併這兩個相鄰區域,得到新區域;去除詞典S中這兩個區域與相鄰區域的相似度,計算合併後區域與相鄰區域的相似度。重複這一步,直到S為空,即最後合併得到的新區域就是整幅影象。
(4) 建立列表region,儲存區域詞典R中所有區域對應的詞典{‘rect’: ,‘size’: ,‘labels’: }:
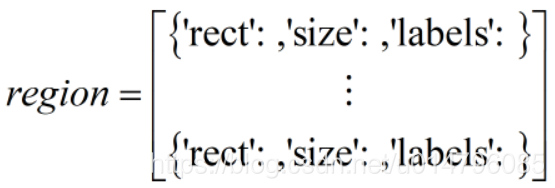
主函式
def main():
img_path = "2.jpg"
# loading astronaut image
img = skimage.io.imread(img_path)
# perform selective search
img_lbl, regions = selective_search(
img_path, neighbor = 8 , sigma = 0.5, scale = 200, min_size = 20)
# 建立集合candidate
candidates = set()
for r in regions:
# excluding same rectangle (with different segments)
if r['rect'] in candidates:
continue
# excluding regions smaller than 2000 pixels
if r['size'] < 2000:
continue
# distorted rects
x, y, w, h = r['rect']
if w / h > 1.2 or h / w > 1.2:
continue
candidates.add(r['rect'])
# draw rectangles on the original image
fig, ax = plt.subplots(ncols=1, nrows=1, figsize=(6, 6))
ax.imshow(img)
for x, y, w, h in candidates:
print(x, y, w, h)
rect = mpatches.Rectangle(
(x, y), w, h, fill=False, edgecolor='red', linewidth=1)
ax.add_patch(rect)
plt.show()
得到列表region,儲存所有舊區域和新區域對應詞典,取出包含畫素數量大於2000的,和寬高比小於1.2的,作為候選框。
問題
關於區域的相似度(顏色、紋理、大小、吻合),不是特別理解,需要後續加以研究。
