Mybatis 學習總結
1 Mybatis入門
1.1 單獨使用jdbc程式設計問題總結
1.1.1 jdbc程式
public static void main(String[] args) { Connection connection = null; PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null; ResultSet resultSet = null; try { //載入資料庫驅動 Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");//通過驅動管理類獲取資料庫連結 connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?characterEncoding=utf-8", "root", "mysql"); //定義sql語句 ?表示佔位符 String sql = "select * from user where username = ?"; //獲取預處理statement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);//設定引數,第一個引數為sql語句中引數的序號(從1開始),第二個引數為設定的引數值 preparedStatement.setString(1, "王五"); //向資料庫發出sql執行查詢,查詢出結果集 resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery(); //遍歷查詢結果集 while(resultSet.next()){ System.out.println(resultSet.getString("id")+" "+resultSet.getString("username")); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ //釋放資源 if(resultSet!=null){ try { resultSet.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } if(preparedStatement!=null){ try { preparedStatement.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } if(connection!=null){ try { connection.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } } }
上邊使用jdbc的原始方法(未經封裝)實現了查詢資料庫表記錄的操作。
1.1.2 jdbc程式設計步驟:
- 載入資料庫驅動
- 建立並獲取資料庫連結
- 建立jdbc statement物件
- 設定sql語句
- 設定sql語句中的引數(使用preparedStatement)
- 通過statement執行sql並獲取結果
- 對sql執行結果進行解析處理
- 釋放資源(resultSet、preparedstatement、connection)
1.1.3 jdbc問題總結如下:
- 資料庫連結建立、釋放頻繁造成系統資源浪費從而影響系統性能,如果使用資料庫連結池可解決此問題。
- Sql語句在程式碼中硬編碼,造成程式碼不易維護,實際應用sql變化的可能較大,sql變動需要改變java程式碼。
- 使用preparedStatement向佔有位符號傳引數存在硬編碼,因為sql語句的where條件不一定,可能多也可能少,修改sql還要修改程式碼,系統不易維護。
- 對結果集解析存在硬編碼(查詢列名),sql變化導致解析程式碼變化,系統不易維護,如果能將資料庫記錄封裝成pojo物件解析比較方便。
1.2 MyBatis介紹
MyBatis 本是apache的一個開源專案iBatis, 2010年這個專案由apache software foundation 遷移到了google code,並且改名為MyBatis,實質上Mybatis對ibatis進行一些改進。
MyBatis是一個優秀的持久層框架,它對jdbc的操作資料庫的過程進行封裝,使開發者只需要關注 SQL 本身,而不需要花費精力去處理例如註冊驅動、建立connection、建立statement、手動設定引數、結果集檢索等jdbc繁雜的過程程式碼。
Mybatis通過xml或註解的方式將要執行的各種statement(statement、preparedStatemnt、CallableStatement)配置起來,並通過java物件和statement中的sql進行對映生成最終執行的sql語句,最後由mybatis框架執行sql並將結果對映成java物件並返回。
1.3 Mybatis架構
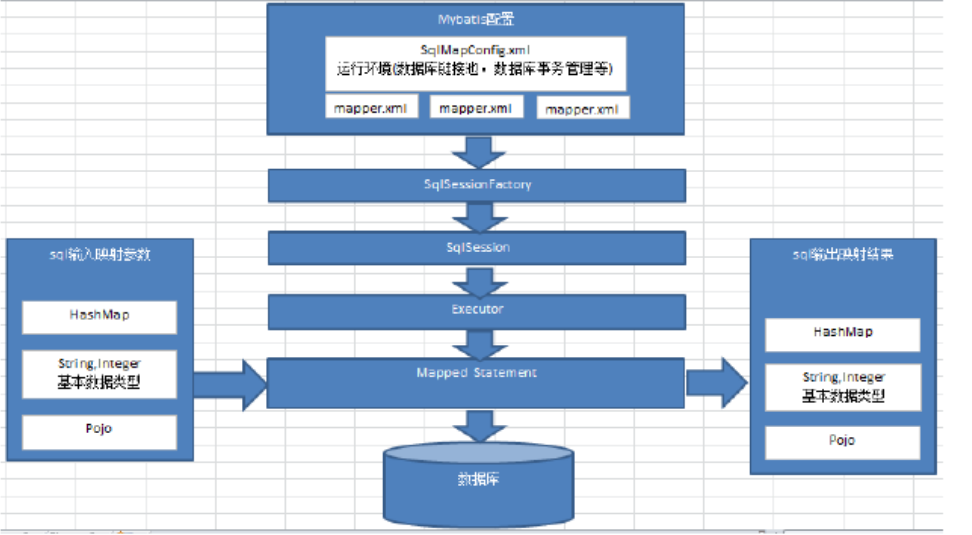
- mybatis配置
SqlMapConfig.xml,此檔案作為mybatis的全域性配置檔案,配置了mybatis的執行環境等資訊。
mapper.xml檔案即sql對映檔案,檔案中配置了操作資料庫的sql語句。此檔案需要在SqlMapConfig.xml中載入。
- 通過mybatis環境等配置資訊構造SqlSessionFactory即會話工廠
- 由會話工廠建立sqlSession即會話,操作資料庫需要通過sqlSession進行。
- mybatis底層自定義了Executor執行器介面操作資料庫,Executor介面有兩個實現,一個是基本執行器、一個是快取執行器。
- Mapped Statement也是mybatis一個底層封裝物件,它包裝了mybatis配置資訊及sql對映資訊等。mapper.xml檔案中一個sql對應一個Mapped Statement物件,sql的id即是Mapped statement的id。
- Mapped Statement對sql執行輸入引數進行定義,包括HashMap、基本型別、pojo,Executor通過Mapped Statement在執行sql前將輸入的java物件對映至sql中,輸入引數對映就是jdbc程式設計中對preparedStatement設定引數。
- Mapped Statement對sql執行輸出結果進行定義,包括HashMap、基本型別、pojo,Executor通過Mapped Statement在執行sql後將輸出結果對映至java物件中,輸出結果對映過程相當於jdbc程式設計中對結果的解析處理過程。
1.4 mybatis下載
mybaits的程式碼由github.com管理,地址:https://github.com/mybatis/mybatis-3/releases
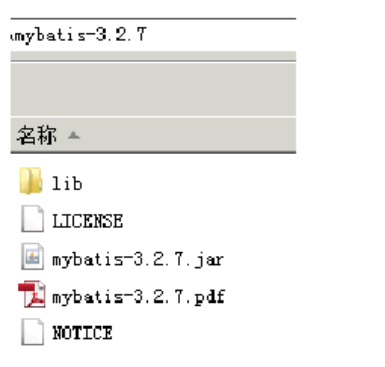
mybatis-3.2.7.jar----mybatis的核心包
lib----mybatis的依賴包
mybatis-3.2.7.pdf----mybatis使用手冊
1.5 建立mysql資料庫
先匯入sql_table.sql,再匯入 sql_data.sql指令碼:

如下:

1.6 Mybatis入門程式
1.6.1 需求
實現以下功能:
根據使用者id查詢一個使用者資訊
根據使用者名稱稱模糊查詢使用者資訊列表
新增使用者
更新使用者
刪除使用者
1.6.2 第一步:建立java工程
使用eclipse建立java工程,jdk使用1.7.0_72。
1.6.3 第二步:加入jar包
加入mybatis核心包、依賴包、資料驅動包。
1.6.4 第三步:log4j.properties
在classpath下建立log4j.properties如下:
# Global logging configuration
log4j.rootLogger=DEBUG, stdout
# Console output...
log4j.appender.stdout=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender
log4j.appender.stdout.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.stdout.layout.ConversionPattern=%5p [%t] - %m%n
mybatis預設使用log4j作為輸出日誌資訊。
1.6.5 第四步:SqlMapConfig.xml
在classpath下建立SqlMapConfig.xml,如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd"> <configuration> <!-- 和spring整合後 environments配置將廢除--> <environments default="development"> <environment id="development"> <!-- 使用jdbc事務管理--> <transactionManager type="JDBC" /> <!-- 資料庫連線池--> <dataSource type="POOLED"> <property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" /> <property name="url"value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?characterEncoding=utf-8"/> <property name="username" value="root" /> <property name="password" value="mysql" /> </dataSource> </environment> </environments> </configuration>
SqlMapConfig.xml是mybatis核心配置檔案,上邊檔案的配置內容為資料來源、事務管理。
1.6.6 第五步:po類
Po類作為mybatis進行sql對映使用,po類通常與資料庫表對應,User.java如下:
public class User { private int id; private String username;// 使用者姓名 private String sex;// 性別 private Date birthday;// 生日 private String address;// 地址 get/set……
1.6.7 第六步:程式編寫
1.6.7.1 查詢
1.6.7.1.1 對映檔案:
在classpath下的sqlmap目錄下建立sql對映檔案Users.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <mapper namespace="test"> </mapper>
namespace :名稱空間,用於隔離sql語句,後面會講另一層非常重要的作用。
在SqlMapConfig.xml中新增:
<!-- 根據id獲取使用者資訊 --> <select id="findUserById" parameterType="int"resultType="cn.itcast.mybatis.po.User"> select * from user where id = #{id} </select> <!-- 自定義條件查詢使用者列表 --> <select id="findUserByUsername" parameterType="java.lang.String" resultType="cn.itcast.mybatis.po.User"> select * from user where username like '%${value}%' </select>
parameterType:定義輸入到sql中的對映型別,#{id}表示使用preparedstatement設定佔位符號並將輸入變數id傳到sql。
resultType:定義結果對映型別。
1.6.7.1.2 載入對映檔案
mybatis框架需要載入對映檔案,將Users.xml新增在SqlMapConfig.xml,如下:
<mappers> <mapper resource="sqlmap/User.xml"/> </mappers>
1.6.7.1.3 測試程式:
public class Mybatis_first { //會話工廠 private SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory; @Before public void createSqlSessionFactory() throws IOException { // 配置檔案 String resource = "SqlMapConfig.xml"; InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); // 使用SqlSessionFactoryBuilder從xml配置檔案中建立SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder() .build(inputStream); } // 根據 id查詢使用者資訊 @Test public void testFindUserById() { // 資料庫會話例項 SqlSession sqlSession = null; try { // 建立資料庫會話例項sqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); // 查詢單個記錄,根據使用者id查詢使用者資訊 User user = sqlSession.selectOne("test.findUserById", 10); // 輸出使用者資訊 System.out.println(user); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (sqlSession != null) { sqlSession.close(); } } } // 根據使用者名稱稱模糊查詢使用者資訊 @Test public void testFindUserByUsername() { // 資料庫會話例項 SqlSession sqlSession = null; try { // 建立資料庫會話例項sqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); // 查詢單個記錄,根據使用者id查詢使用者資訊 List<User> list = sqlSession.selectList("test.findUserByUsername", "張"); System.out.println(list.size()); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (sqlSession != null) { sqlSession.close(); } } } }
1.6.7.1.4 #{}和${}
#{}表示一個佔位符號,通過#{}可以實現preparedStatement向佔位符中設定值,自動進行java型別和jdbc型別轉換,#{}可以有效防止sql注入。 #{}可以接收簡單型別值或pojo屬性值。 如果parameterType傳輸單個簡單型別值,#{}括號中可以是value或其它名稱。
${}表示拼接sql串,通過${}可以將parameterType 傳入的內容拼接在sql中且不進行jdbc型別轉換, ${}可以接收簡單型別值或pojo屬性值,如果parameterType傳輸單個簡單型別值,${}括號中只能是value。
1.6.7.1.5 parameterType和resultType
parameterType:指定輸入引數型別,mybatis通過ognl從輸入物件中獲取引數值拼接在sql中。
resultType:指定輸出結果型別,mybatis將sql查詢結果的一行記錄資料對映為resultType指定型別的物件。
1.6.7.1.6 selectOne和selectList
selectOne查詢一條記錄,如果使用selectOne查詢多條記錄則丟擲異常:
org.apache.ibatis.exceptions.TooManyResultsException: Expected one result (or null) to be returned by selectOne(), but found: 3
at org.apache.ibatis.session.defaults.DefaultSqlSession.selectOne(DefaultSqlSession.java:70)
selectList可以查詢一條或多條記錄。
1.6.7.2 新增
1.6.7.2.1 對映檔案:
在SqlMapConfig.xml中新增:
<!-- 新增使用者 --> <insert id="insertUser"parameterType="cn.itcast.mybatis.po.User"> <selectKey keyProperty="id" order="AFTER"resultType="java.lang.Integer"> select LAST_INSERT_ID() </selectKey> insert into user(username,birthday,sex,address) values(#{username},#{birthday},#{sex},#{address}) </insert>
1.6.7.2.2 測試程式:
// 新增使用者資訊 @Test public void testInsert() { // 資料庫會話例項 SqlSession sqlSession = null; try { // 建立資料庫會話例項sqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); // 新增使用者資訊 User user = new User(); user.setUsername("張小明"); user.setAddress("河南鄭州"); user.setSex("1"); user.setPrice(1999.9f); sqlSession.insert("test.insertUser", user); //提交事務 sqlSession.commit(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (sqlSession != null) { sqlSession.close(); } } }
1.6.7.2.3 mysql自增主鍵返回
通過修改sql對映檔案,可以將mysql自增主鍵返回:
<insert id="insertUser" parameterType="cn.itcast.mybatis.po.User"> <!-- selectKey將主鍵返回,需要再返回 --> <selectKey keyProperty="id" order="AFTER"resultType="java.lang.Integer"> select LAST_INSERT_ID() </selectKey> insert into user(username,birthday,sex,address) values(#{username},#{birthday},#{sex},#{address}); </insert>
新增selectKey實現將主鍵返回
keyProperty:返回的主鍵儲存在pojo中的哪個屬性
order:selectKey的執行順序,是相對與insert語句來說,由於mysql的自增原理執行完insert語句之後才將主鍵生成,所以這裡selectKey的執行順序為after
resultType:返回的主鍵是什麼型別
LAST_INSERT_ID():是mysql的函式,返回auto_increment自增列新記錄id值。
1.6.7.2.4 Mysql使用 uuid實現主鍵
需要增加通過select uuid()得到uuid值
<insert id="insertUser" parameterType="cn.itcast.mybatis.po.User">
<selectKey resultType="java.lang.String" order="BEFORE"
keyProperty="id">
select uuid()
</selectKey>
insert into user(id,username,birthday,sex,address)
values(#{id},#{username},#{birthday},#{sex},#{address})
</insert>
注意這裡使用的order是“BEFORE”
1.6.7.2.5 Oracle使用序列生成主鍵
首先自定義一個序列且用於生成主鍵,selectKey使用如下:
<insert id="insertUser" parameterType="cn.itcast.mybatis.po.User">
<selectKey resultType="java.lang.Integer" order="BEFORE"
keyProperty="id">
SELECT 自定義序列.NEXTVAL FROM DUAL
</selectKey>
insert into user(id,username,birthday,sex,address)
values(#{id},#{username},#{birthday},#{sex},#{address})
</insert>
注意這裡使用的order是“BEFORE”
1.6.7.3 刪除
1.6.7.3.1 對映檔案:
<!-- 刪除使用者 --> <delete id="deleteUserById" parameterType="int"> delete from user where id=#{id} </delete>
1.6.7.3.2 測試程式:
// 根據id刪除使用者 @Test public void testDelete() { // 資料庫會話例項 SqlSession sqlSession = null; try { // 建立資料庫會話例項sqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); // 刪除使用者 sqlSession.delete("test.deleteUserById",18); // 提交事務 sqlSession.commit(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (sqlSession != null) { sqlSession.close(); } } }
1.6.7.4 修改
1.6.7.4.1 對映檔案
<!-- 更新使用者 --> <update id="updateUser"parameterType="cn.itcast.mybatis.po.User"> update user set username=#{username},birthday=#{birthday},sex=#{sex},address=#{address} where id=#{id} </update>
1.6.7.4.2 測試程式
// 更新使用者資訊 @Test public void testUpdate() { // 資料庫會話例項 SqlSession sqlSession = null; try { // 建立資料庫會話例項sqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); // 新增使用者資訊 User user = new User(); user.setId(16); user.setUsername("張小明"); user.setAddress("河南鄭州"); user.setSex("1"); user.setPrice(1999.9f); sqlSession.update("test.updateUser", user); // 提交事務 sqlSession.commit(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (sqlSession != null) { sqlSession.close(); } } }
1.6.8 Mybatis解決jdbc程式設計的問題
- 資料庫連結建立、釋放頻繁造成系統資源浪費從而影響系統性能,如果使用資料庫連結池可解決此問題。
解決:在SqlMapConfig.xml中配置資料鏈接池,使用連線池管理資料庫連結。
- Sql語句寫在程式碼中造成程式碼不易維護,實際應用sql變化的可能較大,sql變動需要改變java程式碼。
解決:將Sql語句配置在XXXXmapper.xml檔案中與java程式碼分離。
- 向sql語句傳引數麻煩,因為sql語句的where條件不一定,可能多也可能少,佔位符需要和引數一一對應。
解決:Mybatis自動將java物件對映至sql語句,通過statement中的parameterType定義輸入引數的型別。
- 對結果集解析麻煩,sql變化導致解析程式碼變化,且解析前需要遍歷,如果能將資料庫記錄封裝成pojo物件解析比較方便。
解決:Mybatis自動將sql執行結果對映至java物件,通過statement中的resultType定義輸出結果的型別。
1.6.9 與hibernate不同
Mybatis和hibernate不同,它不完全是一個ORM框架,因為MyBatis需要程式設計師自己編寫Sql語句,不過mybatis可以通過XML或註解方式靈活配置要執行的sql語句,並將java物件和sql語句對映生成最終執行的sql,最後將sql執行的結果再對映生成java物件。
Mybatis學習門檻低,簡單易學,程式設計師直接編寫原生態sql,可嚴格控制sql執行效能,靈活度高,非常適合對關係資料模型要求不高的軟體開發,例如網際網路軟體、企業運營類軟體等,因為這類軟體需求變化頻繁,一但需求變化要求成果輸出迅速。但是靈活的前提是mybatis無法做到資料庫無關性,如果需要實現支援多種資料庫的軟體則需要自定義多套sql對映檔案,工作量大。
Hibernate物件/關係對映能力強,資料庫無關性好,對於關係模型要求高的軟體(例如需求固定的定製化軟體)如果用hibernate開發可以節省很多程式碼,提高效率。但是Hibernate的學習門檻高,要精通門檻更高,而且怎麼設計O/R對映,在效能和物件模型之間如何權衡,以及怎樣用好Hibernate需要具有很強的經驗和能力才行。
總之,按照使用者的需求在有限的資源環境下只要能做出維護性、擴充套件性良好的軟體架構都是好架構,所以框架只有適合才是最好。
2 Dao開發方法
使用Mybatis開發Dao,通常有兩個方法,即原始Dao開發方法和Mapper介面開發方法。
2.1 需求
將下邊的功能實現Dao:
根據使用者id查詢一個使用者資訊
根據使用者名稱稱模糊查詢使用者資訊列表
新增使用者資訊
2.2 SqlSession的使用範圍
SqlSession中封裝了對資料庫的操作,如:查詢、插入、更新、刪除等。
通過SqlSessionFactory建立SqlSession,而SqlSessionFactory是通過SqlSessionFactoryBuilder進行建立。
2.2.1 SqlSessionFactoryBuilder
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder用於建立SqlSessionFacoty,SqlSessionFacoty一旦建立完成就不需要SqlSessionFactoryBuilder了,因為SqlSession是通過SqlSessionFactory生產,所以可以將SqlSessionFactoryBuilder當成一個工具類使用,最佳使用範圍是方法範圍即方法體內區域性變數。
2.2.2 SqlSessionFactory
SqlSessionFactory是一個介面,介面中定義了openSession的不同過載方法,SqlSessionFactory的最佳使用範圍是整個應用執行期間,一旦建立後可以重複使用,通常以單例模式管理SqlSessionFactory。
2.2.3 SqlSession
SqlSession是一個面向使用者的介面, sqlSession中定義了資料庫操作,預設使用DefaultSqlSession實現類。
執行過程如下:
- 載入資料來源等配置資訊
Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
- 建立資料庫連結
- 建立事務物件
- 建立Executor,SqlSession所有操作都是通過Executor完成,mybatis原始碼如下:
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) { executor = newBatchExecutor(this, transaction); } elseif (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) { executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction); } else { executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction); } if (cacheEnabled) { executor = new CachingExecutor(executor, autoCommit); }
- SqlSession的實現類即DefaultSqlSession,此物件中對操作資料庫實質上用的是Executor
結論:
每個執行緒都應該有它自己的SqlSession例項。SqlSession的例項不能共享使用,它也是執行緒不安全的。因此最佳的範圍是請求或方法範圍。絕對不能將SqlSession例項的引用放在一個類的靜態欄位或例項欄位中。
開啟一個 SqlSession;使用完畢就要關閉它。通常把這個關閉操作放到 finally塊中以確保每次都能執行關閉。如下:
SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); try { // do work } finally { session.close(); }
2.3 原始Dao開發方式
原始Dao開發方法需要程式設計師編寫Dao介面和Dao實現類。
2.3.1 對映檔案
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <mapper namespace="test"> <!-- 根據id獲取使用者資訊 --> <select id="findUserById" parameterType="int"resultType="cn.itcast.mybatis.po.User"> select * from user where id = #{id} </select> <!-- 新增使用者 --> <insert id="insertUser"parameterType="cn.itcast.mybatis.po.User"> <selectKey keyProperty="id" order="AFTER"resultType="java.lang.Integer"> select LAST_INSERT_ID() </selectKey> insert into user(username,birthday,sex,address) values(#{username},#{birthday},#{sex},#{address}) </insert> </mapper>
2.3.2 Dao介面
Public interface UserDao { public User getUserById(int id) throws Exception; public void insertUser(User user) throws Exception; } Public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao { //注入SqlSessionFactory public UserDaoImpl(SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory){ this.setSqlSessionFactory(sqlSessionFactory); } private SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory; @Override public User getUserById(int id) throws Exception { SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); User user = null; try { //通過sqlsession呼叫selectOne方法獲取一條結果集 //引數1:指定定義的statement的id,引數2:指定向statement中傳遞的引數 user = session.selectOne("test.findUserById", 1); System.out.println(user); } finally{ session.close(); } return user; } @Override Public void insertUser(User user) throws Exception { SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); try { sqlSession.insert("insertUser", user); sqlSession.commit(); } finally{ session.close(); } } }
2.3.3 問題
原始Dao開發中存在以下問題:
- Dao方法體存在重複程式碼:通過SqlSessionFactory建立SqlSession,呼叫SqlSession的資料庫操作方法
- 呼叫sqlSession的資料庫操作方法需要指定statement的id,這裡存在硬編碼,不得於開發維護。
2.4 Mapper動態代理方式
2.4.1 實現原理
Mapper介面開發方法只需要程式設計師編寫Mapper介面(相當於Dao介面),由Mybatis框架根據介面定義建立介面的動態代理物件,代理物件的方法體同上邊Dao介面實現類方法。
Mapper介面開發需要遵循以下規範:
- Mapper.xml檔案中的namespace與mapper介面的類路徑相同。
- Mapper介面方法名和Mapper.xml中定義的每個statement的id相同
- Mapper介面方法的輸入引數型別和mapper.xml中定義的每個sql 的parameterType的型別相同
- Mapper介面方法的輸出引數型別和mapper.xml中定義的每個sql的resultType的型別相同
2.4.2 Mapper.xml(對映檔案)
定義mapper對映檔案UserMapper.xml(內容同Users.xml),需要修改namespace的值為 UserMapper介面路徑。將UserMapper.xml放在classpath下mapper目錄 下。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <mapper namespace="cn.itcast.mybatis.mapper.UserMapper"> <!-- 根據id獲取使用者資訊 --> <select id="findUserById" parameterType="int"resultType="cn.itcast.mybatis.po.User"> select * from user where id = #{id} </select> <!-- 自定義條件查詢使用者列表 --> <select id="findUserByUsername" parameterType="java.lang.String" resultType="cn.itcast.mybatis.po.User"> select * from user where username like '%${value}%' </select> <!-- 新增使用者 --> <insert id="insertUser"parameterType="cn.itcast.mybatis.po.User"> <selectKey keyProperty="id" order="AFTER"resultType="java.lang.Integer"> select LAST_INSERT_ID() </selectKey> insert into user(username,birthday,sex,address) values(#{username},#{birthday},#{sex},#{address}) </insert> </mapper>
2.4.3 Mapper.java(介面檔案)
/** * 使用者管理mapper */ Public interface UserMapper { //根據使用者id查詢使用者資訊 public User findUserById(int id) throws Exception; //查詢使用者列表 public List<User> findUserByUsername(String username) throwsException; //新增使用者資訊 public void insertUser(User user)throws Exception; }
介面定義有如下特點:
- Mapper介面方法名和Mapper.xml中定義的statement的id相同
- Mapper介面方法的輸入引數型別和mapper.xml中定義的statement的parameterType的型別相同
- Mapper介面方法的輸出引數型別和mapper.xml中定義的statement的resultType的型別相同
2.4.4 載入UserMapper.xml檔案
修改SqlMapConfig.xml檔案:
<!-- 載入對映檔案 --> <mappers> <mapper resource="mapper/UserMapper.xml"/> </mappers>
2.4.5 測試
Public class UserMapperTest extends TestCase { private SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory; protected void setUp() throws Exception { //mybatis配置檔案 String resource = "sqlMapConfig.xml"; InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); //使用SqlSessionFactoryBuilder建立sessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = newSqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream); } Public void testFindUserById() throws Exception { //獲取session SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); //獲取mapper介面的代理物件 UserMapper userMapper = session.getMapper(UserMapper.class); //呼叫代理物件方法 User user = userMapper.findUserById(1); System.out.println(user); //關閉session session.close(); } @Test public void testFindUserByUsername() throws Exception { SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class); List<User> list = userMapper.findUserByUsername("張"); System.out.println(list.size()); } Public void testInsertUser() throws Exception { //獲取session SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); //獲取mapper介面的代理物件 UserMapper userMapper = session.getMapper(UserMapper.class); //要新增的資料 User user = new User(); user.setUsername("張三"); user.setBirthday(new Date()); user.setSex("1"); user.setAddress("北京市"); //通過mapper介面新增使用者 userMapper.insertUser(user); //提交 session.commit(); //關閉session session.close(); } }
2.4.6 總結
- selectOne和selectList
動態代理物件呼叫sqlSession.selectOne()和sqlSession.selectList()是根據mapper介面方法的返回值決定,如果返回list則呼叫selectList方法,如果返回單個物件則呼叫selectOne方法。
- namespace
mybatis官方推薦使用mapper代理方法開發mapper介面,程式設計師不用編寫mapper介面實現類,使用mapper代理方法時,輸入引數可以使用pojo包裝物件或map物件,保證dao的通用性。
3 SqlMapConfig.xml配置檔案
3.1 配置內容
SqlMapConfig.xml中配置的內容和順序如下:
properties(屬性)
settings(全域性配置引數)
typeAliases(類型別名)
typeHandlers(型別處理器)
objectFactory(物件工廠)
plugins(外掛)
environments(環境集合屬性物件)
environment(環境子屬性物件)
transactionManager(事務管理)
dataSource(資料來源)
mappers(對映器)
3.2 properties(屬性)
SqlMapConfig.xml可以引用java屬性檔案中的配置資訊如下:
在classpath下定義db.properties檔案,
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=mysql
SqlMapConfig.xml引用如下:
<properties resource="db.properties"/> <environments default="development"> <environment id="development"> <transactionManager type="JDBC"/> <dataSource type="POOLED"> <property name="driver" value="${jdbc.driver}"/> <property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/> <property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/> <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/> </dataSource> </environment> </environments>
注意: MyBatis 將按照下面的順序來載入屬性:
- 在 properties 元素體內定義的屬性首先被讀取。
- 然後會讀取properties 元素中resource或 url 載入的屬性,它會覆蓋已讀取的同名屬性。
- 最後讀取parameterType傳遞的屬性,它會覆蓋已讀取的同名屬性。
因此,通過parameterType傳遞的屬性具有最高優先順序,resource或 url 載入的屬性次之,最低優先順序的是 properties 元素體內定義的屬性。
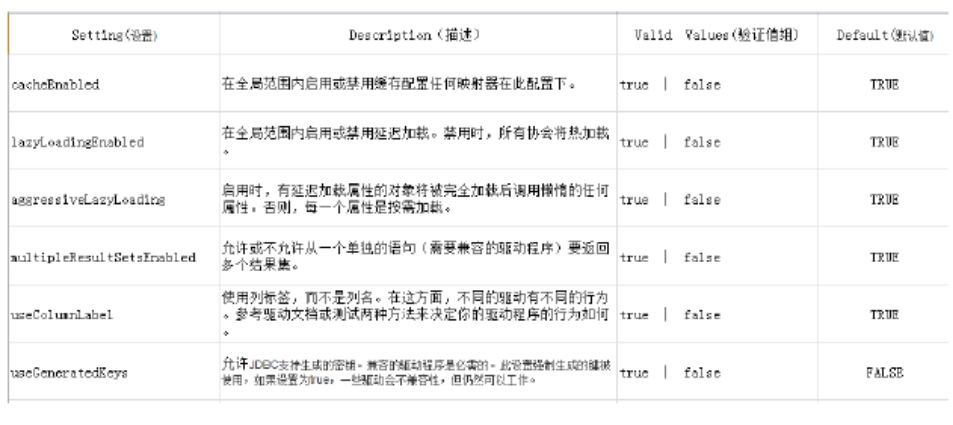
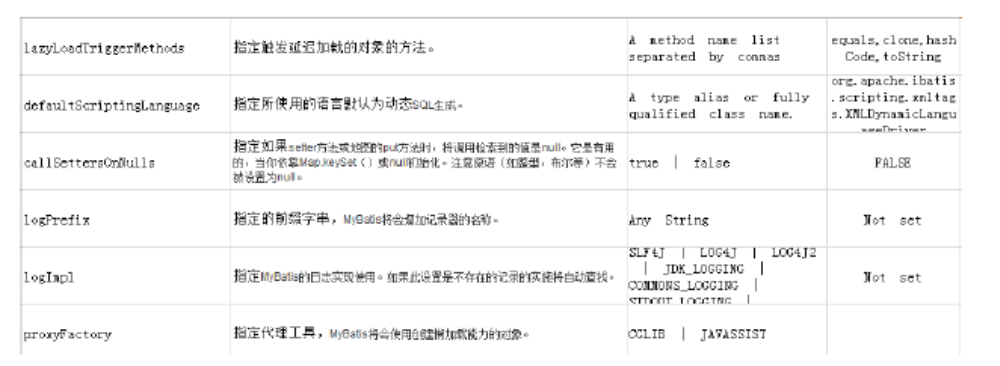
3.3 settings(配置)
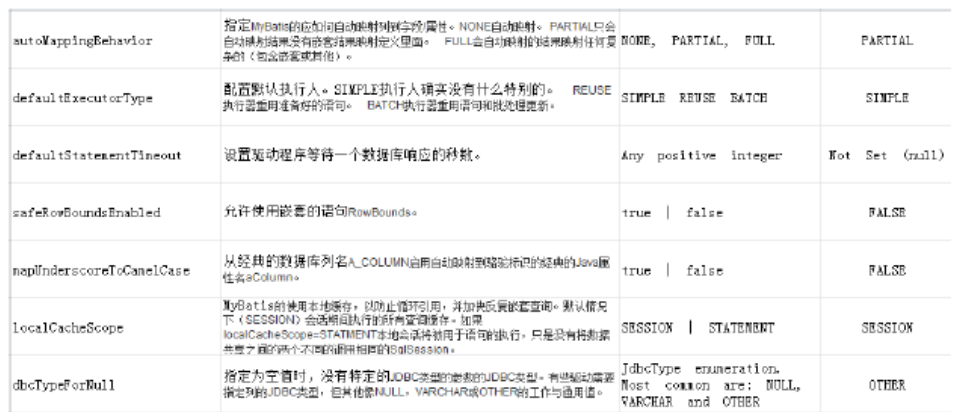
mybatis全域性配置引數,全域性引數將會影響mybatis的執行行為。
詳細參見“學習資料/mybatis-settings.xlsx”檔案
3.4 typeAliases(類型別名)
3.4.1 mybatis支援別名:
| 別名 |
對映的型別 |
| _byte |
byte |
| _long |
long |
| _short |
short |
| _int |
int |
| _integer |
int |
| _double |
double |
| _float |
float |
| _boolean |
boolean |
| string |
String |
| byte |
Byte |
| long |
Long |
| short |
Short |
| int |
Integer |
| integer |
Integer |
| double |
Double |
| float |
Float |
| boolean |
Boolean |
| date |
Date |
| decimal |
BigDecimal |
| bigdecimal |
BigDecimal |
3.4.2 自定義別名:
在SqlMapConfig.xml中配置:
<typeAliases> <!-- 單個別名定義 --> <typeAlias alias="user" type="cn.itcast.mybatis.po.User"/> <!-- 批量別名定義,掃描整個包下的類,別名為類名(首字母大寫或小寫都可以) --> <package name="cn.itcast.mybatis.po"/> <package name="其它包"/> </typeAliases>
3.5 typeHandlers(型別處理器)
型別處理器用於java型別和jdbc型別對映,如下:
<select id="findUserById" parameterType="int" resultType="user"> select * from user where id = #{id} </select>
mybatis自帶的型別處理器基本上滿足日常需求,不需要單獨定義。
mybatis支援型別處理器:
| 型別處理器 |
Java型別 |
JDBC型別 |
| BooleanTypeHandler |
Boolean,boolean |
任何相容的布林值 |
| ByteTypeHandler |
Byte,byte |
任何相容的數字或位元組型別 |
| ShortTypeHandler |
Short,short |
任何相容的數字或短整型 |
| IntegerTypeHandler |
Integer,int |
任何相容的數字和整型 |
| LongTypeHandler |
Long,long |
任何相容的數字或長整型 |
| FloatTypeHandler |
Float,float |
任何相容的數字或單精度浮點型 |
| DoubleTypeHandler |
Double,double |
任何相容的數字或雙精度浮點型 |
| BigDecimalTypeHandler |
BigDecimal |
任何相容的數字或十進位制小數型別 |
| StringTypeHandler |
String |
CHAR和VARCHAR型別 |
| ClobTypeHandler |
String |
CLOB和LONGVARCHAR型別 |
| NStringTypeHandler |
String |
NVARCHAR和NCHAR型別 |
| NClobTypeHandler |
String |
NCLOB型別 |
| ByteArrayTypeHandler |
byte[] |
任何相容的位元組流型別 |
| BlobTypeHandler |
byte[] |
BLOB和LONGVARBINARY型別 |
| DateTypeHandler |
Date(java.util) |
TIMESTAMP型別 |
| DateOnlyTypeHandler |
Date(java.util) |
DATE型別 |
| TimeOnlyTypeHandler |
Date(java.util) |
TIME型別 |
| SqlTimestampTypeHandler |
Timestamp(java.sql) |
TIMESTAMP型別 |
| SqlDateTypeHandler |
Date(java.sql) |
DATE型別 |
| SqlTimeTypeHandler |
Time(java.sql) |
TIME型別 |
| ObjectTypeHandler |
任意 |
其他或未指定型別 |
| EnumTypeHandler |
Enumeration型別 |
VARCHAR-任何相容的字串型別,作為程式碼儲存(而不是索引)。 |
3.6 mappers(對映器)
Mapper配置的幾種方法:
3.6.1 <mapper resource=" " />
使用相對於類路徑的資源
如:<mapper resource="sqlmap/User.xml" />
3.6.2 <mapper url=" " />
使用完全限定路徑
如:<mapper url="file:///D:\workspace_spingmvc\mybatis_01\config\sqlmap\User.xml" />
3.6.3 <mapper class=" " />
使用mapper介面類路徑
如:<mapper class="cn.itcast.mybatis.mapper.UserMapper"/>
注意:此種方法要求mapper介面名稱和mapper對映檔名稱相同,且放在同一個目錄中。
3.6.4 <package name=""/>
註冊指定包下的所有mapper介面
如:<package name="cn.itcast.mybatis.mapper"/>
注意:此種方法要求mapper介面名稱和mapper對映檔名稱相同,且放在同一個目錄中。
4 Mapper.xml對映檔案
Mapper.xml對映檔案中定義了操作資料庫的sql,每個sql是一個statement,對映檔案是mybatis的核心。
4.1 parameterType(輸入型別)
4.1.1 #{}與${}
#{}實現的是向prepareStatement中的預處理語句中設定引數值,sql語句中#{}表示一個佔位符即?。
<!-- 根據id查詢使用者資訊 --> <select id="findUserById" parameterType="int" resultType="user"> select * from user where id = #{id} </select>
使用佔位符#{}可以有效防止sql注入,在使用時不需要關心引數值的型別,mybatis會自動進行java型別和jdbc型別的轉換。#{}可以接收簡單型別值或pojo屬性值,如果parameterType傳輸單個簡單型別值,#{}括號中可以是value或其它名稱。
${}和#{}不同,通過${}可以將parameterType 傳入的內容拼接在sql中且不進行jdbc型別轉換, ${}可以接收簡單型別值或pojo屬性值,如果parameterType傳輸單個簡單型別值,${}括號中只能是value。使用${}不能防止sql注入,但是有時用${}會非常方便,如下的例子:
<!-- 根據名稱模糊查詢使用者資訊 --> <select id="selectUserByName" parameterType="string"resultType="user"> select * from user where username like '%${value}%' </select>
如果本例子使用#{}則傳入的字串中必須有%號,而%是人為拼接在引數中,顯然有點麻煩,如果採用${}在sql中拼接為%的方式則在呼叫mapper介面傳遞引數就方便很多。
//如果使用佔位符號則必須人為在傳引數中加%
List<User> list = userMapper.selectUserByName("%管理員%");
//如果使用${}原始符號則不用人為在引數中加%
List<User>list = userMapper.selectUserByName("管理員");
再比如order by排序,如果將列名通過引數傳入sql,根據傳的列名進行排序,應該寫為:
ORDER BY ${columnName}
如果使用#{}將無法實現此功能。
4.1.2 傳遞簡單型別
參考上邊的例子。
4.1.3 傳遞pojo物件
Mybatis使用ognl表示式解析物件欄位的值,如下例子:
<!—傳遞pojo物件綜合查詢使用者資訊 --> <select id="findUserByUser" parameterType="user"resultType="user"> select * from user where id=#{id} and username like '%${username}%' </select>
上邊紅色標註的是user物件中的欄位名稱。
測試:
Public void testFindUserByUser()throws Exception{ //獲取session SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); //獲限mapper介面例項 UserMapper userMapper = session.getMapper(UserMapper.class); //構造查詢條件user物件 User user = new User(); user.setId(1); user.setUsername("管理員"); //傳遞user物件查詢使用者列表 List<User>list = userMapper.findUserByUser(user); //關閉session session.close(); }<
