Spring中@Autowire的底層原理解析(附詳細原始碼閱讀步驟)
搭建原始碼閱讀環境
首先在IDEA中建立一個Maven工程,然後在pom.xml中加入依賴,因為以後可能會用到其他的功能,所以這裡直接使用的是springboot的依賴
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd" 接著在resources資料夾中建立一個applicationContext.xml,作為spring的配置檔案,內容如下
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-2.5.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-2.5.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-2.5.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="tech.codemine.autowired"/>
</beans>
只需要設定一下spring的掃描路徑即可,然後建立一個包,名為tech.codemine.autowired,在裡面新建幾個測試用的類,分別為Main.java,MyClass.java,MyBean.java
Main.java主要用於啟用spring,內容如下
package tech.codemine.autowired;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
}
}
MyBean.java用於作為一個被注入的bean,內容如下
package tech.codemine.autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class MyBean {
}
MyClass.java用於使用MyBean來注入,內容如下
package tech.codemine.autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class MyClass {
private final MyBean myBean;
@Autowired
public MyClass(MyBean myBean) {
this.myBean = myBean;
}
}
在這裡為了方便觀察Spring的注入過程,使用了構造器來進行bean的注入,只要在構造器上打上debug的斷點就可以看到整個執行棧的情況。
最後使用Debug模式執行Main.java,讓程式在構造器的斷點暫停執行,即可在IDEA的左下角看到執行棧的情況。
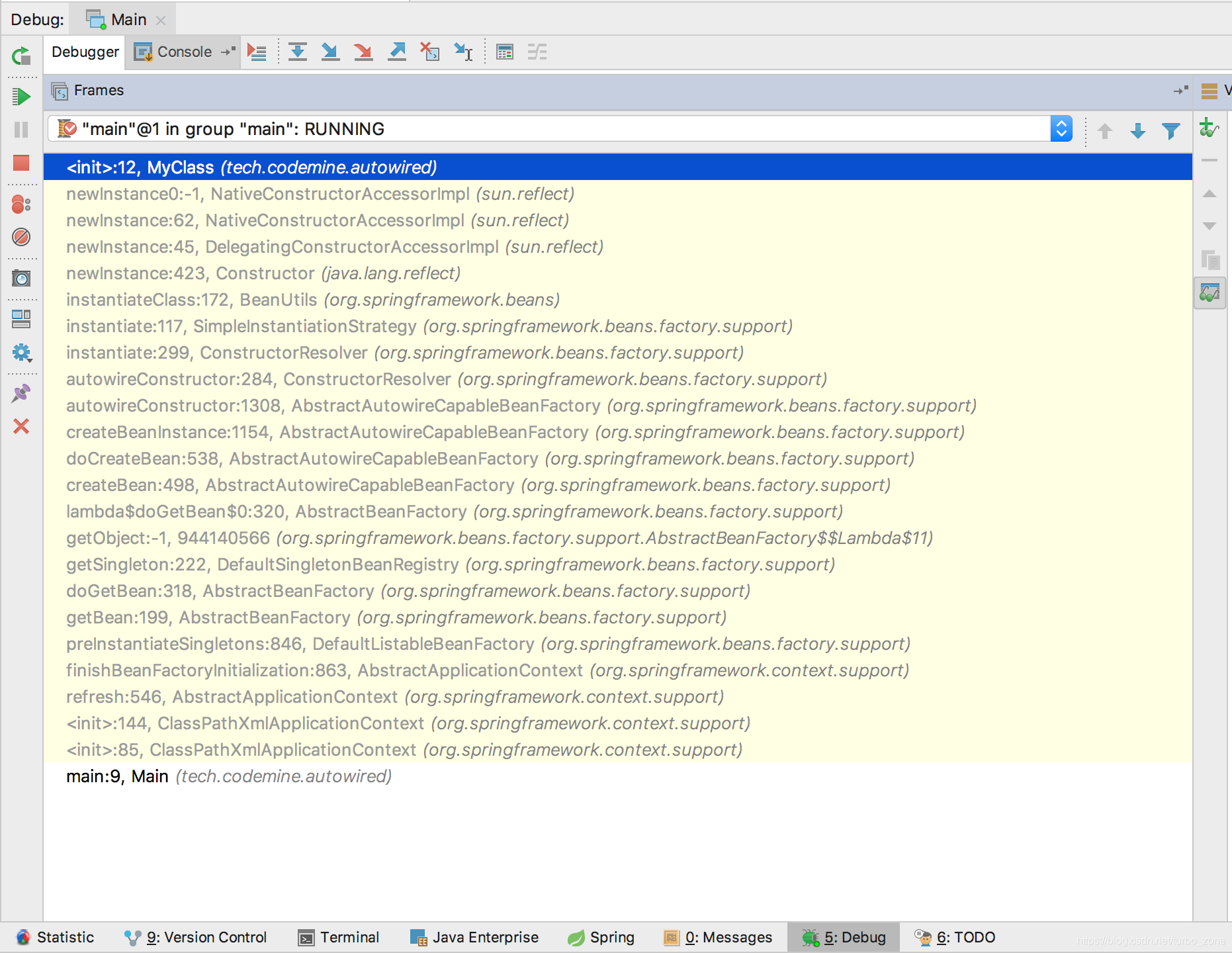
原始碼分析
接下來是對執行棧中每一層原始碼的分析。
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
由於我們new了一個ClassPathXmlApplicationContext物件,所以首先進入的是ClassPathXmlApplicationContext的構造方法
/**
* Create a new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext, loading the definitions
* from the given XML file and automatically refreshing the context.
* @param configLocation resource location
* @throws BeansException if context creation failed
*/
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String configLocation) throws BeansException {
this(new String[] {configLocation}, true, null);
}
這個構造方法呼叫了自身的另外一個構造方法
/**
* Create a new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext with the given parent,
* loading the definitions from the given XML files.
* @param configLocations array of resource locations
* @param refresh whether to automatically refresh the context,
* loading all bean definitions and creating all singletons.
* Alternatively, call refresh manually after further configuring the context.
* @param parent the parent context
* @throws BeansException if context creation failed
* @see #refresh()
*/
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, @Nullable ApplicationContext parent)
throws BeansException {
super(parent);
setConfigLocations(configLocations);
if (refresh) {
refresh();
}
}
從這個構造方法中可以看到大名鼎鼎的refresh()方法,spring從這裡開始進入容器的初始化。
進入refresh()方法可以在這裡看到初始化的所有主體步驟
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
//在這裡進行autowired的邏輯的處理
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
...
}
}
而@Autowired的具體步驟是在倒數第二個方法finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory),在這之前的步驟中構造了一個beanFactory,這個beanFactory中包含了所有我們配置的或是spring預設配置的一些資訊,而autowired就是使用這個beanFactory中的資訊來進行的,我們再往下一層進入finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory)方法。
protected void finishBeanFactoryInitialization(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// Initialize conversion service for this context.
if (beanFactory.containsBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME) &&
beanFactory.isTypeMatch(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class)) {
beanFactory.setConversionService(
beanFactory.getBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class));
}
// Register a default embedded value resolver if no bean post-processor
// (such as a PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer bean) registered any before:
// at this point, primarily for resolution in annotation attribute values.
if (!beanFactory.hasEmbeddedValueResolver()) {
beanFactory.addEmbeddedValueResolver(strVal -> getEnvironment().resolvePlaceholders(strVal));
}
// Initialize LoadTimeWeaverAware beans early to allow for registering their transformers early.
String[] weaverAwareNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(LoadTimeWeaverAware.class, false, false);
for (String weaverAwareName : weaverAwareNames) {
getBean(weaverAwareName);
}
// Stop using the temporary ClassLoader for type matching.
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(null);
// Allow for caching all bean definition metadata, not expecting further changes.
beanFactory.freezeConfiguration();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons();
}
在這個方法中,和之前refresh()方法一樣,首先是對bean進行了一系列的配置操作,並最終進入最後一行,呼叫beanFactory的preInstantiateSingletons()方法進行初始化所有非lazy-init的bean。
再次往下一層,進入preInstantiateSingletons()方法,看看beanFactory是如何進行bean的初始化的,要進行初始化就必須對所有被@Autowired註解的屬性進行注入操作,一下是preInstantiateSingletons()的主要程式碼,為了便於理解,把所有的講解都以註釋的形式寫在程式碼中。
@Override
public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException {
...
// Iterate over a copy to allow for init methods which in turn register new bean definitions.
// While this may not be part of the regular factory bootstrap, it does otherwise work fine.
List<String> beanNames = new ArrayList<>(this.beanDefinitionNames);
// Trigger initialization of all non-lazy singleton beans...
// beanNames變數中包含了所有使用者自定義的bean以及Spring自帶的bean,在這裡的beanNames的值詳見下面的截圖
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
RootBeanDefinition bd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
if (!bd.isAbstract() && bd.isSingleton() && !bd.isLazyInit()) {
if (isFactoryBean(beanName)) {
// 如果是FactoryBean就進行以下操作
...
}
else {
// 我們定義的bean都不是工廠bean,所以直接進入這個方法,beanName此時為我們定義的MyClass
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}
// Trigger post-initialization callback for all applicable beans...
...
}
beanNames和beanName的主要內容如下

可以看到這裡包含了我們自定義的兩個bean以及一些spring內部定義的一些預設bean,這些預設bean的作用會在後續部落格中說明。
回到autowired,接下來進入getBean()方法,這個方法很簡單,呼叫了自身的一個doGetBean()方法
@Override
public Object getBean(String name) throws BeansException {
return doGetBean(name, null, null, false);
}
進入doGetBean()方法,這個方法有點複雜,去掉無關程式碼只留下有用的部分,同樣加上一些中文註釋
/**
* Return an instance, which may be shared or independent, of the specified bean.
* @param name the name of the bean to retrieve
* @param requiredType the required type of the bean to retrieve
* @param args arguments to use when creating a bean instance using explicit arguments
* (only applied when creating a new instance as opposed to retrieving an existing one)
* @param typeCheckOnly whether the instance is obtained for a type check,
* not for actual use
* @return an instance of the bean
* @throws BeansException if the bean could not be created
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected <T> T doGetBean(final String name, @Nullable final Class<T> requiredType,
@Nullable final Object[] args, boolean typeCheckOnly) throws BeansException {
final String beanName = transformedBeanName(name);
Object bean;
// Eagerly check singleton cache for manually registered singletons.
Object sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
if (sharedInstance != null && args == null) {
...
}
else {
...
try {
// 可以把mbd看做是對bean的一種包裝,在這裡本質上是代表了MyClass這個bean,同時儲存了很多其他後續會用到的資訊,比如bean的Scope是singleton還是prototype之類的bena屬性
final RootBeanDefinition mbd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
checkMergedBeanDefinition(mbd, beanName, args);
// Guarantee initialization of beans that the current bean depends on.
String[] dependsOn = mbd.getDependsOn();
if (dependsOn != null) {
// 如果這個bean有其他的依賴則保證先初始化所有的依賴
for (String dep : dependsOn) {
if (isDependent(beanName, dep)) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Circular depends-on relationship between '" + beanName + "' and '" + dep + "'");
}
registerDependentBean(dep, beanName);
try {
getBean(dep);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"'" + beanName + "' depends on missing bean '" + dep + "'", ex);
}
}
}
// Create bean instance.
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
// 如果是單例則開始對bean進行解析生成
sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, () -> {
try {
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
// Explicitly remove instance from singleton cache: It might have been put there
// eagerly by the creation process, to allow for circular reference resolution.
// Also remove any beans that received a temporary reference to the bean.
destroySingleton(beanName);
throw ex;
}
});
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
...
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
cleanupAfterBeanCreationFailure(beanName);
throw ex;
}
}
// Check if required type matches the type of the actual bean instance.
if (requiredType != null && !requiredType.isInstance(bean)) {
...
}
return (T) bean;
}
在以上程式碼的getSingleton()方法中進入下一層
/**
* Return the (raw) singleton object registered under the given name,
* creating and registering a new one if none registered yet.
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param singletonFactory the ObjectFactory to lazily create the singleton
* with, if necessary
* @return the registered singleton object
*/
public Object getSingleton(String beanName, ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory) {
...
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null) {
...
try {
singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();
newSingleton = true;
}
...
return singletonObject;
}
}
在getSingleton()方法中,主要作用是呼叫了singletonFactory的getObject()方法,在方法呼叫棧的接下來幾個層次主要是巢狀呼叫了各種doGetBean()
的過載方法,並最終進入了AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory類的createBeanInstance()方法,程式碼如下
/**
* Create a new instance for the specified bean, using an appropriate instantiation strategy:
* factory method, constructor autowiring, or simple instantiation.
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param mbd the bean definition for the bean
* @param args explicit arguments to use for constructor or factory method invocation
* @return a BeanWrapper for the new instance
* @see #obtainFromSupplier
* @see #instantiateUsingFactoryMethod
* @see #autowireConstructor
* @see #instantiateBean
*/
protected BeanWrapper createBeanInstance(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args) {
...
// Candidate constructors for autowiring?
Constructor<?>[] ctors = determineConstructorsFromBeanPostProcessors(beanClass, beanName);
if (ctors != null || mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR ||
mbd.hasConstructorArgumentValues() || !ObjectUtils.isEmpty(args)) {
return autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, ctors, args);
}
// Preferred constructors for default construction?
ctors = mbd.getPreferredConstructors();
if (ctors != null) {
return autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, ctors, null);
}
// No special handling: simply use no-arg constructor.
return instantiateBean(beanName, mbd);
}
終於我們看到了和Autowired直接相關的程式碼,由於我們使用的是構造器自動注入,所以會進入第一個if判斷,在這裡進行自動注入,接著進入autowireConstructor()方法看看具體是如何注入的
/**
* "autowire constructor" (with constructor arguments by type) behavior.
* Also applied if explicit constructor argument values are specified,
* matching all remaining arguments with beans from the bean factory.
* <p>This corresponds to constructor injection: In this mode, a Spring
* bean factory is able to host components that expect constructor-based
* dependency resolution.
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param mbd the bean definition for the bean
* @param ctors the chosen candidate constructors
* @param explicitArgs argument values passed in programmatically via the getBean method,
* or {@code null} if none (-> use constructor argument values from bean definition)
* @return a BeanWrapper for the new instance
*/
protected BeanWrapper autowireConstructor(
String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Constructor<?>[] ctors, @Nullable Object[] explicitArgs) {
return new ConstructorResolver(this).autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, ctors, explicitArgs);
}
這裡簡單地呼叫了autowireConstructor()方法,將bean使用構造器初始化時需要的構造器以及構造引數都傳遞給了這個方法,最終在autowireConstructor()方法中進行初始化,方法的主要程式碼如下,重點關注argsToUse變數,這個變數包含了要注入的bean的具體的值,如果說在上一個方法中只是對構造器傳入的bean的形式進行約束,那麼在這個方法中,會將所有涉及到的bean的具體的值進行生成,保證再次往下進行方法呼叫的時候傳入的是已經進行初始化完畢的可以直接使用的bean值
/**
* "autowire constructor" (with constructor arguments by type) behavior.
* Also applied if explicit constructor argument values are specified,
* matching all remaining arguments with beans from the bean factory.
* <p>This corresponds to constructor injection: In this mode, a Spring
* bean factory is able to host components that expect constructor-based
* dependency resolution.
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param mbd the merged bean definition for the bean
* @param chosenCtors chosen candidate constructors (or {@code null} if none)
* @param explicitArgs argument values passed in programmatically via the getBean method,
* or {@code null} if none (-> use constructor argument values from bean definition)
* @return a BeanWrapper for the new instance
*/
public BeanWrapper autowireConstructor(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd,
@Nullable Constructor<?>[] chosenCtors, @Nullable Object[] explicitArgs) {
BeanWrapperImpl bw = new BeanWrapperImpl();
this.beanFactory.initBeanWrapper(bw);
Constructor<?> constructorToUse = null;
ArgumentsHolder argsHolderToUse = null;
Object[] argsToUse = null;
if (explicitArgs != null) {
argsToUse = explicitArgs;
}
else {
Object[] argsToResolve = null;
synchronized (mbd.constructorArgumentLock) {
constructorToUse = (Constructor<?>) mbd.resolvedConstructorOrFactoryMethod;
if (constructorToUse != null && mbd.constructorArgumentsResolved) {
// Found a cached constructor...
argsToUse = mbd.resolvedConstructorArguments;
if (argsToUse == null) {
argsToResolve = mbd.preparedConstructorArguments;
}
}
}
if (argsToResolve != null) {
// 最關鍵一步,將構造器依賴的bean進行初始化
argsToUse = resolvePreparedArguments(beanName, mbd, bw, constructorToUse, argsToResolve, true);
}
}
...
bw.setBeanInstance(instantiate(beanName, mbd, constructorToUse, argsToUse));
return bw;
}
resolvePreparedArguments是全場最關鍵的部分,它的程式碼如下
/**
* Resolve the prepared arguments stored in the given bean definition.
*/
private Object[] resolvePreparedArguments(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, BeanWrapper bw,
Executable executable, Object[] argsToResolve, boolean fallback) {
TypeConverter customConverter = this.beanFactory.getCustomTypeConverter(
