java String類介紹
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-11-21
對String的概述
- String :代表字串,java中其他字串都是String的例項化過程。
- public final class String extends Object
說明該字串是繼承於Object 而且是 final型 不可繼承。
字串的賦值方式
- String str = “abc”;
- char data[] = {‘a’,‘b’,‘c’};String str = new String(data);
- 注意:字串是常量,它們的值建立後就不能被更改。
String的構造方法
- public String() 空參構造// 幾乎沒什麼用 因為string是不可變的。
- public String(byte[] bytes) 將位元組陣列轉化為字串
- public String(byte[] bytes,int index,int length) 把位元組陣列的一部分轉化為字串
- public String(String original):把字串常量轉化為字串
String 常見問題
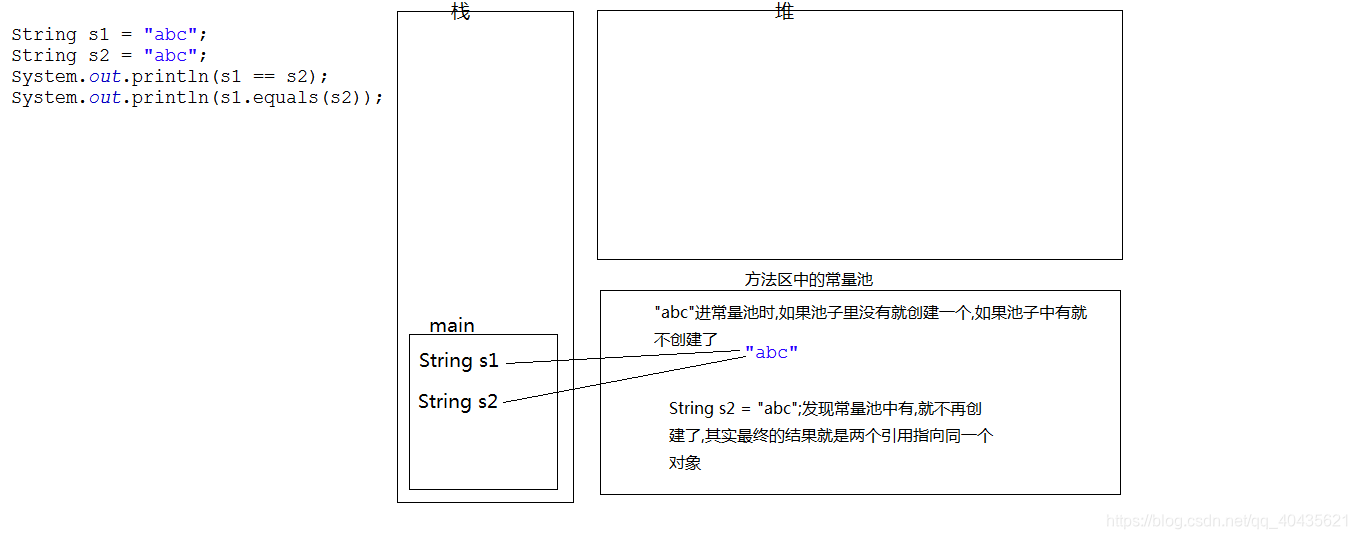
- 1.判斷定義為string型別的s1和s2是否相等
- String s1 = “abc";
- String s2 = “abc”;
- System.out.println(s1 == s2);//true
- System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));//true
- 2.判斷定義為string型別的s1和s2是否相等
- String s1 = new String(“abc”);
- String s2 = “abc”;
- System.out.println(s1 == s2 );//false
- System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));//true
- 3.下面這句話中,在記憶體中建立了幾個物件
- String s1 = new String(“abc”);//兩個
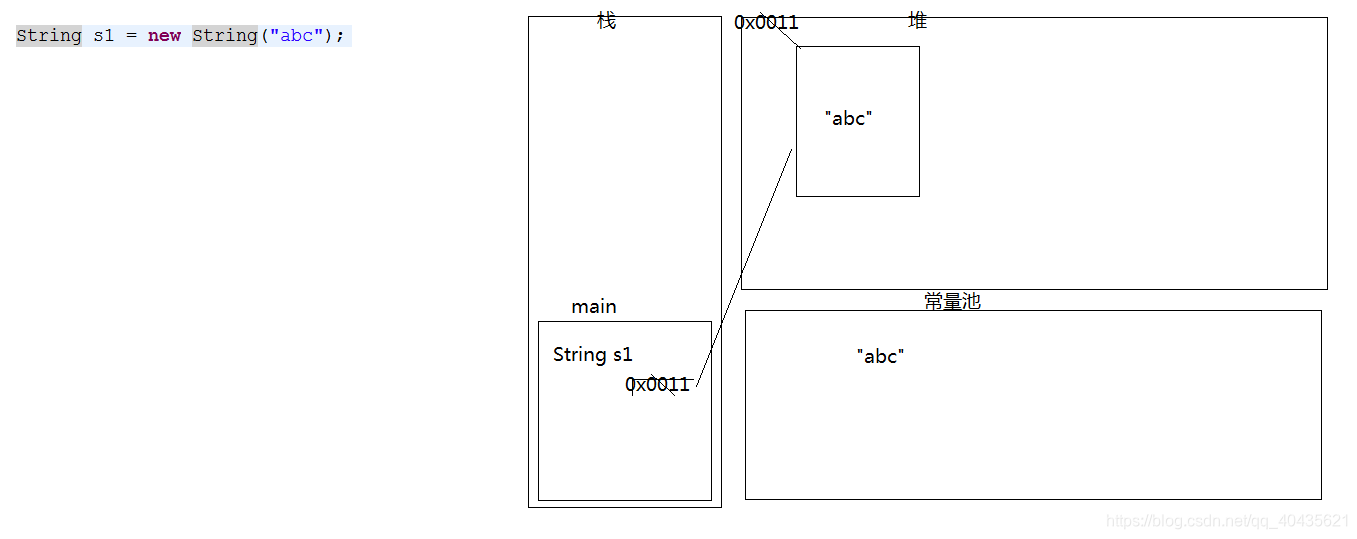
- String s1 = new String(“abc”);//兩個
- 4.判斷定義為String型別的s1和s2是否相等
- String s1 = " a" + “b”+ “c”;
- String s2 = “abc”;
- System.out.println(s1 == s2);//true
- System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));//true
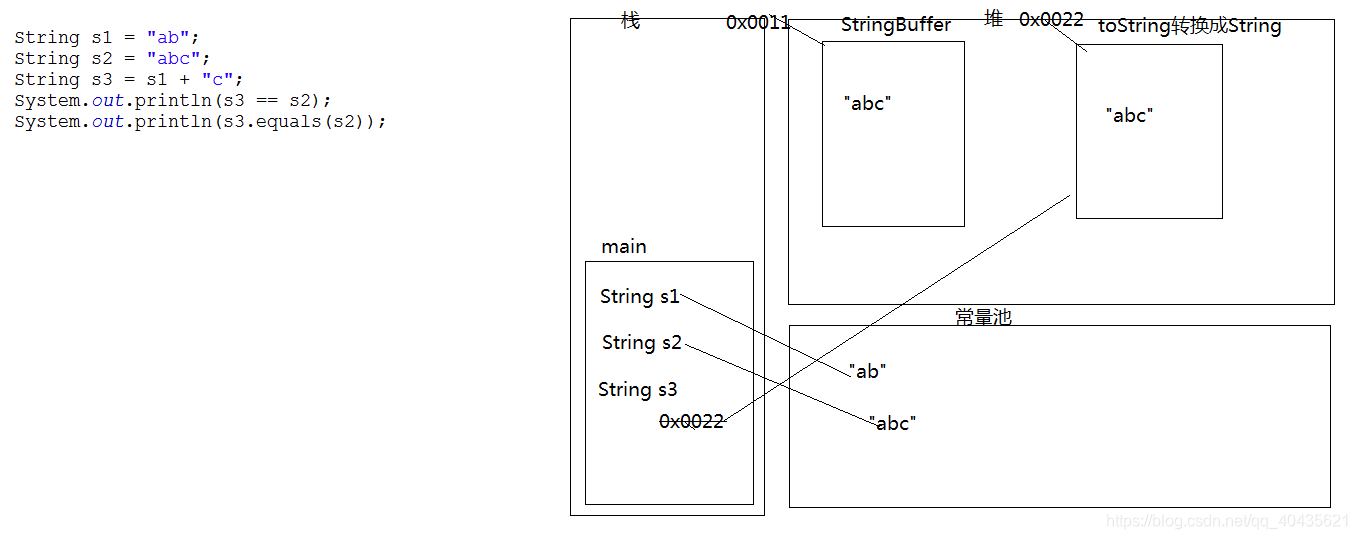
- 5.判斷定義為String型別的s1和s2是否相等
- String s1 = “ab”;
- String s2 = “abc”;
- String s3 = s1+“c”;
- System.out.println(s3 == s2 );//false
- System.out.println(s3.equals(s2));//true
常見string的判斷功能
- boolean equals(Object obj):比較字串的內容是否相同,區分大小寫
//String 重寫的toString()方法
public boolean equals(Object anObject) {
if (this == anObject) { //如果地址相同
return true; //返回 true
}
if (anObject instanceof String) { //判斷 anObject 是否為String類的物件 如果不是 返回false
String anotherString = (String)anObject;//將anObject強轉為String(安全)
int n = value.length; //拿物件的長度為n
if (n == anotherString.value.length) { // 拿要判斷的anotherString長度是否等於n
char v1[] = value; //將物件的字串陣列給v1
char v2[] = anotherString.value;//將要比較的字串陣列給v2
int i = 0; // 一一比較 ,有一個不一樣,那麼直接返回false
while (n-- != 0) {
if (v1[i] != v2[i])
return false;
i++;
}
return true;// 如果還沒返回,那麼證明正確。返回true
}
}
return false;
}
- boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String str):比較字串的內容是否相同,忽略大小寫
- boolean contains(String str):判斷大字串中是否包含小字串
s.contains(s2);//使用方法
public boolean contains(CharSequence s) {
return indexOf(s.toString()) > -1; //我們要呼叫indexOf()方法,這方法下面
//有介紹 ,如果能找到那麼返回下標值,否則返回-1(大於-1 那麼就是存在)
}
- boolean startsWith(String str):判斷字串是否以某個指定的字串開頭
s.startsWith(s0); //呼叫方法
public boolean startsWith(String prefix) {
return startsWith(prefix, 0); //呼叫startsWith()方法,這裡是有引數的,也是告訴
//我們可以有從特定下標開始
}
public boolean startsWith(String prefix, int toffset) {
char ta[] = value; //拿呼叫者的字元陣列
int to = toffset; //拿下錶值 (這裡我們是0)
char pa[] = prefix.value; //拿小串的字元陣列
int po = 0;
int pc = prefix.value.length; // 拿小串的字元陣列長度
// Note: toffset might be near -1>>>1.
if ((toffset < 0) || (toffset > value.length - pc)) {//如果下標為負,那麼返回
//false,如果兩串的具體比較點,不一樣長,那麼返回false
return false;
}
while (--pc >= 0) {//一一比較 如果有一個為false 返回false
if (ta[to++] != pa[po++]) {
return false;
}
}
return true;//最後返回true
}
- boolean endsWith(String str):判斷字串是否以某個指定的字串結尾
s.endsWith(s1);//呼叫方法
public boolean endsWith(String suffix) {
return startsWith(suffix, value.length - suffix.value.length);
}//其實都是用了一個startsWith(String str,int index)方法
- boolean isEmpty():判斷字串是否為空。
public boolean isEmpty() {
return value.length == 0;
}
String的獲取功能
- int length():獲取字串的長度。
//從上面的原始碼,我們也可以看出 ,String類是將String翻譯為
//字元陣列 private final char value[] 而且是final型的
public int length() { //利用value長度來算
return value.length;
}
- char charAt(int index):獲取指定索引位置的字元
public char charAt(int index) {
if ((index < 0) || (index >= value.length)) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
}
return value[index];//換出陣列後,再用陣列索引
}
- int indexOf(int ch):返回指定字元在此字串中第一次出現處的索引。
- int indexOf(String str):返回指定字串在此字串中第一次出現處的索引。
- int indexOf(int ch,int fromIndex):返回指定字元在此字串中從指定位置後第一次出現處的索引。
- int indexOf(String str,int fromIndex):返回指定字串在此字串中從指定位置後第一次出現處的索引。
- String substring(int start):從指定位置開始擷取字串,預設到末尾。
s.substring(0); // 使用方法
public String substring(int beginIndex) {
if (beginIndex < 0) {//如果索引小於0,報陣列越界指標異常
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(beginIndex);
}
int subLen = value.length - beginIndex;//需要複製的長度
if (subLen < 0) {//長度小於0,陣列越界異常
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(subLen);
}
return (beginIndex == 0) ? this : new String(value, beginIndex, subLen);
} //value 陣列 ,開始下標,陣列長度
public String(char value[], int offset, int count) {
if (offset < 0) {//下標越界
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(offset);
}
if (count <= 0) {
if (count < 0) {//陣列長度小於0,不合理 陣列越界異常
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(count);
}
if (offset <= value.length) {//長度為0,返回空陣列,進而生成空字串
this.value = "".value;
return;
}
}
// Note: offset or count might be near -1>>>1.
if (offset > value.length - count) {//開始點 大於原陣列長度-count ,找不到
//開始點,陣列越界異常
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(offset + count);
}
//呼叫Arrays.copyOfRange方法複製 ,這裡跨出了這個類,Arrays類可在我另外的
this.value = Arrays.copyOfRange(value, offset, offset+count);
}
- String substring(int start,int end):從指定位置開始到指定位置結束擷取字串。
//和上面已經分析過
常見的字串轉化
- byte[] getBytes():把字串轉換為位元組陣列。
//原始碼太多 我們還是先看用法吧
s.getBytes();//返回位元組陣列
- char[] toCharArray():把字串轉換為字元陣列。
public char[] toCharArray() {
// Cannot use Arrays.copyOf because of class initialization order issues
char result[] = new char[value.length];
System.arraycopy(value, 0, result, 0, value.length);
//這個方法 是java外的方法寫的,按理來說更加高效
return result;
}
- static String valueOf(char[] chs):把字元陣列轉成字串。
- static String valueOf(int i):把int型別的資料轉成字串。
- 注意:String類的valueOf方法可以把任意型別的資料轉成字串
- String toLowerCase():把字串轉成小寫。(瞭解)
- String toUpperCase():把字串轉成大寫。
- String concat(String str):把字串拼接。
Integer.parseInt(str);轉化為整數 (當然還有其他資料)
String類的其他功能
- String的替換功能
- String replace(char old,char new)
public String replace(char oldChar, char newChar) {
if (oldChar != newChar) {
int len = value.length;
int i = -1;
char[] val = value; /* avoid getfield opcode */
while (++i < len) {
if (val[i] == oldChar) {
break;
}
}
if (i < len) {
char buf[] = new char[len];
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
buf[j] = val[j];
}
while (i < len) {
char c = val[i];
buf[i] = (c == oldChar) ? newChar : c;
i++;
}
return new String(buf, true);
}
}
return this;
}
* String replace(String old,String new)
//和上面一致
- String的去除字串兩側空格
- String trim()
public String trim() {
int len = value.length;//拿到字串長度
int st = 0;
char[] val = value; /* avoid getfield opcode */
//複製字元陣列
while ((st < len) && (val[st] <= ' ')) {//在陣列長度內迴圈
st++;
}
while ((st < len) && (val[len - 1] <= ' ')) {
len--;
}
return ((st > 0) || (len < value.length)) ? substring(st, len) : this;
}
- String的按字典順序比較兩個字串
- int compareTo(String str)
//如果引數字串等於此字串,則返回值 0;如果此字串按字典順序小於字串引數,則返
//回一個小於 0 的值;如果此字串按字典順序大於字串引數,則返回一個大於 0 的值。
public int compareTo(String anotherString) {
int len1 = value.length; //拿到物件長度
int len2 = anotherString.value.length;//拿到被比較者長度
int lim = Math.min(len1, len2);//拿到長度較小者
char v1[] = value;//陣列賦值
char v2[] = anotherString.value;
int k = 0;
while (k < lim) { //迴圈到小於最小長度(也就是較小陣列長度)
char c1 = v1[k]; //拿到各自的第k個字元
char c2 = v2[k];
if (c1 != c2) { //比較字元如果不相等,那麼相減得到一個數(當字元s1的k
//字元大於s2的k字元時返回正數,反之返回負數)
return c1 - c2;
}
k++;//如果相等 k++ 繼續迴圈
}
return len1 - len2;
}
- int compareToIgnoreCase(String str)
// 和上面分析一致
