clang 開發應用xcode 編譯檢查的外掛 二:開發篇
1.抽象語法樹AST
在實現語法檢測之前,需要了解一個叫AST(抽象語法樹)的東西
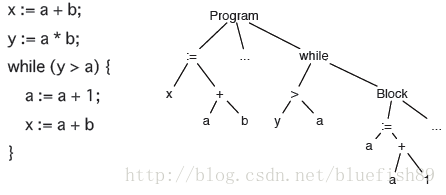
抽象語法樹(abstract syntax code,AST)是原始碼的抽象語法結構的樹狀表示,樹上的每個節點都表示原始碼中的一種結構,之所以說是抽象的,是因為抽象語法樹並不會表示出真實語法出現的每一個細節,看個例子:
語法樹是編譯器對我們所書寫的程式碼的“理解”,如上圖中的x = a + b;語句,編譯器會先將operator =作為節點,將語句拆分為左節點和右節點,隨後繼續分析其子節點,直到葉子節點為止。對於一個基本的運算表示式,我想我們都能很輕鬆的寫出它的 AST,但我們在日常業務開發時所寫的程式碼,可不都是簡單而基礎的表示式而已,諸如
- (void)viewDidLoad{
[self doSomething];
}這樣的程式碼,其 AST 是什麼樣的呢?好訊息是 Clang 提供了對應的命令,讓我們能夠輸出 Clang 對特定檔案編譯所輸出的 AST,先建立一個簡單的 CommandLine 示例工程,在main函式之後如下程式碼:
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
@autoreleasepool {
// insert code here...
NSLog 隨後,在 Terminal 中進入 main.m 所在資料夾,執行如下指令:
clang -fmodules -fsyntax-only -Xclang -ast-dump main.m可看到一個清晰的樹狀結構,如類定義、方法定義、方法呼叫在 AST 中所對應的節點
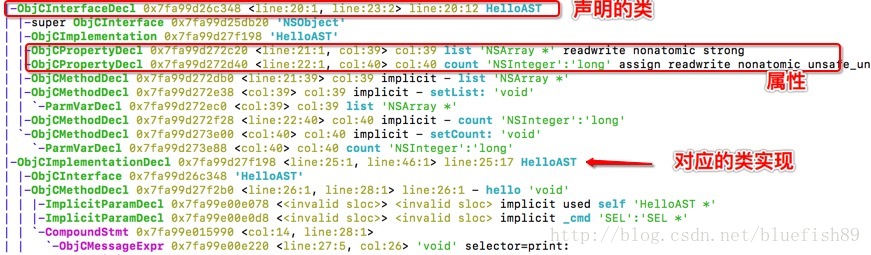
比如我們定義的HelloAST類
ObjCInterfaceDecl:該型別節點為 objc 類定義(宣告)。
ObjCPropertyDecl:屬性定義,下面包括了
-ObjCMethodDecl 0x7fa99d272db0 <line:21:39> col:39 implicit - list 'NSArray *'
-ObjCMethodDecl 0x7fa99d272e38 <col:39> col:39 implicit - setList: 'void'ObjCMethodDecl:該節點定義了一個 objc 方法(包含類、例項方法,包含普通方法和協議方法),這裡為list屬性的get/set方法
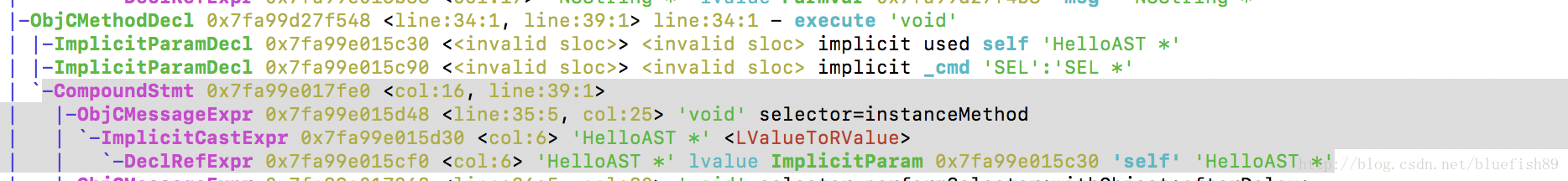
ObjCMessageExpr:說明該節點是一個標準的 objc 訊息傳送表示式([obj foo])
這些名稱對應的都是 Clang 中定義的類,其中所包含的資訊為我們的分析提供了可能。Clang 提供的各種類資訊,可以在這裡進行進一步查閱。
同時,我們也看到在函式定義的時候,ImplicitParamDecl節點聲明瞭隱式引數self和_cmd,這正是函式體內self關鍵字的來源。
從以上可分析出,
在一個 oc 的程式中,幾乎所有程式碼都可以被劃分為兩類:Decl(宣告),Stmt(語句),上述各個ObjCXXXDecl類都是Decl的子類,ObjCXXXExpr也是Stmt的子類,根據RecursiveASTVisitor中宣告的方法,我們可以看到對應的入口方法:bool VisitDecl (Decl *D)以及bool VisitStmt (Stmt *S)
2.語法檢查
首先,先把MyPluginASTAction類的ParseArgs方法中的錯誤報告去掉,這樣可以讓編譯工作能夠繼續進行下去。修改後如下:
//基於consumer的AST前端Action抽象基類
class MyPluginASTAction : public PluginASTAction
{
std::set<std::string> ParsedTemplates;
protected:
std::unique_ptr<ASTConsumer> CreateASTConsumer(CompilerInstance &CI,
llvm::StringRef) override
{
return llvm::make_unique<MobCodeConsumer>(CI, ParsedTemplates);
}
bool ParseArgs(const CompilerInstance &CI,
const std::vector<std::string> &args) override {
return true;
}
};自定義ASTConsumer:
//用於客戶讀取AST的抽象基類
class MyPluginConsumer : public ASTConsumer
{
CompilerInstance &Instance;
std::set<std::string> ParsedTemplates;
public:
MyPluginConsumer(CompilerInstance &Instance,
std::set<std::string> ParsedTemplates)
: Instance(Instance), ParsedTemplates(ParsedTemplates) ,visitor(Instance) {}
bool HandleTopLevelDecl(DeclGroupRef DG) override
{
return true;
}
void HandleTranslationUnit(ASTContext& context) override
{
this->visitor.setASTContext(context);
this->visitor.TraverseDecl(context.getTranslationUnitDecl());
this->visitor.logResult();
}
private:
MyPluginVisitor visitor;
};這裡需要引用一個叫`RecursiveASTVisitor`的類模版,該型別主要作用是前序或後續地深度優先搜尋整個AST,並訪問每一個節點的基類,主要利用它來遍歷一些需要處理的節點。同樣,需要建立一個實現`RecursiveASTVisitor`的模版類。如:
//前序或後續地深度優先搜尋整個AST,並訪問每一個節點的基類)等基類
class MyPluginVisitor : public RecursiveASTVisitor<MyPluginVisitor>
{
private:
CompilerInstance &Instance;
ASTContext *Context;
public:
void setASTContext (ASTContext &context)
{
this -> Context = &context;
}
MyPluginVisitor (CompilerInstance &Instance):Instance(Instance)
{
}
}這裡要說明的是MyPluginConsumer::HandleTopLevelDecl方法表示每次分析到一個頂層定義時(Top level decl)就會回撥到此方法。返回true表示處理該組定義,否則忽略該部分處理。而MyPluginConsumer::HandleTranslationUnit方法則為ASTConsumer的入口函式,當所有單元被解析成AST時會回撥該方法。而方法中呼叫了visitor的TraverseDecl方法來對已解析完成AST節點進行遍歷。在遍歷過程中只要在Visitor類中捕獲不同的宣告和定義即可對程式碼進行語法檢測。
3.例子:
a.類名檢查
//前序或後續地深度優先搜尋整個AST,並訪問每一個節點的基類)等基類
class MyPluginVisitor : public RecursiveASTVisitor<MyPluginVisitor>
{
private:
CompilerInstance &Instance;
ASTContext *Context;
public:
void setASTContext (ASTContext &context)
{
this -> Context = &context;
}
MyPluginVisitor (CompilerInstance &Instance):Instance(Instance)
{
}
//類名檢查
bool VisitObjCInterfaceDecl(ObjCInterfaceDecl *declaration)
{
if (isUserSourceCode(declaration))
{
checkClassNameForLowercaseName(declaration);
checkClassNameForUnderscoreInName(declaration);
}
return true;
}
/**
判斷是否為使用者原始碼
@param decl 宣告
@return true 為使用者原始碼,false 非使用者原始碼
*/
bool isUserSourceCode (Decl *decl)
{
std::string filename = Instance.getSourceManager().getFilename(decl->getSourceRange().getBegin()).str();
if (filename.empty())
return false;
//非XCode中的原始碼都認為是使用者原始碼
if(filename.find("/Applications/Xcode.app/") == 0)
return false;
return true;
}
/**
檢測類名是否存在小寫開頭
@param decl 類宣告
*/
void checkClassNameForLowercaseName(ObjCInterfaceDecl *decl)
{
StringRef className = decl -> getName();
printf("類名:%s",className);
//類名稱必須以大寫字母開頭
char c = className[0];
if (isLowercase(c))
{
//修正提示
std::string tempName = className;
tempName[0] = toUppercase(c);
StringRef replacement(tempName);
SourceLocation nameStart = decl->getLocation();
SourceLocation nameEnd = nameStart.getLocWithOffset(className.size() - 1);
FixItHint fixItHint = FixItHint::CreateReplacement(SourceRange(nameStart, nameEnd), replacement);
//報告警告
DiagnosticsEngine &D = Instance.getDiagnostics();
int diagID = D.getCustomDiagID(DiagnosticsEngine::Warning, "類名不能小寫開頭");
SourceLocation location = decl->getLocation();
D.Report(location, diagID).AddFixItHint(fixItHint);
}
}
/**
檢測類名是否包含下劃線
@param decl 類宣告
*/
void checkClassNameForUnderscoreInName(ObjCInterfaceDecl *decl)
{
StringRef className = decl -> getName();
//類名不能包含下劃線
size_t underscorePos = className.find('_');
if (underscorePos != StringRef::npos)
{
//修正提示
std::string tempName = className;
std::string::iterator end_pos = std::remove(tempName.begin(), tempName.end(), '_');
tempName.erase(end_pos, tempName.end());
StringRef replacement(tempName);
SourceLocation nameStart = decl->getLocation();
SourceLocation nameEnd = nameStart.getLocWithOffset(className.size() - 1);
FixItHint fixItHint = FixItHint::CreateReplacement(SourceRange(nameStart, nameEnd), replacement);
//報告錯誤
DiagnosticsEngine &diagEngine = Instance.getDiagnostics();
unsigned diagID = diagEngine.getCustomDiagID(DiagnosticsEngine::Warning, "Class name with `_` forbidden");
SourceLocation location = decl->getLocation().getLocWithOffset(underscorePos);
diagEngine.Report(location, diagID).AddFixItHint(fixItHint);
}
}
}
接著,cmd+B重新編譯出MyPlugin.dylib,然後回到使用外掛的工程(testPlugin),clear一下再buid,可見如下:
從上面程式碼可以看到,整個VisitObjCInterfaceDecl方法的處理過程是:先判斷是否為自己專案的原始碼,然後再分別檢查類名字是否小寫開頭和類名稱存在下劃線,如果有這些情況則報告警告並提供修改建議。
其中的isUserSourceCode方法判斷比較重要,如果不實現該判斷,則所有經過編譯的程式碼檔案中的型別都會被檢測,包括系統庫中的型別定義。該方法的基本處理思路是通過獲取定義(Decl)所在的原始碼檔案路徑,通過比對路徑來區分哪些是專案引入程式碼,哪些是系統程式碼。
checkClassNameForLowercaseName和checkClassNameForUnderscoreInName方法處理邏輯基本相同,通過decl -> getName()來獲取一個指向類名稱的StringRef物件,然後通過比對類名中的字元來實現相關的檢測。
首先,需要從編譯器例項(CompilerInstance)中取得診斷器(DiagnosticsEngine),由於是一個自定義診斷報告,因此診斷標識需要通過診斷器的getCustomDiagID方法取得,方法中需要傳入報告型別和報告說明。然後呼叫診斷器的Report方法,把有問題的原始碼位置和診斷標識傳進去。如:
DiagnosticsEngine &diagEngine = Instance.getDiagnostics();
unsigned diagID = diagEngine.getCustomDiagID(DiagnosticsEngine::Error, "Class name with `_` forbidden");
SourceLocation location = decl->getLocation().getLocWithOffset(underscorePos);
diagEngine.Report(location, diagID);至於修正提示則是在診斷報告的基礎上進行的,其通過FixItHint物件來包含一個修改提示行為,主要描述了某段原始碼需要修改成指定的內容。如:
FixItHint fixItHint = FixItHint::CreateReplacement(SourceRange(nameStart, nameEnd), replacement);
diagEngine.Report(location, diagID).AddFixItHint(fixItHint);b.查詢無用方法
記錄所有定義的方法以及所有被呼叫的方法,再取差集即可,有兩個關鍵點:
方法所屬的物件型別(Interface)
方法的選擇子(Selector)
我們需要記錄所有定義的方法以及所有被呼叫過的方法,並在掃描完整個 AST 之後對它們進行比較,我所採用的方式是以類名作為 key,以ObjCMethodDecl陣列作為 value,構造一個 Map 來儲存這些資訊:
typedef std::vector<ObjCMethodDecl *> MethodVector;
typedef std::map<StringRef ,MethodVector> InterfaceMethodsMap;
typedef std::vector<Selector> SelectorVector;在MyPluginVisitor定義成員變數
InterfaceMethodsMap definedMethodsMap;
InterfaceMethodsMap usedMethodsMap;
SelectorVector usedSelectors;新增方法,訪問所有的訊息呼叫,如[obj sendMsg],並以類名作為 key記錄下來
bool VisitObjCMessageExpr(ObjCMessageExpr *expr){
ObjCInterfaceDecl *interfaceDecl = expr -> getReceiverInterface();
StringRef clsName = interfaceDecl->getName();
MethodVector methodVec;
if(usedMethodsMap.find(clsName) != usedMethodsMap.end()) {
methodVec = usedMethodsMap.at(clsName);
}else{
methodVec = MethodVector();
usedMethodsMap.insert(std::make_pair(clsName, methodVec));
}
methodVec.push_back(expr->getMethodDecl());
InterfaceMethodsMap::iterator it = usedMethodsMap.find(clsName);
it->second = methodVec;
return true;
}
記錄使用@selector()的方法
bool VisitObjCSelectorExpr(ObjCSelectorExpr *expr){
usedSelectors.push_back(expr->getSelector());
return true;
}記錄所有的方法定義:
//declaration
bool VisitObjCMethodDecl(ObjCMethodDecl *methDecl){// 包括了 protocol 方法的定義
if(!isUserSourceCode(methDecl)){
return true;
}
ObjCInterfaceDecl *interfaceDecl = methDecl->getClassInterface();
if(!interfaceDecl || interfaceHasProtocolMethod(interfaceDecl, methDecl)){
return true;
}
StringRef clsName = interfaceDecl->getName();
MethodVector methodVec;
if(definedMethodsMap.find(clsName) != definedMethodsMap.end()) {
methodVec = definedMethodsMap.at(clsName);
}else{
methodVec = MethodVector();
definedMethodsMap.insert(std::make_pair(clsName, methodVec));
}
methodVec.push_back(methDecl);
InterfaceMethodsMap::iterator it = definedMethodsMap.find(clsName);
it->second = methodVec;
return true;
}
//
bool interfaceHasProtocolMethod(ObjCInterfaceDecl *interfaceDecl ,ObjCMethodDecl *methDecl){
for(auto*protocolDecl : interfaceDecl->all_referenced_protocols()){
if(protocolDecl->lookupMethod(methDecl->getSelector(), methDecl->isInstanceMethod())) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}以上,在ObjCInterfaceDecl的文件中,我們可以找到all_referenced_protocols()方法,可以讓我們拿到當前類遵循的所有協議,而其中的ObjCProtocolDecl類則有lookUpMethod()方法,可以用於檢索協議定義中是否有某個方法。也就是說,當我們遇到一個方法定義時,我們需要多做一步判斷:若該方法是協議方法,則忽略,否則記錄下來,用於後續判斷是否被使用
最後:
//查詢無用方法
void logResult(){
DiagnosticsEngine &D = Instance.getDiagnostics();
for(InterfaceMethodsMap::iterator definedIt = definedMethodsMap.begin(); definedIt != definedMethodsMap.end(); ++definedIt){
StringRef clsName = definedIt->first;
MethodVector definedMethods = definedIt->second;
if(usedMethodsMap.find(clsName) == usedMethodsMap.end()) {
// the class could not be found ,all of its method is unused.
for(auto*methDecl : definedMethods){
int diagID = D.getCustomDiagID(DiagnosticsEngine::Warning,"無用方法定義 : %0 ");
D.Report(methDecl->getLocStart(), diagID) << methDecl->getSelector().getAsString();
outfile << "無用方法定義" << std::endl;
}
continue;
}
MethodVector usedMethods = usedMethodsMap.at(clsName);
for(auto*defined : definedMethods){
bool found =false;
for(auto*used : usedMethods){
if(defined->getSelector() == used->getSelector()){// find used method
found =true;
break;
}
}
if(!found) {
for(auto sel : usedSelectors){
if(defined->getSelector() == sel){// or find @selector
found =true;
break;
}
}
}
if(!found){
int diagID = D.getCustomDiagID(DiagnosticsEngine::Warning,"Method Defined ,but never used. SEL : %0 ");
D.Report(defined->getLocStart(), diagID) << defined->getSelector().getAsString();
}
}
}
}logResult方法在ASTConsumer自定義類中呼叫,
void HandleTranslationUnit(ASTContext& context) override
{
this->visitor.setASTContext(context);
this->visitor.TraverseDecl(context.getTranslationUnitDecl());
this->visitor.logResult();
}摘錄:
https://my.oschina.net/vimfung/blog/866109
https://github.com/LiuShulong/SLClangTutorial/blob/master/%E6%89%8B%E6%8A%8A%E6%89%8B%E6%95%99%E4%BD%A0%E7%BC%96%E5%86%99clang%E6%8F%92%E4%BB%B6%E5%92%8Clibtool.md
http://kangwang1988.github.io/tech/2016/10/31/check-code-style-using-clang-plugin.html
http://blog.gocy.tech/