大話設計模式(C++)第二章-策略模式
阿新 • • 發佈:2018-11-22
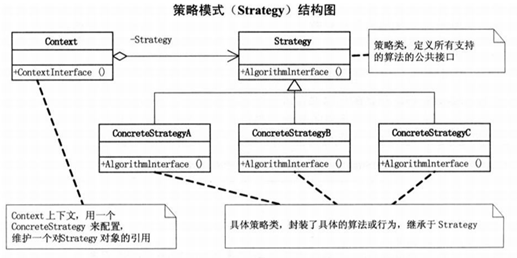
策略模式:他定義了演算法家族,分別封裝起來,讓他們之間可以互相替換,此模式讓演算法的變化,不會影響到使用演算法的客戶。
三、優點與解析
(1)策略模式是一種定義一系列演算法的方法,從概念上來看,所有這些演算法完成的都是相同的工作,只是實現不同,他可以以相同的方式呼叫所有的演算法,減少了各種演算法類與使用演算法類之間的耦合。
(2)策略模式的Strategy類曾是為Context定義了一些列的可供重用的演算法或行為。整合有助於析取出這些演算法中的公共功能。
(3)策略模式簡化了單元測試,因為每個演算法都有自己的類,可以通過自己的介面單獨測試。
(4)策略模式就是用來封裝演算法的。
(5)只要在分析過程中聽到需要在不同時間應用不同的業務規則,就可以考慮使用策略模式處理這種變化的可能性。
(6)簡單工廠模式需要讓客戶端認識兩個類,而策略模式和簡單工廠模式結合的用法,客戶端只需要認識一個類Context即可。
C++實現:
#include<iostream> #include<cmath> #include<cstdlib> using namespace std; class CashSuper //抽象類 { public: virtual double acceptCash(double money) = 0; }; //子類,具體的實現,每種付費型別,正常付費型別 class CashNormal :public CashSuper { public: double acceptCash(double money) { return money; } }; //返現型別 class CashReturn :public CashSuper { private: double moneyCondition; double moneyReturn; public: CashReturn(double moneyCondition, double moneyReturn) { this->moneyCondition = moneyCondition; this->moneyReturn = moneyReturn; } double acceptCash(double money) { double result = money; if (money > moneyCondition) result = money - floor(money / moneyCondition) * moneyReturn; return result; } }; //打折扣型別 class CashRebate :public CashSuper { private: double moneyRebate; public: CashRebate(double moneyRebate) { this->moneyRebate = moneyRebate; } double acceptCash(double money) { return money*moneyRebate; } }; //-------------------------------------------------分割線---------------------------------// //策略與簡單工廠模式結合的 class CashContext { private: CashSuper *cs; public: CashContext(int type) :cs(nullptr) //在建構函式中直接例項化 { switch (type) { case 1: { cs = new CashNormal(); break; } case 2: { cs = new CashReturn(300, 100); break; } case 3: { cs = new CashRebate(0.8); break; } default: break; } } ~CashContext() //在解構函式中將建構函式中,例項化的物件釋放 { if (cs != nullptr) { delete cs; cs = nullptr; } } double GetResult(double money) { return cs->acceptCash(money); } }; //-------------------------------------------------分割線---------------------------------// //客戶端 int main() { double total = 0; double totalPrices = 0; //正常收費 CashContext* cc1 = nullptr; cc1 = new CashContext(1); totalPrices = cc1->GetResult(300); total += totalPrices; cout << "Type: 正常收費 totalPrices:" << totalPrices << " total:" << total << endl; totalPrices = 0; //返現型別 CashContext *cc2 = nullptr; cc2 = new CashContext(2); totalPrices = cc2->GetResult(700); total += totalPrices; cout << "Type:滿300返100 totalPrices:" << totalPrices << " total:" << total << endl; totalPrices = 0; //打折型別 CashContext *cc3 = nullptr; cc3 = new CashContext(3); totalPrices = cc3->GetResult(300); total += totalPrices; cout << "Type:打8折 totalPrices:" << totalPrices << " total:" << total << endl; totalPrices = 0; if (cc1 != nullptr) { delete cc1; cc1 = nullptr; } if (cc2 != nullptr) { delete cc2; cc2 = nullptr; } if (cc3 != nullptr) { delete cc3; cc3 = nullptr; } //while (1); return 0; }
本文轉自:
作者:西青年
來源:CSDN
原文:https://blog.csdn.net/xiqingnian/article/details/41855391
版權宣告:本文為博主原創文章,轉載請附上博文連結!