Day3 -- Find Eventual Safe States
## Find Eventual Safe States
- from : https://leetcode.com/
- mode : random pick
- detail : https://leetcode.com/problems/find-eventual-safe-states/
- degree : Medium
In a directed graph, we start at some node and every turn, walk along a directed edge of the graph. If we reach a node that is terminal (that is, it has no outgoing directed edges), we stop.
Now, say our starting node is eventually safe if and only if we must eventually walk to a terminal node. More specifically, there exists a natural number K so that for any choice of where to walk, we must have stopped at a terminal node in less than K steps.
Which nodes are eventually safe? Return them as an array in sorted order.
The directed graph has N nodes with labels 0, 1, ..., N-1, where N is the length of graph. The graph is given in the following form: graph[i] is a list of labels j such that (i, j) is a directed edge of the graph.
Example:
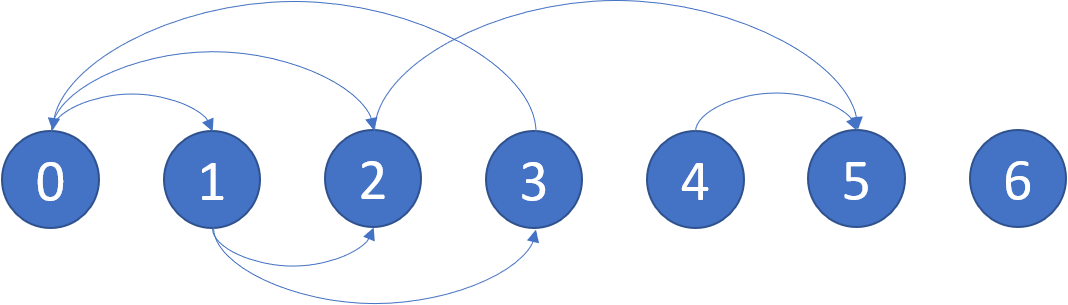
Input: graph = [[1,2],[2,3],[5],[0],[5],[],[]]
Output: [2,4,5,6]
Here is a diagram of the above graph.
Note:
graph will have length at most 10000.
The number of edges in the graph will not exceed 32000.
Each graph[i] will be a sorted list of different integers, chosen within the range [0, graph.length - 1].
solution:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# Time : 2018/11/22
class Solution:
def __init__(self, graph):
self.graph = graph
self.safe = []
def eventualSafeNodes(self):
"""
:type graph: List[List[int]]
:rtype: List[int]
"""
for i in range(len(self.graph)):
print "for", i
req = self.temp(i)
print "res", req
if req == 1:
self.safe.append(i)
return self.safe
def temp(self, i, step_node=None):
if not step_node:
step_node = []
if i in step_node:
return 0
else:
step_node.append(i)
if not self.graph[i]:
return 1
else:
for j in self.graph[i]:
if not self.temp(j, step_node):
return 0
return 1
if __name__ == '__main__':
s = Solution([[1,2],[2,3],[5],[0],[5],[],[]])
s.eventualSafeNodes()
print "req", s.safe總結
- 解題的關鍵點是節點的的子節點不能進入任何一個迴圈
- 節點狀態判斷:我的演算法是直接迴圈判斷
- 官網的深度優先判斷定義了黑白灰三狀態
